Python机器学习15——XGboost和 LightGBM详细用法(交叉验证,网格搜参,变量筛选)
本系列基本不讲数学原理,只从代码角度去让读者们利用最简洁的Python代码实现机器学习方法。
集成模型发展到现在的XGboost,LightGBM,都是目前竞赛项目会采用的主流算法。是真正的具有做项目的价值。这两个方法都是具有很多GBM没有的特点,比如收敛快,精度好,速度快等等。但由于他们底层不是Python,没有进sklearn库,要自己单独安装,用法和sklearn库也不完全相同。
两种模型都有自己的原生用法和sklearn库接口的用法,下面把回归和分类问题案例都一一介绍。只是案例演示,因此使用都采用sklearn库的自带数据集,会方便一点。
模块安装
或者Win+R,打开CMD,输入下面两句
pip install xgboost
pip install lightgbm
然后就等自动装了
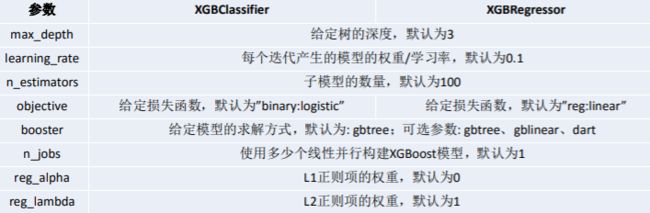
参数详情
两个模型都要大量的超参数,后面可能用到。先了解一下,后面有不明白的再回头看
还有eta 表示学习率,默认值0.3;
gamma 表示叶子结点进一步分裂的阈值。即分裂这个节点让损失函数下降超过这个值才会进行分裂,默认值0;
max_leaves 表示最大叶子节点数,默认0;
max_bin 最大桶数量,默认值256;
min_child_weigh 表示子节点包含实例权重的最小和,防止过拟合用的,越大越不容易过拟合,默认值0;
subsmaple 表示训练样本的采样率,即划分多少去训练,若是训练前就划分了训练测试集就不用管,默认值1;
colsample_bytree 表示列采样率,默认值1;
colsample_bylevel 每一级每次分裂的采样率,默认值1;
scale_pos_weight 控制正负样本的权重平衡,取值应该设为负类样本量/正类样本量,默认值1;
predictor 预测器类型,默认值cpu_predictor, 还可以换显卡加速:gpu_predictor。
seed 随机数种子,默认0;
slient 打印运行的信息,默认打印,默认值0;
objective [默认值=reg:linear]
reg:linear– 线性回归
reg:logistic – 逻辑回归
binary:logistic – 二分类逻辑回归,输出为概率
binary:logitraw – 二分类逻辑回归,输出的结果为wTx
count:poisson – 计数问题的poisson回归,输出结果为poisson分布。在poisson回归中,max_delta_step的默认值为0.7 (used to safeguard optimization)
multi:softmax – 设置 XGBoost 使用softmax目标函数做多分类,需要设置参数num_class(类别个数)
multi:softprob – 如同softmax,但是输出结果为ndata*nclass的向量,其中的值是每个数据分为每个类的概率。
eval_metric [默认值=取决于目标函数选择]
rmse: 均方根误差
mae: 平均绝对值误差
logloss: negative log-likelihood
error: 二分类错误率。其值通过错误分类数目与全部分类数目比值得到。对于预测,预测值大于0.5被认为是正类,其它归为负类。 error@t: 不同的划分阈值可以通过 ‘t’进行设置
merror: 多分类错误率
mlogloss: 多分类log损失
auc: 曲线下的面积
ndcg: Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain
map: 平均正确率
一般来说,我们都会使用xgboost.train(params, dtrain)函数来训练我们的模型。这里的params指的是booster参数。
XGboost原生用法
分类
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#import pickle
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#鸢尾花
iris=load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
X.shape,y.shape划分训练测试集,将数据变为xgb需要的格式
# 做数据切分
X_train, X_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=0)
xgb_train = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
xgb_test = xgb.DMatrix( X_test,y_test )设置参数
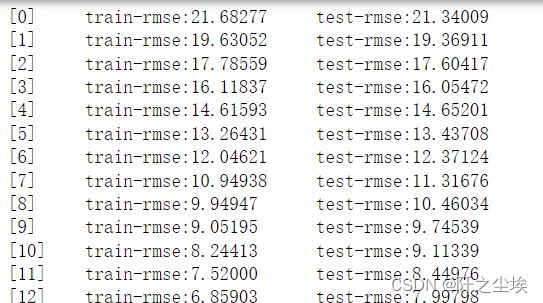
params = {'objective':'multi:softmax','num_class':3,'booster':'gbtree','max_depth':5, 'eta':0.1, 'subsample':0.7, 'colsample_bytree':0.7}训练
num_round=50
watchlist = [(xgb_train,'train'), (xgb_test,'test')]
model = xgb.train(params, xgb_train, num_round, watchlist)预测
pred = model.predict(xgb_test)
prederror_rate=np.sum(pred!=y_test)/y_test.shape[0]
error_rate #错误率回归问题
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
X,y=load_boston(return_X_y=True)
X.shape,y.shapeX_train,X_test,y_train,y_test= train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=0)
print(X_train.shape,X_test.shape,y_train.shape,y_test.shape)
xgb_train = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
xgb_test = xgb.DMatrix( X_test,y_test )设置参数
params = {'objective':'reg:squarederror','booster':'gbtree','max_depth':5, 'eta':0.1, 'min_child_weight':1}
num_round=50
watchlist = [(xgb_train,'train'), (xgb_test,'test')]
model = xgb.train(params, xgb_train, num_round, watchlist)pred = model.predict(xgb_test)
pred,y_test计算均方误差,拟合优度
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error,r2_score
reg=LinearRegression()
reg.fit(y_test.reshape(-1, 1),pred.reshape(-1, 1))
reg.score(y_test.reshape(-1, 1),pred.reshape(-1, 1))mean_squared_error(y_test,pred),r2_score(y_test,pred)交叉验证
#交叉验证
result=xgb.cv(params=params,dtrain=xgb_train,nfold=10,metrics='rmse',#'auc'
num_boost_round=300,as_pandas=True,seed=123)
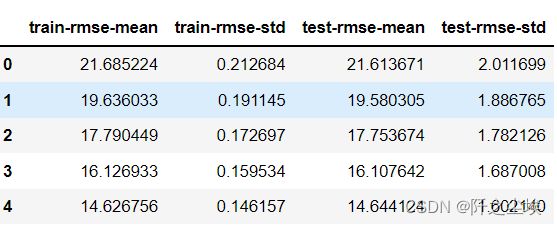
result.shape
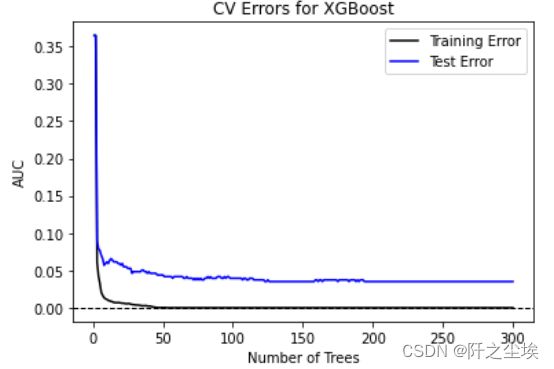
result.head()画出交叉验证误差图
# Plot CV Errors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(1, 301), result['train-rmse-mean'], 'k', label='Training Error')
plt.plot(range(1, 301), result['test-rmse-mean'], 'b', label='Test Error')
plt.xlabel('Number of Trees')
plt.ylabel('RMSE')
plt.axhline(0, linestyle='--', color='k', linewidth=1)
plt.legend()
plt.title('CV Errors for XGBoost')
plt.show()自定义目标函数和损失函数
XGboost还可以自定义损失函数和评价函数
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
X,y=load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
X.shape,y.shapeX_train,X_test,y_train,y_test= train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=8)
print(X_train.shape,X_test.shape,y_train.shape,y_test.shape)
xgb_train = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
xgb_test = xgb.DMatrix( X_test,y_test )params = {'booster':'gbtree','max_depth':5, 'eta':0.1}
num_round=50
watchlist = [(xgb_train,'train'), (xgb_test,'test')]定义损失函数和评价函数
def logregobj(preds,dtrain):
labels=dtrain.get_label()
preds=1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-preds))
grad=preds-labels
hess=preds*(1.0-preds)
return grad,hess
def evalerror(preds,dtrain):
labels=dtrain.get_label()
return 'error',float(sum(labels!=(preds>0.0)))/len(labels)训练
model = xgb.train(params, xgb_train, num_round, watchlist,obj=logregobj,feval=evalerror)交叉验证也可以使用自定义函数
result=xgb.cv(params=params,dtrain=xgb_train,nfold=10,metrics='auc',#'auc'
num_boost_round=300,as_pandas=True,seed=123,obj=logregobj,feval=evalerror)
result.head()# Plot CV Errors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(1, 301), result['train-error-mean'], 'k', label='Training Error')
plt.plot(range(1, 301), result['test-error-mean'], 'b', label='Test Error')
plt.xlabel('Number of Trees')
plt.ylabel('AUC')
plt.axhline(0, linestyle='--', color='k', linewidth=1)
plt.legend()
plt.title('CV Errors for XGBoost')
plt.show()XGboost的sklearn库接口
sklearn库接口就好用很多,符合sklearn库的一些常用的函数,例如交叉验证,网格化搜参,变量筛选,都可以用。
回归
import xgboost as xgb
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold, train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, mean_squared_error
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris, load_boston
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
X, y= load_boston(return_X_y=True)拟合评价(经典sklearn用法)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective='reg:squarederror', n_estimators=300, max_depth=6,
subsample=0.6, colsample_bytree=0.8, learning_rate=0.1, random_state=0)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
model.score(X_test, y_test)pred = model.predict(X_test)
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, pred))
rmse回归交叉验证
rng = np.random.RandomState(123)
kf = KFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=True, random_state=rng)
print("在3折数据上的交叉验证")
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
xgb_model = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective='reg:squarederror', n_estimators=300, max_depth=6,subsample=0.6,
colsample_bytree=0.8, learning_rate=0.1, random_state=0).fit(X[train_index],y[train_index])
predictions = xgb_model.predict(X[test_index])
actuals = y[test_index]
print("均方根误差:")
print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(actuals, predictions)))
print('拟合优度')
print(xgb_model.score(X[test_index],y[test_index]))回归网格化搜索最优超参数
# 回归网格化搜索最优超参数
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective='reg:squarederror',subsample=0.6, colsample_bytree=0.8, random_state=0,nthread=8)
param_dict = {'max_depth': [5,6,7,8],'n_estimators': [100,200,300],'learning_rate':[0.05,0.1,0.2]}
clf = GridSearchCV(model, param_dict, cv=10,verbose=1 , scoring='r2')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(clf.best_score_)
print(clf.best_params_)分类交叉验证
#二分类
rng = np.random.RandomState(123)
X,y=load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
print(X.shape,y.shape)
kf = KFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=True, random_state=rng)
print("在3折数据上的交叉验证")
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
xgb_model = xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='binary:logistic', n_estimators=300,random_state=0,eta=0.1,max_depth=6,
use_label_encoder=False,eval_metric=['logloss','auc','error']).fit(X[train_index],y[train_index])
predictions = xgb_model.predict(X[test_index])
actuals = y[test_index]
print("混淆矩阵:")
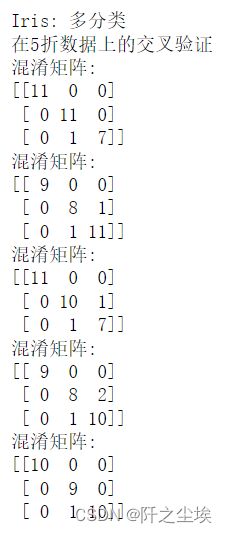
print(confusion_matrix(actuals, predictions))# 多分类:混淆矩阵
print("\nIris: 多分类")
iris = load_iris()
y = iris['target']
X = iris['data']
kf = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=rng)
print("在5折数据上的交叉验证")
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
xgb_model = xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='multi:softmax', n_estimators=300,random_state=0,eta=0.1,max_depth=6,
use_label_encoder=False,eval_metric=['logloss','auc','error']).fit(X[train_index],y[train_index])
predictions = xgb_model.predict(X[test_index])
actuals = y[test_index]
print("混淆矩阵:")
print(confusion_matrix(actuals, predictions))分类网格化搜索最优超参数
# 网格化搜索最优超参数
print("参数最优化:")
X,y=load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
xgb_model = xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='binary:logistic',random_state=0,use_label_encoder=False,eval_metric=['logloss','auc','error'])
param_dict = {'max_depth': [2,4,6],'n_estimators': [50,100,200],'eta':[0.05,0.1,0.2]}
clf = GridSearchCV(xgb_model, param_dict, verbose=1)
clf.fit(X,y)
print(clf.best_score_)
print(clf.best_params_)早停
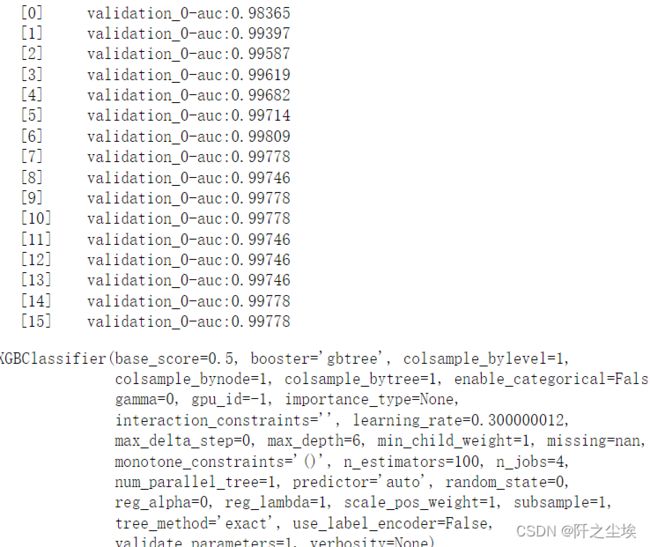
和神经网络一样,可以使用早停防止过拟合
#早停
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y,test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
clf = xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='binary:logistic',use_label_encoder=False,random_state=0)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train, early_stopping_rounds=10,
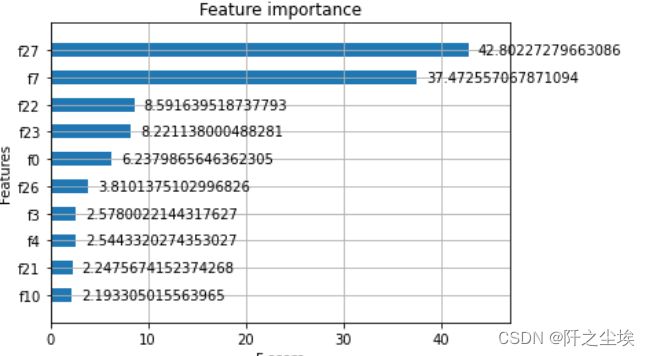
eval_metric="auc",eval_set=[(X_val, y_val)])变量重要性
xgb包自带的画图用法
#变量重要性
xgb.plot_importance(clf,height=0.5,importance_type='gain',max_num_features=10)sklearn库用法
clf.feature_importances_cancer=load_breast_cancer()
cancer.feature_names
sorted_index = clf.feature_importances_.argsort()
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.barh(range(len(cancer.feature_names)), clf.feature_importances_[sorted_index])
plt.yticks(np.arange(len(cancer.feature_names)),cancer.feature_names[sorted_index])
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.title('GradientBoosting')
#plt.savefig('梯度提升特征排序.png')
plt.tight_layout()变量筛选
根据变量重要性,小于阈值的变量就扔掉
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
selection =SelectFromModel(clf,threshold=0.05,prefit=True)
select_X_train=selection.transform(X_train)
select_X_train.shapethreshold=0.05,表示变量重要性小于0.05就扔掉,最后只留下了四个变量(和上图也一致)
将测试集也筛选一下
select_X_val=selection.transform(X_val)
select_X_val.shape查看一些筛出来了那些变量
print(selection.get_support())
print(selection.get_support(True))
[cancer.feature_names[i] for i in selection.get_support(True)]xgb到这了
lightgbm用起来其实和xgboost差不多,就是参数有细微的差别,用sklearn库会更加一致,当然也展示一下原生用法。
LightGBM原生用法
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import lightgbm as lgb
from lightgbm import plot_importance
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 加载鸢尾花数据集
iris = load_iris()
X,y = iris.data,iris.target
# 数据集分割
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=123457)
# 参数
params = {
'booster': 'gbtree',
'objective': 'multiclass', #回归:'objective': 'regression'
'num_class': 3,
'num_leaves': 31,
'subsample': 0.8,
'bagging_freq': 1,
'feature_fraction ': 0.8,
'slient': 1,
'learning_rate ': 0.01,
'seed': 0
}
# 构造训练集
dtrain = lgb.Dataset(X_train,y_train)
dtest = lgb.Dataset(X_test,y_test)
num_rounds = 500
model = lgb.train(params,dtrain, num_rounds, valid_sets=[dtrain, dtest],
verbose_eval=100, early_stopping_rounds=10)
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 计算准确率
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1))
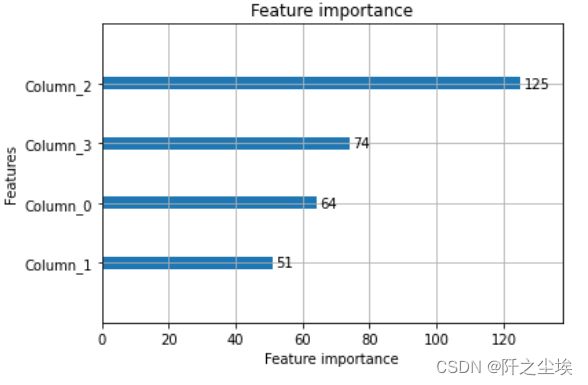
print('accuarcy:%.2f%%'%(accuracy*100))# 显示重要特征
plot_importance(model)
plt.show()
# 模型保存
#gbm.save_model('model.txt')
# 模型加载
#gbm = lgb.Booster(model_file='model.txt')LightGBM的sklearn接口
回归
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from lightgbm import plot_importance
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 导入数据集
boston = load_boston()
X ,y = boston.data,boston.target
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=0)
model = LGBMRegressor(
boosting_type='gbdt',
num_leaves=31,
max_depth=-1,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
objective='regression', # 默认是二分类
min_split_gain=0.0,
min_child_samples=20,
subsample=1.0,
subsample_freq=0,
colsample_bytree=1.0,
reg_alpha=0.0,
reg_lambda=0.0,
random_state=None,
silent=True
)
model.fit(X_train,y_train, eval_set=[(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test)],
verbose=100, early_stopping_rounds=50)# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)
print('mse', mse)
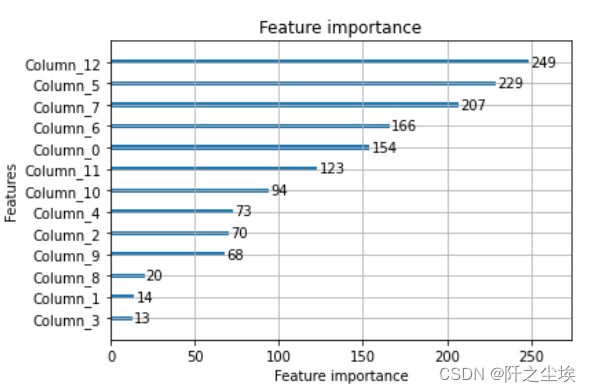
# 显示重要特征
plot_importance(model)
plt.show()分类
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from lightgbm import plot_importance
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 加载样本数据集
iris = load_iris()
X,y = iris.data,iris.target
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=12343)
model = LGBMClassifier(
max_depth=3,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=200, # 使用多少个弱分类器
objective='multiclass',
num_class=3,
booster='gbtree',
min_child_weight=2,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
reg_alpha=0,
reg_lambda=1,
seed=0 # 随机数种子
)
model.fit(X_train,y_train, eval_set=[(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test)],
verbose=100, early_stopping_rounds=50)
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
model.predict_proba
#计算准确率
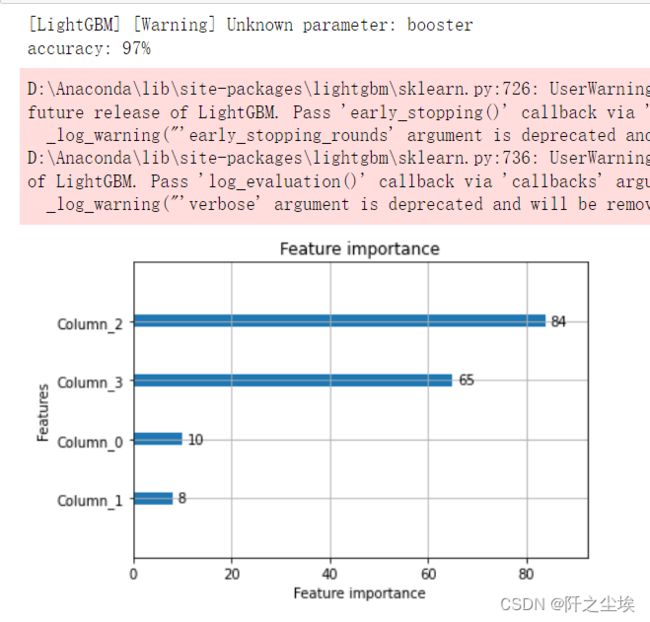
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
print('accuracy:%3.f%%'%(accuracy*100))
# 显示重要特征
plot_importance(model)
plt.show()当然,上面使用验证集去早停和评估什么的比较麻烦,模型定义好后,训练可以简单一点
model.fit(X_train,y_train)评价预测什么的和sklearn库完全一样,可以参考我以前的文章。原生用法也可以参考xgb。
print(model.score(X_test,y_test))
model.predict(X_test)