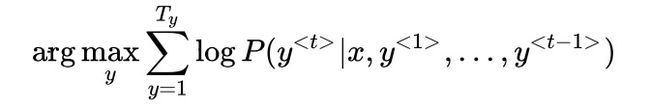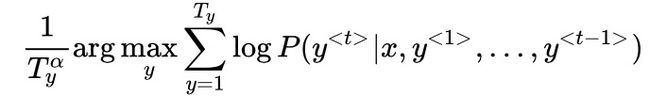吴恩达深度学习 5.3 序列模型和注意力机制
1. 知识点
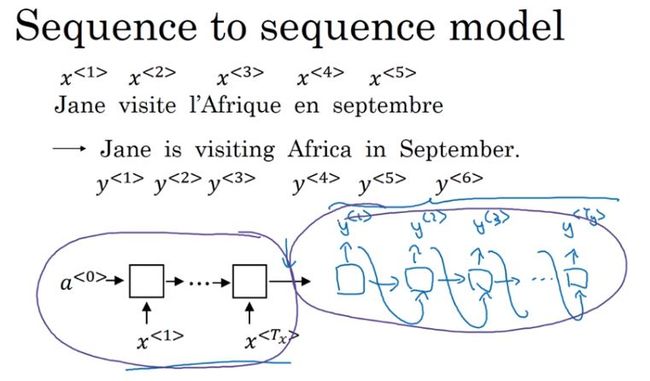
- sequence to sequence模型:编码网络和解码网络
- image to sequence模型:卷积,全连接,输出序列,对序列解码
- 机器翻译:条件语言模型,相对于语言模型总是以零向量开始,机器翻译以每个单词的一系列向量作为输入。
- 机器翻译,寻找最大的概率输出:
- 机器学习为什么不用贪心算法:原因一,机器翻译的目标是一次性输入整体概率最大的序列,而不是逐步寻找概率最大的单词;原因二,贪心算法需要计算词库中每个单词出现的概率,计算量过大。
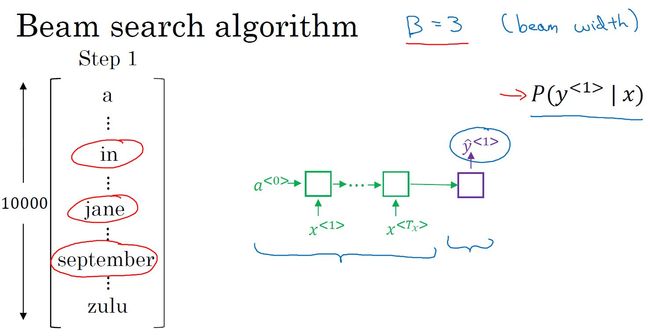
- 集束搜索:
- 对输入序列用编码网络进行编码,输出编码向量,维度为词库大小,值为每个单词的概率。设置集束宽带,比如3,则取前3个最大输出概率的单词。
- 对得到的3个单词,对词库中的每个单词进行配对,分别计算词对出现的概率。同样选择前3个单词对。
- 与第2)步类似,直到遇到结束符。
- 集束搜索的改进:1)最大化的目标为概率相乘,值会非常小,取对数运算,使运算更稳定。2)用输出单词长度值Ty和超参数
 对目标进行归一化,使其得到更好的效果。
对目标进行归一化,使其得到更好的效果。
- 集束搜索误差分析:用RNN模型计算人工翻译和集束搜索机器翻译哪个概率更大,如果人工大于机器,可能是机器翻译错了,如果机器大于人工,可能是RNN错了。
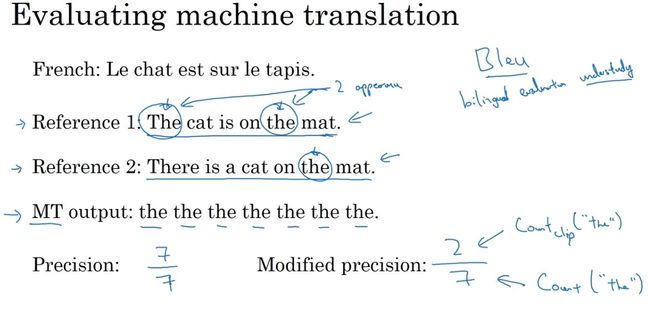
- Bleu Score评估翻译系统的准确性:观察机器翻译输出的每个词是否出现在参考中。并设置每个词的得分上限,避免机器输出中重复出现在参考中的词。
- 二元词组的bleu scroe:将二元启组作为评估的对象,得出机器翻译的二元词组的得分和其相应的得分上限,改进精确度
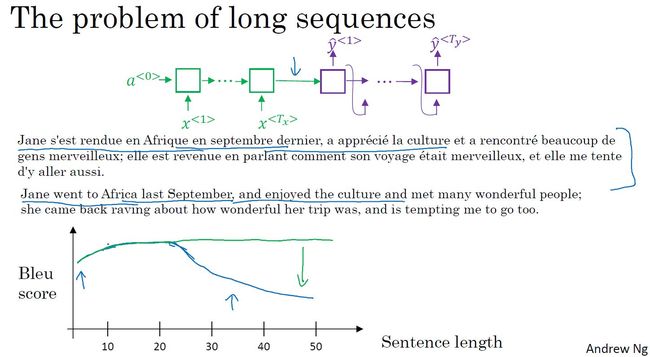
- 长句子存在的问题:RNN模型对短句子翻译效果较好,对于长句子,其bleu score会在句子长度超过一定值时下降。
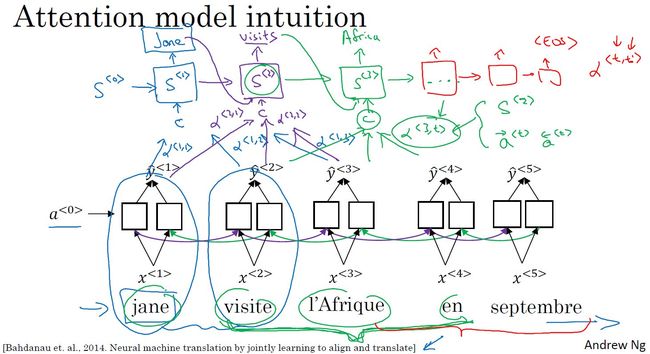
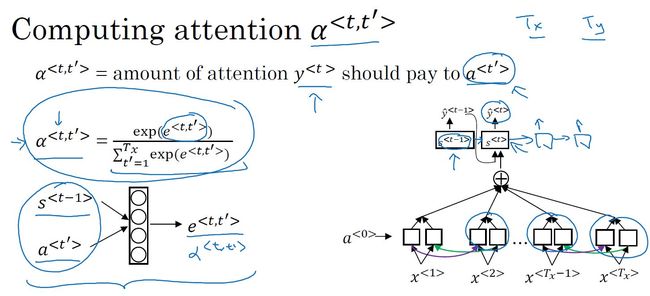
- 注意力模型:根据激活值和上下文对当前输出的影响力权重,进行运算,获得输出。
- 注意力模型详解:
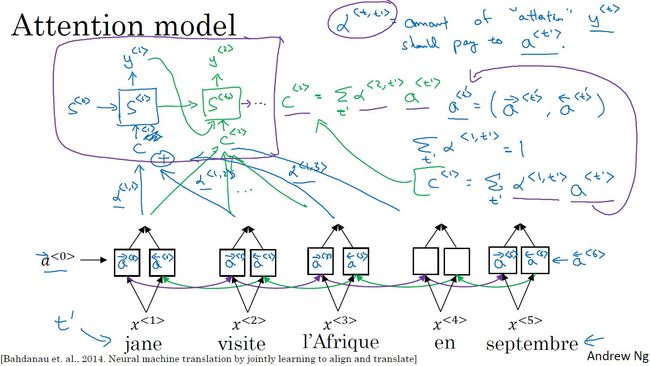
- 激活值
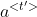 :表示输入句子通过双向RNN得到的每一步激活值。
:表示输入句子通过双向RNN得到的每一步激活值。 - 注意力权重
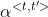 :表示第t’步输入对第t步输入的注意力权重。
:表示第t’步输入对第t步输入的注意力权重。 =1,即第t步输出受所有步影响权重之和为1。
=1,即第t步输出受所有步影响权重之和为1。 - 权重之和
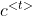 :
: 表示当前步t受所有步影响的权重之和为t步受每一步t’的影响权重乘以每一步t'的激活值之和。
表示当前步t受所有步影响的权重之和为t步受每一步t’的影响权重乘以每一步t'的激活值之和。
- 注意力权重的计算:
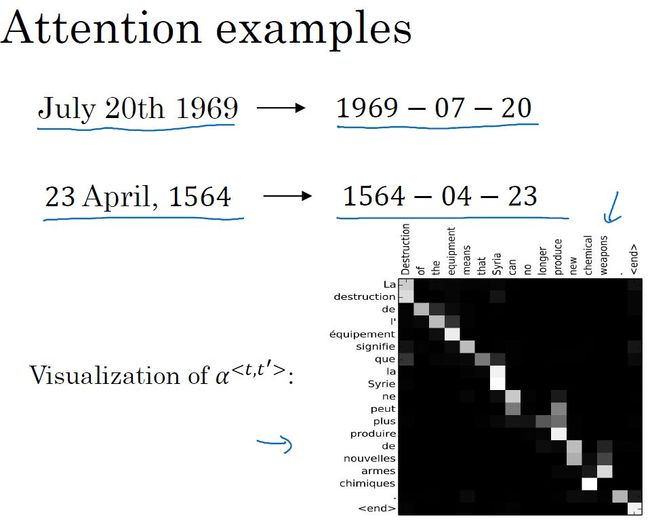
- 注意力例子和注意力权重的可视化:
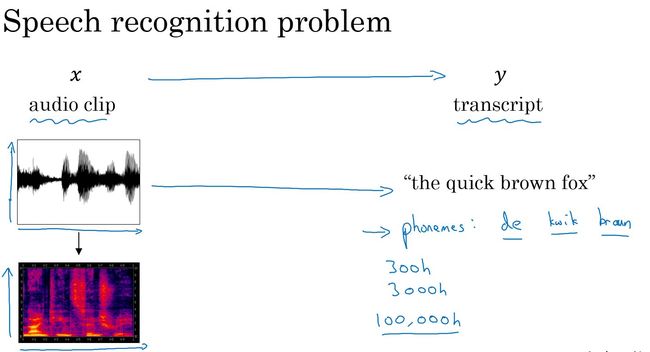
- 语音识别问题:将一段音频信息转化为文本。输入为声谱图,输出为对应的文本。
- 用注意力模型的语音识别:
- CTC损失函数的语音识别:语音识别系统的输入是音频信息,以小的时间间隔进行采样,可能对于一个10秒的语音片断,会采样到1000个输入片断,而输出则是几个单词。CTC损失函数允许在RNN模型输出重复的字符和空白字符,以实现输入和输出长度保持一致。
- 触发字检测:用关键字语音来触发操作
- 触发字检测算法:将音频信号转化了声谱图,输入RNN语音识别模型,在输出没有出现触发关键字前,触发标识为假,出现触发关键字后,触发标识置为真。
2. 应用实例
实现思路:
机器翻译和触发词检测
将人类可读日期翻译成机器可读日期
- 加载数据,获得训练样本,人类可读日期对应机器可读日期元组列表dataset,人类可读日期中使用的安符映射到整数值索引human_vocab,机器可读日期中使用的字符映射到整数值索引machine_voacb。逆索性。
- 将数据预处理,输出人类日期索引X,机器日期索引Y,人类日期索引独热编码Xoh,机器日期独热Yoh。
带注意力的神经机器翻译
- 图是注意力模型和注意力变量的计算(怎么用激活值a训练出注意力变量的,没咋看懂。。)。
- 将需要的层定义为全局变量。复制向量RepeatVector(),向量连接concatenate(),全连接层Dense(),激活层Activation(),点乘层Dot()。
- 单步attention计算。输入a(不带注意力的LSTM的隐藏状态),s_prev(带注意力的LSTM的前一个隐藏状态),重复Tx(输入长度)个s_prev,以和a进行连接(a,s_prev),通过两个全连接神经网络计算,对全连接运算结果进行softmax激活运算,对softmax结果和输入a进行点乘运算,获得当前步的注意力context。
- 创建模型实例。输入参数,输入序列长度Tx,输出序列长度Ty,不带注意力的LSTM的隐藏状态的大小为n_a,带注意力的LSTM的隐藏状态大小n_s,人类字典大小human_vocab_size,机器字典大小machine_vocab_size。初始化输入列表X,隐藏状态s0,单元状态c0,输出列表outputs.
- 定义不含注意力的的双向LSTM,获得隐藏状态a,进行Ty步迭代,用a和s计算当前步注意力context,用注意力context、隐藏状态s和单元状态c运算带注意力的LSTM post_activation_LSTM_cell(),对隐藏状态s进行全连接和softmax激活运算,运算结果追加到输出序列outputs。
触发词检测
- 加载要使用的包。将录音转换成频谱图graph_spectorgram(),定义频谱图时间步数Tx=5511,输出步数为Ty=1375。
- 加载背景音、正例、负例音频。
- 在背景音上叠加正例词和负例词。
- 检查时间段与背景音频中已经插入的正负例音频时间段是否有重复,is_overlapping(segment_time,existing_segments),入参segment_time为待检查时间段起止时间元组(segment_start,segment_end)。入参existing_segments为现有时间段超止时间元组列表。若有冲突则返回True。
- 在背景音频中随机插入音频片段,insert_audio_clip(background,audio_clip,previous_segments)。入参background表示背景录音,audio_clip表示要插入的音频,previos_segments表示已放置的音频片段时间列表。计算插入音频的长度为segment_ms,随机产生长度为segment_ms的时间段,判断生成的时间段与已有的时间段是否有冲突,如冲突,则重新生成随机时间段,直到不冲突。将随机生成的时间段加入到背景音频已添加的正负例音频片段列表中。叠加背景音频和要插入的音频。函数返回合成后的背景音频和版本更新后的正负例音频片段起止时间列表。
- 在正例词后面的标签向量y中插入1,insert_ones(y,segment_end_ms),segment_end_ms为音频位置(单位为ms),y为(1,1375)维数组,y初始化为0。计算音频频谱图位置为segment_end_y。在标签y的segment_end_y位置的后面一个位置置1,共置50个位置,若遇y末尾则提前终止。返回为更新后的y。
- 创建一个新的训练样例,create_training_example(background,activates,negatives),入参为背景音频,正例音频片断列表,负例音频片段列表。初始化标签向量y为0(维度为(1,Ty))。从正例表表随机选择0-4个片段。将正例列表中片段依次插入背景音频中,并在y中插入标签。负例列表做同样的处理(负例不用插入标签)。将处理后的背景音频导出为.wav格式,并绘制频谱图。返回频谱图和标签y。
- 已经实现了生成单个训练示例所需的代码,为了节省时间 ,加载已经生成的训练样例和开发集示例。
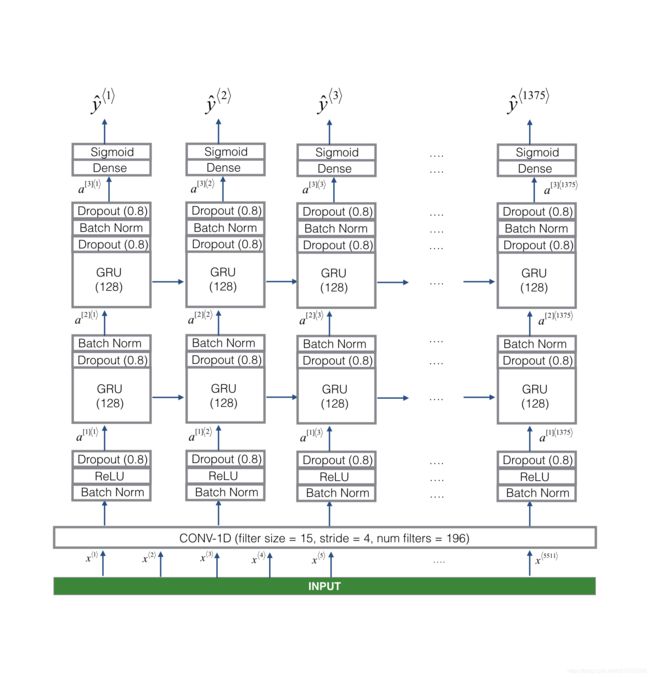
- 搭建模型。导入需要使用的包。搭建模型(如图)。以节省时间,加载训练好的模型。使用Adam优化器和二进制交叉熵损失进一步训练模型。测试模型准确率。
- 做出预测。detect_triggerword(filename),对音频filename进行预测,输出predictions。在正例出现后增加鸣响声,clime_on_active(filename,predictions,threshold),对预测值高于阈值,且距上一次加入鸣响声超过75个连续步,叠加鸣响声。
from keras.layers import Bidirectional, Concatenate, Permute, Dot, Input, LSTM, Multiply
from keras.layers import RepeatVector, Dense, Activation, Lambda
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.models import load_model, Model
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from faker import Faker
import random
from tqdm import tqdm
from babel.dates import format_date
from nmt_utils import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
Using TensorFlow backend.
m = 10000
dataset, human_vocab, machine_vocab, inv_machine_vocab = load_dataset(m)
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 10000/10000 [00:00<00:00, 14551.92it/s]
dataset[:10]
[('9 may 1998', '1998-05-09'),
('10.09.70', '1970-09-10'),
('4/28/90', '1990-04-28'),
('thursday january 26 1995', '1995-01-26'),
('monday march 7 1983', '1983-03-07'),
('sunday may 22 1988', '1988-05-22'),
('tuesday july 8 2008', '2008-07-08'),
('08 sep 1999', '1999-09-08'),
('1 jan 1981', '1981-01-01'),
('monday may 22 1995', '1995-05-22')]
Tx = 30
Ty = 10
X, Y, Xoh, Yoh = preprocess_data(dataset, human_vocab, machine_vocab, Tx, Ty)
print("X.shape:", X.shape)
print("Y.shape:", Y.shape)
print("Xoh.shape:", Xoh.shape)
print("Yoh.shape:", Yoh.shape)
X.shape: (10000, 30)
Y.shape: (10000, 10)
Xoh.shape: (10000, 30, 37)
Yoh.shape: (10000, 10, 11)
index = 0
print("Source date:", dataset[index][0])
print("Target date:", dataset[index][1])
print()
print("Source after preprocessing (indices):", X[index])
print("Target after preprocessing (indices):", Y[index])
print()
print("Source after preprocessing (one-hot):", Xoh[index])
print("Target after preprocessing (one-hot):", Yoh[index])
Source date: 9 may 1998
Target date: 1998-05-09Source after preprocessing (indices): [12 0 24 13 34 0 4 12 12 11 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36 36
36 36 36 36 36 36]
Target after preprocessing (indices): [ 2 10 10 9 0 1 6 0 1 10]Source after preprocessing (one-hot): [[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 1.]]
Target after preprocessing (one-hot): [[0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
# 将共享层定义为全局变量
repeator = RepeatVector(Tx)
concatenator = Concatenate(axis=-1)
densor1 = Dense(10, activation = "tanh")
densor2 = Dense(1, activation = "relu")
activator = Activation(softmax, name='attention_weights') # 在这个 notebook 我们正在使用自定义的 softmax(axis = 1)
dotor = Dot(axes = 1)
# GRADED FUNCTION: one_step_attention
def one_step_attention(a, s_prev):
"""
执行一步 attention: 输出一个上下文向量,输出作为注意力权重的点积计算的上下文向量
"alphas" Bi-LSTM的 隐藏状态 "a"
参数:
a -- Bi-LSTM的输出隐藏状态 numpy-array 维度 (m, Tx, 2*n_a)
s_prev -- (post-attention) LSTM的前一个隐藏状态, numpy-array 维度(m, n_s)
返回:
context -- 上下文向量, 下一个(post-attetion) LSTM 单元的输入
"""
# 使用 repeator 重复 s_prev 维度 (m, Tx, n_s) 这样你就可以将它与所有隐藏状态"a" 连接起来。 (≈ 1 line)
s_prev = repeator(s_prev)
# 使用 concatenator 在最后一个轴上连接 a 和 s_prev (≈ 1 line)
concat = concatenator([a, s_prev])
# 使用 densor1 传入参数 concat, 通过一个小的全连接神经网络来计算“中间能量”变量 e。(≈1 lines)
e = densor1(concat)
# 使用 densor2 传入参数 e , 通过一个小的全连接神经网络来计算“能量”变量 energies。(≈1 lines)
energies = densor2(e)
# 使用 activator 传入参数 "energies" 计算注意力权重 "alphas" (≈ 1 line)
alphas = activator(energies)
# 使用 dotor 传入参数 "alphas" 和 "a" 计算下一个((post-attention) LSTM 单元的上下文向量 (≈ 1 line)
context = dotor([alphas, a])
return context
n_a = 32
n_s = 64
post_activation_LSTM_cell = LSTM(n_s, return_state = True)
output_layer = Dense(len(machine_vocab), activation=softmax)
# GRADED FUNCTION: model
def model(Tx, Ty, n_a, n_s, human_vocab_size, machine_vocab_size):
"""
参数:
Tx -- 输入序列的长度
Ty -- 输出序列的长度
n_a -- Bi-LSTM的隐藏状态大小
n_s -- post-attention LSTM的隐藏状态大小
human_vocab_size -- python字典 "human_vocab" 的大小
machine_vocab_size -- python字典 "machine_vocab" 的大小
返回:
model -- Keras 模型实例
"""
# 定义模型的输入,维度 (Tx,)
# 定义 s0 和 c0, 初始化解码器 LSTM 的隐藏状态,维度 (n_s,)
X = Input(shape=(Tx, human_vocab_size))
s0 = Input(shape=(n_s,), name='s0')
c0 = Input(shape=(n_s,), name='c0')
s = s0
c = c0
# 初始化一个空的输出列表
outputs = []
# 第一步:定义 pre-attention Bi-LSTM。 记得使用 return_sequences=True. (≈ 1 line)
a = Bidirectional(LSTM(n_a, return_sequences=True), input_shape=(m, Tx, n_a * 2))(X)
# 第二步:迭代 Ty 步
for t in range(Ty):
# 第二步.A: 执行一步注意机制,得到在 t 步的上下文向量 (≈ 1 line)
context = one_step_attention(a, s)
# 第二步.B: 使用 post-attention LSTM 单元得到新的 "context"
# 别忘了使用: initial_state = [hidden state, cell state] (≈ 1 line)
s, _, c = post_activation_LSTM_cell(context, initial_state=[s, c])
# 第二步.C: 使用全连接层处理post-attention LSTM 的隐藏状态输出 (≈ 1 line)
out = output_layer(s)
# 第二步.D: 追加 "out" 到 "outputs" 列表 (≈ 1 line)
outputs.append(out)
# 第三步:创建模型实例,获取三个输入并返回输出列表。 (≈ 1 line)
model = Model(inputs=[X, s0, c0], outputs=outputs)
return model
model = model(Tx, Ty, n_a, n_s, len(human_vocab), len(machine_vocab))
model.summary()
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 30, 37) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
s0 (InputLayer) (None, 64) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
bidirectional_1 (Bidirectional) (None, 30, 64) 17920 input_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVector) (None, 30, 64) 0 s0[0][0]
lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
concatenate_1 (Concatenate) (None, 30, 128) 0 bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[0][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[1][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[2][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[3][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[4][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[5][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[6][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[7][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[8][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 30, 10) 1290 concatenate_1[0][0]
concatenate_1[1][0]
concatenate_1[2][0]
concatenate_1[3][0]
concatenate_1[4][0]
concatenate_1[5][0]
concatenate_1[6][0]
concatenate_1[7][0]
concatenate_1[8][0]
concatenate_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 30, 1) 11 dense_1[0][0]
dense_1[1][0]
dense_1[2][0]
dense_1[3][0]
dense_1[4][0]
dense_1[5][0]
dense_1[6][0]
dense_1[7][0]
dense_1[8][0]
dense_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
attention_weights (Activation) (None, 30, 1) 0 dense_2[0][0]
dense_2[1][0]
dense_2[2][0]
dense_2[3][0]
dense_2[4][0]
dense_2[5][0]
dense_2[6][0]
dense_2[7][0]
dense_2[8][0]
dense_2[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dot_1 (Dot) (None, 1, 64) 0 attention_weights[0][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[1][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[2][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[3][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[4][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[5][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[6][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[7][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[8][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[9][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
c0 (InputLayer) (None, 64) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
lstm_1 (LSTM) [(None, 64), (None, 33024 dot_1[0][0]
s0[0][0]
c0[0][0]
dot_1[1][0]
lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[0][2]
dot_1[2][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[1][2]
dot_1[3][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[2][2]
dot_1[4][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[3][2]
dot_1[5][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[4][2]
dot_1[6][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[5][2]
dot_1[7][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[6][2]
dot_1[8][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[7][2]
dot_1[9][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
lstm_1[8][2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 11) 715 lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
lstm_1[9][0]
==================================================================================================
Total params: 52,960
Trainable params: 52,960
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
### START CODE HERE ### (≈2 lines)
opt = Adam(lr=0.005, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01)
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=opt, metrics=['accuracy'])
### END CODE HERE ###
s0 = np.zeros((m, n_s))
c0 = np.zeros((m, n_s))
outputs = list(Yoh.swapaxes(0,1))
model.fit([Xoh, s0, c0], outputs, epochs=1, batch_size=100)
model.load_weights('models/model.h5')
EXAMPLES = ['3 May 1979', '5 April 09', '21th of August 2016', 'Tue 10 Jul 2007', 'Saturday May 9 2018', 'March 3 2001', 'March 3rd 2001', '1 March 2001']
for example in EXAMPLES:
source = string_to_int(example, Tx, human_vocab)
source = np.array(list(map(lambda x: to_categorical(x, num_classes=len(human_vocab)), source)))
source = np.expand_dims(source, axis=0)
prediction = model.predict([source, s0, c0])
prediction = np.argmax(prediction, axis = -1)
output = [inv_machine_vocab[int(i)] for i in prediction]
print("source:", example)
print("output:", ''.join(output))
source: 3 May 1979
output: 1979-05-03
source: 5 April 09
output: 2009-05-05
source: 21th of August 2016
output: 2016-08-21
source: Tue 10 Jul 2007
output: 2007-07-10
source: Saturday May 9 2018
output: 2018-05-09
source: March 3 2001
output: 2001-03-03
source: March 3rd 2001
output: 2001-03-03
source: 1 March 2001
output: 2001-03-01
model.summary()
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 30, 37) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
s0 (InputLayer) (None, 64) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
bidirectional_1 (Bidirectional) (None, 30, 64) 17920 input_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVector) (None, 30, 64) 0 s0[0][0]
lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
concatenate_1 (Concatenate) (None, 30, 128) 0 bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[0][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[1][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[2][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[3][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[4][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[5][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[6][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[7][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[8][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
repeat_vector_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 30, 10) 1290 concatenate_1[0][0]
concatenate_1[1][0]
concatenate_1[2][0]
concatenate_1[3][0]
concatenate_1[4][0]
concatenate_1[5][0]
concatenate_1[6][0]
concatenate_1[7][0]
concatenate_1[8][0]
concatenate_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 30, 1) 11 dense_1[0][0]
dense_1[1][0]
dense_1[2][0]
dense_1[3][0]
dense_1[4][0]
dense_1[5][0]
dense_1[6][0]
dense_1[7][0]
dense_1[8][0]
dense_1[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
attention_weights (Activation) (None, 30, 1) 0 dense_2[0][0]
dense_2[1][0]
dense_2[2][0]
dense_2[3][0]
dense_2[4][0]
dense_2[5][0]
dense_2[6][0]
dense_2[7][0]
dense_2[8][0]
dense_2[9][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dot_1 (Dot) (None, 1, 64) 0 attention_weights[0][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[1][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[2][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[3][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[4][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[5][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[6][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[7][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[8][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
attention_weights[9][0]
bidirectional_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
c0 (InputLayer) (None, 64) 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
lstm_1 (LSTM) [(None, 64), (None, 33024 dot_1[0][0]
s0[0][0]
c0[0][0]
dot_1[1][0]
lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[0][2]
dot_1[2][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[1][2]
dot_1[3][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[2][2]
dot_1[4][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[3][2]
dot_1[5][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[4][2]
dot_1[6][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[5][2]
dot_1[7][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[6][2]
dot_1[8][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[7][2]
dot_1[9][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
lstm_1[8][2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 11) 715 lstm_1[0][0]
lstm_1[1][0]
lstm_1[2][0]
lstm_1[3][0]
lstm_1[4][0]
lstm_1[5][0]
lstm_1[6][0]
lstm_1[7][0]
lstm_1[8][0]
lstm_1[9][0]
==================================================================================================
Total params: 52,960
Trainable params: 52,960
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
attention_map = plot_attention_map(model, human_vocab, inv_machine_vocab, "Tuesday 09 Oct 1993", num = 7, n_s = 64)
import numpy as np
from pydub import AudioSegment
import random
import sys
import io
import os
import glob
import IPython
from td_utils import *
%matplotlib inline
IPython.display.Audio("./raw_data/activates/1.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
IPython.display.Audio("./raw_data/negatives/4.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
IPython.display.Audio("./raw_data/backgrounds/1.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
IPython.display.Audio("audio_examples/example_train.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
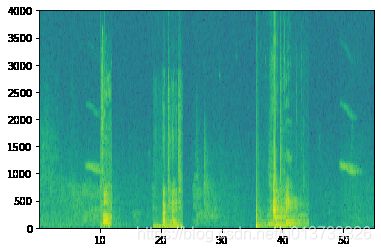
x = graph_spectrogram("audio_examples/example_train.wav")_, data = wavfile.read("audio_examples/example_train.wav")
print("Time steps in audio recording before spectrogram", data[:,0].shape)
print("Time steps in input after spectrogram", x.shape)
Time steps in audio recording before spectrogram (441000,)
Time steps in input after spectrogram (101, 5511)
Tx = 5511 # 从频谱图输入到模型的时间步数
n_freq = 101 # 在频谱图的每个时间步输入模型的频率数
Ty = 1375 # 我们模型输出中的时间步数
# 使用pydub加载音频片段
activates, negatives, backgrounds = load_raw_audio()
print("background len: " + str(len(backgrounds[0]))) # 应该是10,000,因为它是一个10秒的剪辑
print("activate[0] len: " + str(len(activates[0]))) # 也许大约1000,因为 "activate" 音频剪辑通常大约1秒(但变化很大)
print("activate[1] len: " + str(len(activates[1]))) # 不同的 "activate" 剪辑可以具有不同的长度
background len: 10000
activate[0] len: 721
activate[1] len: 731
def get_random_time_segment(segment_ms):
"""
获取 10,000 ms音频剪辑中时间长为 segment_ms 的随机时间段。
参数:
segment_ms -- 音频片段的持续时间,以毫秒为单位("ms" 代表 "毫秒")
返回:
segment_time -- 以ms为单位的元组(segment_start,segment_end)
"""
segment_start = np.random.randint(low=0, high=10000-segment_ms) # 确保段不会超过10秒背景
segment_end = segment_start + segment_ms - 1
return (segment_start, segment_end)
# GRADED FUNCTION: is_overlapping
def is_overlapping(segment_time, previous_segments):
"""
检查段的时间是否与现有段的时间重叠。
参数:
segment_time -- 新段的元组(segment_start,segment_end)
previous_segments -- 现有段的元组列表(segment_start,segment_end)
返回:
如果时间段与任何现有段重叠,则为True,否则为False
"""
segment_start, segment_end = segment_time
# 第一步:将重叠标识 overlap 初始化为“False”标志 (≈ 1 line)
overlap = False
# 第二步:循环遍历 previous_segments 的开始和结束时间。
# 比较开始/结束时间,如果存在重叠,则将标志 overlap 设置为True (≈ 3 lines)
for previous_start, previous_end in previous_segments:
if segment_start <= previous_end and segment_end >= previous_start:
overlap = True
return overlap
Overlap 1 = False
Overlap 2 = True
# GRADED FUNCTION: insert_audio_clip
def insert_audio_clip(background, audio_clip, previous_segments):
"""
在随机时间步骤中在背景噪声上插入新的音频片段,确保音频片段与现有片段不重叠。
参数:
background -- 10秒背景录音。
audio_clip -- 要插入/叠加的音频剪辑。
previous_segments -- 已放置的音频片段的时间
返回:
new_background -- 更新的背景音频
"""
# 以ms为单位获取音频片段的持续时间
segment_ms = len(audio_clip)
# 第一步:使用其中一个辅助函数来选择要插入的随机时间段
# 新的音频剪辑。 (≈ 1 line)
segment_time = get_random_time_segment(segment_ms)
# 第二步:检查新的segment_time是否与previous_segments之一重叠。
# 如果重叠如果是这样,请继续随机选择新的 segment_time 直到它不重叠。(≈ 2 lines)
while is_overlapping(segment_time, previous_segments):
segment_time = get_random_time_segment(segment_ms)
# 第三步: 将新的 segment_time 添加到 previous_segments 列表中 (≈ 1 line)
previous_segments.append(segment_time)
# 第四步: 叠加音频片段和背景
new_background = background.overlay(audio_clip, position = segment_time[0])
return new_background, segment_time
np.random.seed(5)
audio_clip, segment_time = insert_audio_clip(backgrounds[0], activates[0], [(3790, 4400)])
audio_clip.export("insert_test.wav", format="wav")
print("Segment Time: ", segment_time)
IPython.display.Audio("insert_test.wav")
Segment Time: (2915, 3635)
CSDN不支持播放音频
# 预期的音频
IPython.display.Audio("audio_examples/insert_reference.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
# GRADED FUNCTION: insert_ones
def insert_ones(y, segment_end_ms):
"""
更新标签向量y。段结尾的后面50个输出的标签应设为 1。
严格来说,我们的意思是 segment_end_y 的标签应该是 0,而随后的50个标签应该是1。
参数:
y -- numpy数组的维度 (1, Ty), 训练样例的标签
segment_end_ms -- 以ms为单位的段的结束时间
返回:
y -- 更新标签
"""
# 背景持续时间(以频谱图时间步长表示)
segment_end_y = int(segment_end_ms * Ty / 10000.0)
# 将1添加到背景标签(y)中的正确索引
for i in range(segment_end_y + 1, segment_end_y + 51):
if i < Ty:
y[0, i] = 1
return y
arr1 = insert_ones(np.zeros((1, Ty)), 9700)
plt.plot(insert_ones(arr1, 4251)[0,:])
print("sanity checks:", arr1[0][1333], arr1[0][634], arr1[0][635])
# GRADED FUNCTION: create_training_example
def create_training_example(background, activates, negatives):
"""
创建具有给定背景,正例和负例的训练示例。
参数:
background -- 10秒背景录音
activates -- "activate" 一词的音频片段列表
negatives -- 不是 "activate" 一词的音频片段列表
返回:
x -- 训练样例的频谱图
y -- 频谱图的每个时间步的标签
"""
# 设置随机种子
np.random.seed(18)
# 让背景更安静
background = background - 20
# 第一步:初始化 y (标签向量)为0 (≈ 1 line)
y = np.zeros((1, Ty))
# 第二步:将段时间初始化为空列表 (≈ 1 line)
previous_segments = []
# 从整个 "activate" 录音列表中选择0-4随机 "activate" 音频片段
number_of_activates = np.random.randint(0, 5)
random_indices = np.random.randint(len(activates), size=number_of_activates)
random_activates = [activates[i] for i in random_indices]
# 第三步: 循环随机选择 "activate" 剪辑插入背景
for random_activate in random_activates:
# 插入音频剪辑到背景
background, segment_time = insert_audio_clip(background, random_activate, previous_segments)
# 从 segment_time 中取 segment_start 和 segment_end
segment_start, segment_end = segment_time
# 在 "y" 中插入标签
y = insert_ones(y, segment_end_ms=segment_end)
# 从整个负例录音列表中随机选择0-2个负例录音
number_of_negatives = np.random.randint(0, 3)
random_indices = np.random.randint(len(negatives), size=number_of_negatives)
random_negatives = [negatives[i] for i in random_indices]
# 第四步: 循环随机选择负例片段并插入背景中
for random_negative in random_negatives:
# 插入音频剪辑到背景
background, _ = insert_audio_clip(background, random_negative, previous_segments)
# 标准化音频剪辑的音量
background = match_target_amplitude(background, -20.0)
# 导出新的训练样例
file_handle = background.export("train" + ".wav", format="wav")
print("文件 (train.wav) 已保存在您的目录中。")
# 获取并绘制新录音的频谱图(正例和负例叠加的背景)
x = graph_spectrogram("train.wav")
return x, y
x, y = create_training_example(backgrounds[0], activates, negatives)
文件 (train.wav) 已保存在您的目录中。
IPython.display.Audio("train.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
plt.plot(y[0])# 加载预处理的训练样例
X = np.load("./XY_train/X.npy")
Y = np.load("./XY_train/Y.npy")
# 加载预处理开发集示例
X_dev = np.load("./XY_dev/X_dev.npy")
Y_dev = np.load("./XY_dev/Y_dev.npy")
from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint
from keras.models import Model, load_model, Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout, Input, Masking, TimeDistributed, LSTM, Conv1D
from keras.layers import GRU, Bidirectional, BatchNormalization, Reshape
from keras.optimizers import Adam
# GRADED FUNCTION: model
def model(input_shape):
"""
用 Keras 创建模型的图 Function creating the model's graph in Keras.
参数:
input_shape -- 模型输入数据的维度(使用Keras约定)
返回:
model -- Keras 模型实例
"""
X_input = Input(shape = input_shape)
# 第一步:卷积层 (≈4 lines)
X = Conv1D(196, 15, strides=4)(X_input) # CONV1D
X = BatchNormalization()(X) # Batch normalization 批量标准化
X = Activation('relu')(X) # ReLu activation ReLu 激活
X = Dropout(0.8)(X) # dropout (use 0.8)
# 第二步:第一个 GRU 层 (≈4 lines)
X = GRU(units = 128, return_sequences=True)(X) # GRU (使用128个单元并返回序列)
X = Dropout(0.8)(X) # dropout (use 0.8)
X = BatchNormalization()(X) # Batch normalization 批量标准化
# 第三步: 第二个 GRU 层 (≈4 lines)
X = GRU(units = 128, return_sequences=True)(X) # GRU (使用128个单元并返回序列)
X = Dropout(0.8)(X) # dropout (use 0.8)
X = BatchNormalization()(X) # Batch normalization 批量标准化
X = Dropout(0.8)(X) # dropout (use 0.8)
# 第四步: 时间分布全连接层 (≈1 line)
X = TimeDistributed(Dense(1, activation = "sigmoid"))(X) # time distributed (sigmoid)
model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X)
return model
model = model(input_shape = (Tx, n_freq))
model.summary()
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 5511, 101) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv1d_1 (Conv1D) (None, 1375, 196) 297136
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_1 (Batch (None, 1375, 196) 784
_________________________________________________________________
activation_1 (Activation) (None, 1375, 196) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 1375, 196) 0
_________________________________________________________________
gru_1 (GRU) (None, 1375, 128) 124800
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 1375, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_2 (Batch (None, 1375, 128) 512
_________________________________________________________________
gru_2 (GRU) (None, 1375, 128) 98688
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_3 (Dropout) (None, 1375, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_3 (Batch (None, 1375, 128) 512
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_4 (Dropout) (None, 1375, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
time_distributed_1 (TimeDist (None, 1375, 1) 129
=================================================================
Total params: 522,561
Trainable params: 521,657
Non-trainable params: 904
_________________________________________________________________
model = load_model('./models/tr_model.h5')
opt = Adam(lr=0.0001, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=opt, metrics=["accuracy"])
model.fit(X, Y, batch_size = 5, epochs=1)
Epoch 1/1
26/26 [==============================] - 30s 1s/step - loss: 0.0893 - acc: 0.9717
loss, acc = model.evaluate(X_dev, Y_dev)
print("Dev set accuracy = ", acc)
25/25 [==============================] - 3s 122ms/step
Dev set accuracy = 0.9296872615814209
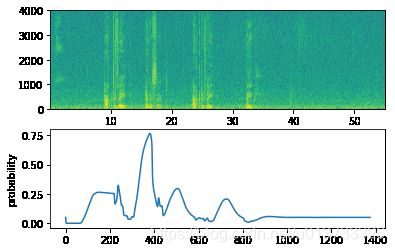
def detect_triggerword(filename):
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
x = graph_spectrogram(filename)
# 频谱图输出(freqs,Tx),我们想要(Tx,freqs)输入到模型中
x = x.swapaxes(0,1)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
predictions = model.predict(x)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(predictions[0,:,0])
plt.ylabel('probability')
plt.show()
return predictions
chime_file = "audio_examples/chime.wav"
def chime_on_activate(filename, predictions, threshold):
audio_clip = AudioSegment.from_wav(filename)
chime = AudioSegment.from_wav(chime_file)
Ty = predictions.shape[1]
# 第一步:将连续输出步初始化为0
consecutive_timesteps = 0
# 第二步: 循环y中的输出步
for i in range(Ty):
# 第三步: 增加连续输出步
consecutive_timesteps += 1
# 第四步: 如果预测高于阈值并且已经过了超过75个连续输出步
if predictions[0,i,0] > threshold and consecutive_timesteps > 75:
# 第五步:使用pydub叠加音频和背景
audio_clip = audio_clip.overlay(chime, position = ((i / Ty) * audio_clip.duration_seconds)*1000)
# 第六步: 将连续输出步重置为0
consecutive_timesteps = 0
audio_clip.export("chime_output.wav", format='wav')
IPython.display.Audio("./raw_data/dev/1.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
IPython.display.Audio("./raw_data/dev/2.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
filename = "./raw_data/dev/1.wav"
prediction = detect_triggerword(filename)
chime_on_activate(filename, prediction, 0.5)
IPython.display.Audio("./chime_output.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
filename = "./raw_data/dev/2.wav"
prediction = detect_triggerword(filename)
chime_on_activate(filename, prediction, 0.5)
IPython.display.Audio("./chime_output.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频
# 将音频预处理为正确的格式
def preprocess_audio(filename):
# 将音频片段修剪或填充到 10000ms
padding = AudioSegment.silent(duration=10000)
segment = AudioSegment.from_wav(filename)[:10000]
segment = padding.overlay(segment)
# 将帧速率设置为 44100
segment = segment.set_frame_rate(44100)
# 导出为wav
segment.export(filename, format='wav')
your_filename = "audio_examples/my_audio.wav"
preprocess_audio(your_filename)
IPython.display.Audio(your_filename) # 听你上传的音频
CSDN不支持播放音频
chime_threshold = 0.5
prediction = detect_triggerword(your_filename)
chime_on_activate(your_filename, prediction, chime_threshold)
IPython.display.Audio("./chime_output.wav")
CSDN不支持播放音频