PyTorch 框架学习 更新中...
基础知识
Tensor 形式
import torch
from torch import tensor
Scalar:
通常就是一个数值
x = tensor(42.)
x # tensor(42.)
x.dim() # 0
2 * x # tensor(84.)
x.item() # 42.0
Vector
例如: [-5., 2., 0.],在深度学习中通常指特征,例如词向量特征,某一维度特征等
v = tensor([1.5, -0.5, 3.0])
v # tensor([ 1.5000, -0.5000, 3.0000])
v.dim() # 1
v.size() # torch.Size([3])
Matrix
一般计算的都是矩阵,通常都是多维的
M = tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])
M
'''
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]])
'''
M.matmul(M)
'''
tensor([[ 7., 10.],
[15., 22.]])
'''
tensor([1., 0.]).matmul(M)
'''
tensor([1., 2.])
'''
M * M
'''
tensor([[ 1., 4.],
[ 9., 16.]])
'''
tensor([1., 2.]).matmul(M) # tensor([ 7., 10.])
矩阵构造
torch.empty : 创建一个空矩阵
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
x
'''
tensor([[1.0469e-38, 9.3674e-39, 9.9184e-39],
[8.7245e-39, 9.2755e-39, 8.9082e-39],
[9.9184e-39, 8.4490e-39, 9.6429e-39],
[1.0653e-38, 1.0469e-38, 4.2246e-39],
[1.0378e-38, 9.6429e-39, 9.2755e-39]])
'''
torch.rand: 创建一个随机数矩阵
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
x
'''
tensor([[0.1452, 0.4816, 0.4507],
[0.1991, 0.1799, 0.5055],
[0.6840, 0.6698, 0.3320],
[0.5095, 0.7218, 0.6996],
[0.2091, 0.1717, 0.0504]])
'''
torch.zeros :初始化一个全零的矩阵
x = torch.zeros(5, 3, dtype=torch.long)
x
'''
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
'''
torch.tensor: 自定义一个矩阵
x = torch.tensor([5.5, 3])
x # tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])
torch.randn_like :构造一个形状相同的随机数矩阵
x = x.new_ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.double)
x = torch.randn_like(x, dtype=torch.float)
x
矩阵的大小
x.size()
计算
直接使用+
y = torch.rand(5, 3)
x + y
'''
tensor([[ 0.6497, -0.5561, 2.2990],
[ 0.5333, 0.4522, 2.1114],
[-2.4560, 0.1690, 1.2198],
[ 2.0695, -0.5944, -0.3466],
[-0.2388, 0.5630, 0.8880]])
'''
torch.add : 加法操作
torch.add(x, y)
'''
tensor([[ 0.6497, -0.5561, 2.2990],
[ 0.5333, 0.4522, 2.1114],
[-2.4560, 0.1690, 1.2198],
[ 2.0695, -0.5944, -0.3466],
[-0.2388, 0.5630, 0.8880]])
'''
索引
x[:, 1]
'''
tensor([-1.1208, -0.0828, -0.4144, -0.7263, 0.1368])
'''
改变维度
view: 改变矩阵的维度
x = torch.randn(4, 4)
y = x.view(16)
z = x.view(-1, 8) # -1表示根据后面的值自动计算
print(x.size(), y.size(), z.size()) # torch.Size([4, 4]) torch.Size([16]) torch.Size([2, 8])
与numpy协同操作
numpy()转换为ndarray
a = torch.ones(5)
b = a.numpy()
b # array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=float32)
torch.from_numpy : 转换为tensor
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
b # tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64)
自动求导机制
定义一个可导的矩阵
import torch
#方法1
x = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)
x
'''
tensor([[-0.6812, 0.1245, 0.4627, -0.5860],
[ 1.2594, -0.4262, 0.9005, -0.4189],
[ 0.6924, -1.0704, 0.3465, -0.8244]], requires_grad=True)
'''
#方法2
x = torch.randn(3,4)
x.requires_grad=True
x
'''
tensor([[-1.0556, 1.2333, -0.9068, 1.1550],
[-0.3289, -1.9466, 0.1828, -1.7511],
[-0.4664, 0.5741, 0.9633, -0.3505]], requires_grad=True)
'''
b = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)
t = x + b
y = t.sum()
y # tensor(-2.1930, grad_fn=)
y.backward()
b.grad
'''
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
'''
x.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, t.requires_grad # (True, True, True)
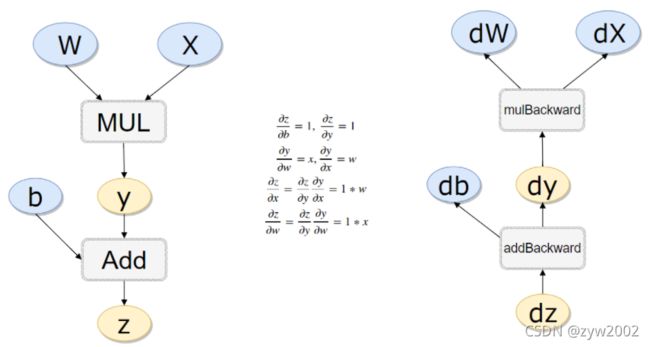
#计算流程
x = torch.rand(1)
b = torch.rand(1, requires_grad = True)
w = torch.rand(1, requires_grad = True)
y = w * x
z = y + b
x.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, w.requires_grad, y.requires_grad # (False, True, True, True)
x.is_leaf, w.is_leaf, b.is_leaf, y.is_leaf, z.is_leaf # (True, True, True, False, False)
# 计算反向传播
z.backward(retain_graph=True)#如果不清空会累加起来
w.grad # tensor([0.2456])
b.grad # tensor([8.])
线性回归模型
x_values = [i for i in range(11)]
x_train = np.array(x_values, dtype=np.float32)
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 1)
x_train.shape # (11, 1)
y_values = [2*i + 1 for i in x_values]
y_train = np.array(y_values, dtype=np.float32)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
y_train.shape # (11, 1)
# 线性回归其实就是一个不加激活函数的全连接层
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
input_dim = 1
output_dim = 1
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim, output_dim)
model
'''
LinearRegressionModel(
(linear): Linear(in_features=1, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
'''
# 指定好参数和损失函数
epochs = 1000
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch += 1
# 注意转行成tensor
inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
labels = torch.from_numpy(y_train)
# 梯度要清零每一次迭代
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播
outputs = model(inputs)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 返向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新权重参数
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('epoch {}, loss {}'.format(epoch, loss.item()
# 测试模型预测结果
predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train).requires_grad_()).data.numpy()
predicted
# 模型的保存与读取
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pkl')
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pkl'))
使用GPU进行训练
只需要把数据和模型传入到cuda里面就可以了
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
input_dim = 1
output_dim = 1
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim, output_dim)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch += 1
inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train).to(device)
labels = torch.from_numpy(y_train).to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('epoch {}, loss {}'.format(epoch, loss.item()))
Hub模块
https://github.com/pytorch/hub
https://pytorch.org/hub/research-models
import torch
model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.4.2', 'deeplabv3_resnet101', pretrained=True)
model.eval()
torch.hub.list('pytorch/vision:v0.4.2')
# Download an example image from the pytorch website
import urllib
url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg")
try: urllib.URLopener().retrieve(url, filename)
except: urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
# sample execution (requires torchvision)
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
input_image = Image.open(filename)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(input_image)
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model
# move the input and model to GPU for speed if available
if torch.cuda.is_available():
input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda')
model.to('cuda')
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_batch)['out'][0]
output_predictions = output.argmax(0)
# create a color pallette, selecting a color for each class
palette = torch.tensor([2 ** 25 - 1, 2 ** 15 - 1, 2 ** 21 - 1])
colors = torch.as_tensor([i for i in range(21)])[:, None] * palette
colors = (colors % 255).numpy().astype("uint8")
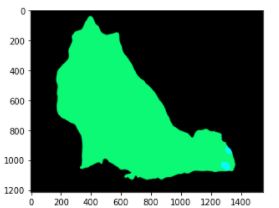
# plot the semantic segmentation predictions of 21 classes in each color
r = Image.fromarray(output_predictions.byte().cpu().numpy()).resize(input_image.size)
r.putpalette(colors)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(r)
plt.show()
气温预测模型
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
%matplotlib inline
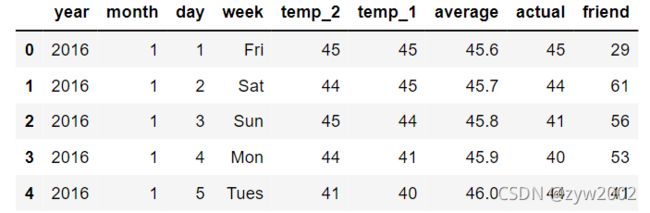
features = pd.read_csv('temps.csv')
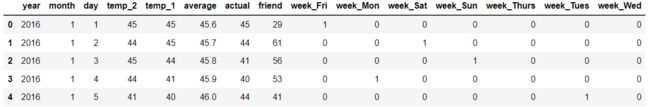
features.head()
year,moth,day,week分别表示的具体的时间
temp_2:前天的最高温度值
temp_1:昨天的最高温度值
average:在历史中,每年这一天的平均最高温度值
actual:这就是我们的标签值了,当天的真实最高温度
friend:这一列可能是凑热闹的,你的朋友猜测的可能值,咱们不管它就好了
print('数据维度:', features.shape) # 数据维度: (348, 9)
# 处理时间数据
import datetime
# 分别得到年,月,日
years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day']
# datetime格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
dates[:5]
'''
[datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 1, 0, 0),
datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 2, 0, 0),
datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 3, 0, 0),
datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 4, 0, 0),
datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 5, 0, 0)]
'''
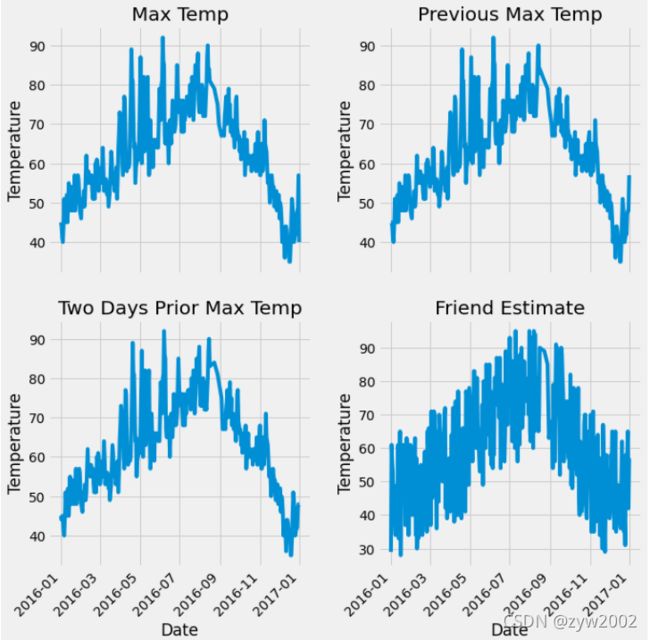
# 准备画图
# 指定默认风格
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
# 设置布局
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize = (10,10))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation = 45)
# 标签值
ax1.plot(dates, features['actual'])
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax1.set_title('Max Temp')
# 昨天
ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'])
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax2.set_title('Previous Max Temp')
# 前天
ax3.plot(dates, features['temp_2'])
ax3.set_xlabel('Date'); ax3.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax3.set_title('Two Days Prior Max Temp')
# 我的朋友
ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'])
ax4.set_xlabel('Date'); ax4.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax4.set_title('Friend Estimate')
plt.tight_layout(pad=2)
# 独热编码
features = pd.get_dummies(features)
features.head(5)
# 标签
labels = np.array(features['actual'])
# 在特征中去掉标签
features= features.drop('actual', axis = 1)
# 名字单独保存一下,以备后患
feature_list = list(features.columns)
# 转换成合适的格式
features = np.array(features)
features.shape # (348, 14)
from sklearn import preprocessing
input_features = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(features)
input_features[0]
'''
array([ 0. , -1.5678393 , -1.65682171, -1.48452388, -1.49443549,
-1.3470703 , -1.98891668, 2.44131112, -0.40482045, -0.40961596,
-0.40482045, -0.40482045, -0.41913682, -0.40482045])
'''
构建网络模型
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = float)
y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype = float)
# 权重参数初始化
weights = torch.randn((14, 128), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases = torch.randn(128, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
weights2 = torch.randn((128, 1), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases2 = torch.randn(1, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
learning_rate = 0.001
losses = []
for i in range(1000):
# 计算隐层
hidden = x.mm(weights) + biases
# 加入激活函数
hidden = torch.relu(hidden)
# 预测结果
predictions = hidden.mm(weights2) + biases2
# 通计算损失
loss = torch.mean((predictions - y) ** 2)
losses.append(loss.data.numpy())
# 打印损失值
if i % 100 == 0:
print('loss:', loss)
#返向传播计算
loss.backward()
#更新参数
weights.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights.grad.data)
biases.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases.grad.data)
weights2.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights2.grad.data)
biases2.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases2.grad.data)
# 每次迭代都得记得清空
weights.grad.data.zero_()
biases.grad.data.zero_()
weights2.grad.data.zero_()
biases2.grad.data.zero_()
predictions.shape # torch.Size([348, 1])
构建更简单的网络模型
input_size = input_features.shape[1]
hidden_size = 128
output_size = 1
batch_size = 16
my_nn = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size),
torch.nn.Sigmoid(),
torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size),
)
cost = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(my_nn.parameters(), lr = 0.001)
# 训练网络
losses = []
for i in range(1000):
batch_loss = []
# MINI-Batch方法来进行训练
for start in range(0, len(input_features), batch_size):
end = start + batch_size if start + batch_size < len(input_features) else len(input_features)
xx = torch.tensor(input_features[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
yy = torch.tensor(labels[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
prediction = my_nn(xx)
loss = cost(prediction, yy)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer.step()
batch_loss.append(loss.data.numpy())
# 打印损失
if i % 100==0:
losses.append(np.mean(batch_loss))
print(i, np.mean(batch_loss))
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = torch.float)
predict = my_nn(x).data.numpy()
# 转换日期格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
# 创建一个表格来存日期和其对应的标签数值
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': dates, 'actual': labels})
# 同理,再创建一个来存日期和其对应的模型预测值
months = features[:, feature_list.index('month')]
days = features[:, feature_list.index('day')]
years = features[:, feature_list.index('year')]
test_dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
test_dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in test_dates]
predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': test_dates, 'prediction': predict.reshape(-1)})
# 真实值
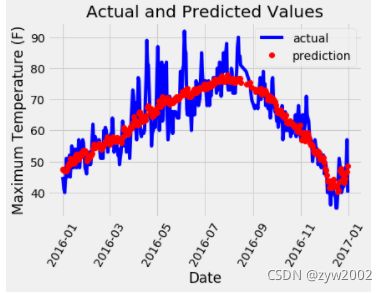
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label = 'actual')
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label = 'prediction')
plt.xticks(rotation = '60');
plt.legend()
# 图名
plt.xlabel('Date'); plt.ylabel('Maximum Temperature (F)'); plt.title('Actual and Predicted Values');
神经网络分类
%matplotlib inline
from pathlib import Path
import requests
DATA_PATH = Path("data")
PATH = DATA_PATH / "mnist"
PATH.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
URL = "http://deeplearning.net/data/mnist/"
FILENAME = "mnist.pkl.gz"
if not (PATH / FILENAME).exists():
content = requests.get(URL + FILENAME).content
(PATH / FILENAME).open("wb").write(content)
import pickle
import gzip
with gzip.open((PATH / FILENAME).as_posix(), "rb") as f:
((x_train, y_train), (x_valid, y_valid), _) = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin-1")
from matplotlib import pyplot
import numpy as np
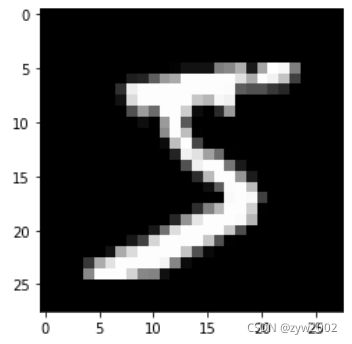
pyplot.imshow(x_train[0].reshape((28, 28)), cmap="gray")
print(x_train.shape) # (50000, 784)
import torch
x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid = map(
torch.tensor, (x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid)
)
n, c = x_train.shape
x_train, x_train.shape, y_train.min(), y_train.max()
print(x_train, y_train)
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.min(), y_train.max())
import torch.nn.functional as F
loss_func = F.cross_entropy
def model(xb):
return xb.mm(weights) + bias
bs = 64
xb = x_train[0:bs] # a mini-batch from x
yb = y_train[0:bs]
weights = torch.randn([784, 10], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
bs = 64
bias = torch.zeros(10, requires_grad=True)
print(loss_func(model(xb), yb))
创建一个model来更简化代码
必须继承nn.Module且在其构造函数中需调用nn.Module的构造函数
无需写反向传播函数,nn.Module能够利用autograd自动实现反向传播
Module中的可学习参数可以通过named_parameters()或者parameters()返回迭代器
from torch import nn
class Mnist_NN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.hidden1 = nn.Linear(784, 128)
self.hidden2 = nn.Linear(128, 256)
self.out = nn.Linear(256, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden1(x))
x = F.relu(self.hidden2(x))
x = self.out(x)
return x
net = Mnist_NN()
print(net)
for name, parameter in net.named_parameters():
print(name, parameter,parameter.size())
使用TensorDataset和DataLoader来简化
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_ds = TensorDataset(x_train, y_train)
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=bs, shuffle=True)
valid_ds = TensorDataset(x_valid, y_valid)
valid_dl = DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs * 2)
def get_data(train_ds, valid_ds, bs):
return (
DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=bs, shuffle=True),
DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs * 2),
)
一般在训练模型时加上model.train(),这样会正常使用Batch Normalization和 Dropout
测试的时候一般选择model.eval(),这样就不会使用Batch Normalization和 Dropou
import numpy as np
def fit(steps, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, valid_dl):
for step in range(steps):
model.train()
for xb, yb in train_dl:
loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
losses, nums = zip(
*[loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb) for xb, yb in valid_dl]
)
val_loss = np.sum(np.multiply(losses, nums)) / np.sum(nums)
print('当前step:'+str(step), '验证集损失:'+str(val_loss))
from torch import optim
def get_model():
model = Mnist_NN()
return model, optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
def loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt=None):
loss = loss_func(model(xb), yb)
if opt is not None:
loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.zero_grad()
return loss.item(), len(xb)
train_dl, valid_dl = get_data(train_ds, valid_ds, bs)
model, opt = get_model()
fit(25, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, valid_dl)