Matlab K-means聚类算法改进对多光谱遥感图像进行分类(二)
上一篇Matlab K-means聚类算法对多光谱遥感图像进行分类(一)中,自编K-means函数运行时间长,是因为程序中Kmeans_of_muldim()函数中使用了逐像元循环,用了139秒,下面对逐像元循环进行改进,把数据reshape为列向量,以整体进行运算。
function:MKmeans_of_muldim()
(注:muldim = multiple dimensions)
function [new_class_label] = MKmeans_of_muldim(data,k,change_threshold,iteration)
% 功能:实现多光谱遥感数据非监督分类算法之K-means聚类算法
% 优化了循环体,使矩阵运算速度加快
%Author: Mr. BAI
% 输入:data是s*fl*b的矩阵,s为列数(sample),fl为行数(fileline),b为波段数(band);
% k 为类别数,如果有背景值,背景值会归到某一地类中去,到时再用矢量边界图形裁剪一下即可。我考虑过将出现次数最多
% 的背景值单独划归一类,但是程序设计时不好判断,取数组中元素出现次数最多的像元为一类,有点大胆,因为无背
% 景的图像像元值也可能出现这种情况;
% change_threshold变化阈值,ENVI中默认为0.05;
% iteration为最大迭代次数,ENVI中默认为1
% 输出:new_class_label为聚类后的矩阵,赋予每个行列号一个类别标签,之后可在GIS或者ENVI中出图
% Reference:https://www.cnblogs.com/dongteng/p/5415071.html
[fl,s,b] = size(data);
tfl = fl*s;
dat = zeros(tfl,b);
for i=1:b
dat(:,i) = reshape(data(:,:,i),tfl,1);
end
%original_seed为迭代前的种子,存放一个k行,b个波段数值列的数组
old_seed = zeros(k,b);
%newseed为迭代后的新种子,存放一个k行,b个波段数值列的数组
new_seed = zeros(k,b);
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 产生k个随机种子作为遥感图像各地物类别的种子像元
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
index_record = zeros(1,k);
for i = 1:k
index_i = round(rand()*tfl);
judge = find(index_record == index_i);
%如果已经有这个值了,那么重新循环取值
if isempty(judge) == 0
i = i-1;
continue;
end
index_record(i) = index_i;
%计算取到的随机值对应图像的行列号
fl_index = floor(index_i/s);%行号
sample_index = index_i - fl_index*s;%列号
%将该种子像元的b个波段值存入
old_seed(i,:) = data(fl_index,sample_index,:);
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% 下面进行迭代,如果本次分别所有类新得到的像元数目变化在change_threshold内,则认为分类完毕。
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
n = 1;
new_class_label = zeros(tfl,1);%改进的地方
while n
distance_matrix = zeros(tfl,k);
for kind = 1:k
sum = 0;
for i=1:b
temp = power(abs(dat(:,i)-old_seed(kind,i)),2);
sum = sum+temp;
end
%每个像元与初始7个类别中心的欧式距离
ou_distance = sqrt(sum);%sum数组为tfl行,1列数据,存放了图像所有像元与第kind类中心的欧式距离
%size(ou_distance)
distance_matrix(:,kind) = ou_distance;
end
%给给各类别赋值类别标注
[M,I] = min(distance_matrix,[],2);%行取最小值,并返回最小值在该行的列标,即为距离最小所在的类别
new_class_label = I;
%计算新的各类别中心
for i=1:k
id = find(new_class_label==i);
for j=1:b
temp1 = dat(id,j);
new_seed(i,j)= mean(temp1);
end
end
new_class_pixcel_number = zeros(1,k);
for i=1:k
new_class_pixcel_number(i) = length(find(new_class_label==i));
end
%Change threshold:0.05
if n == 1
old_class_pixcel_number = ones(1,k);
end
%size(new_class_pixcel_number)
if max(abs((new_class_pixcel_number-old_class_pixcel_number)./old_class_pixcel_number)) < change_threshold || n>iteration
new_class_label = reshape(new_class_label,fl,s);
break;
end
n=n+1;
if max(abs((new_class_pixcel_number-old_class_pixcel_number)./old_class_pixcel_number)) >change_threshold
%old_class_label = new_class_label;
old_class_pixcel_number = new_class_pixcel_number;
old_seed = new_seed;
continue;
end
end
end
main函数
clc;
clear;
t0 = cputime;
cd 'E:\MATLAB\'
data=imread('nantong_city_landsat8.tif');%读取纯数据
[multi_data,r]=geotiffread('nantong_city_landsat8.tif'); % read the geo information
info=geotiffinfo('nantong_city_landsat8.tif'); % read the geo information
class_result = MKmeans_of_muldim(data,5,0.05,30);
geotiffwrite('MK-means_class.tif',class_result,r,'GeoKeyDirectoryTag',info.GeoTIFFTags.GeoKeyDirectoryTag);
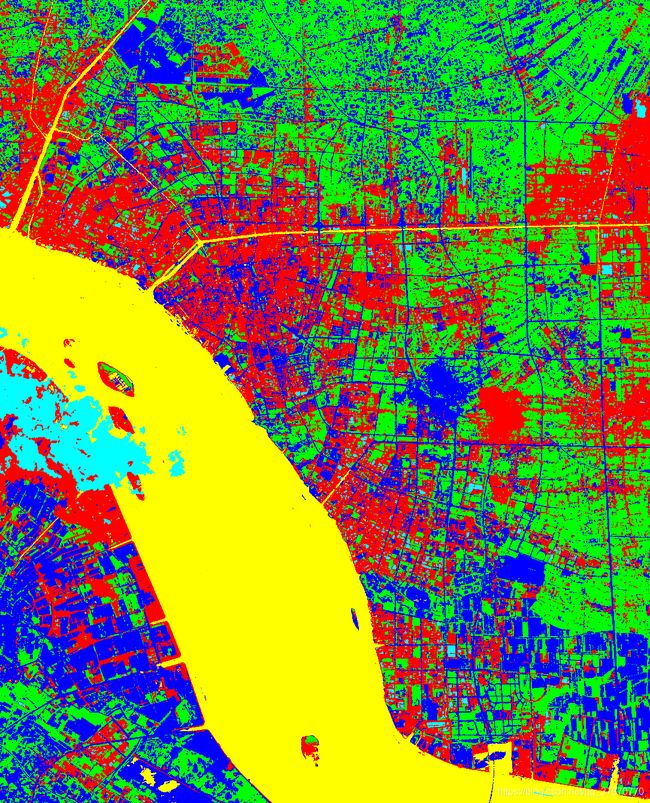
figure, imshow(label2rgb(class_result)) % 显示分割结果
title('MKmeans of muldim聚类结果');
t1 = cputime;
during = t1 - t0;
disp('耗时:');
disp(during);
改进后,耗时:
速度飞起!
耗时:
14.328125
而使用kmeans()matlab自带函数耗时:
耗时:
38.796875
结果图展示
MKmeans_of_muldim()
kmeans()matlab自带函数结果图

效果一模一样,说明只要迭代次数达到一定程度,对于多光谱遥感图像,二者效果是相当的。但改进版速度更快,可以填写变化阈值及迭代次数,灵活调整。