基于粒子群优化算法的无人机路径规划与轨迹算法的实现(Matlab代码实现)
欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️❤️
博主优势:博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码实现
1 概述
随着科学与技术的发展,因体积小和飞行速度快,军用和民用无人机已经得到了广泛的应用。无人机的智能化是目前无人机发展的主要发展方向之一,而无人机三维路径规划是无人机智能化的重要部分,也是智能控制和决策方向研究的热点。无人机三维路径规划是指在如地形、规避地方雷达武器和满足可飞行条件等约束条件下,在不同的三维环境中寻找一个从起点到达终点的最优路径。近年来,国内外大量研究人员对提高无人机路径规划的航行效率展开研究。研究发现,通过引入优化算法可以有效地提高无人机的路径规划能力且具有较好的稳定性。
2 运行结果
部分代码:
clc
clear all
close all
%%
%----------------------------------------------------------------
%Map params
%----------------------------------------------------------------
reduce_path_generated = true;
width = 6;
height = 6;
resolution = 0.01;
% prm param
nodes = 1500;
ConnectionDistance = 1;
%param to draw circles
ang=0:0.01:2*pi;
r_ext=0.75; % 0.7 if we use the line
r_int = 0.6 ;
xp_ext=r_ext*cos(ang);
yp_ext=r_ext*sin(ang);
xp_int=r_int*cos(ang);
yp_int=r_int*sin(ang);
% key points
trans = [3 3];
start = [-1.5 -1.5] + trans;
goal_1 = [0 2] + trans;
goal_2 = [1.5 -1.5] + trans;
% constraint circle at point B
r_constraint_circle = 0.3;
x_constraint_circle = 3;
y_constraint_circle = 4.5;
%%
%----------------------------------------------------------------
%Read obstacle data
%----------------------------------------------------------------
obs_fileID = fopen('obs','r');
obs_format = '%f %f';
obs_size = [2 inf];
obs = fscanf(obs_fileID, obs_format, obs_size);
num_obs = length(obs);
% transform coordinates
% X = -Y
% Y = X
obs_exg = obs ;
obs(1,:) = -obs_exg(2,:) ;
obs(2,:) = obs_exg(1,:) ;
obs = obs + 3;
%%
%----------------------------------------------------------------
%Map Creation
%----------------------------------------------------------------
map = robotics.BinaryOccupancyGrid(width,height,1/resolution)
map_check = robotics.BinaryOccupancyGrid(width,height,1/resolution)
% populate obstacle
for obs_i = 1:length(obs)
setOccupancy(map, obs(:, obs_i)', 1);
setOccupancy(map_check, obs(:, obs_i)', 1);
end
inflate(map,.75);
inflate(map_check,.6);
% constraint_circle
x = (0:resolution/1.1:width);
y = (0:resolution/1.1:height);
for i = 1:(1.1*width/resolution)
for j = 1:(1.1*height/resolution)
if sqrt((x(i)- x_constraint_circle)^2+(y(j)-y_constraint_circle-resolution/2)^2) < r_constraint_circle ...
&& y(j) > y_constraint_circle+0.5*r_constraint_circle
setOccupancy(map, [x(i) y(j)], 1)
end
end
end
figure
show(map)
%%
%------------------------------------------------------------------
%PRM
%------------------------------------------------------------------
planner = robotics.PRM(map,nodes);
planner.ConnectionDistance = ConnectionDistance;
planner
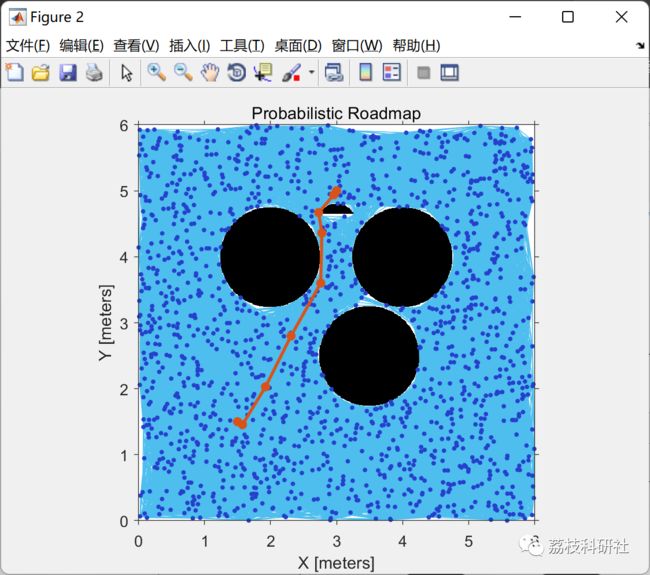
path1 = findpath(planner,start,goal_1);
figure()
show(planner)
print('prm_ptA_ptB','-dpng');
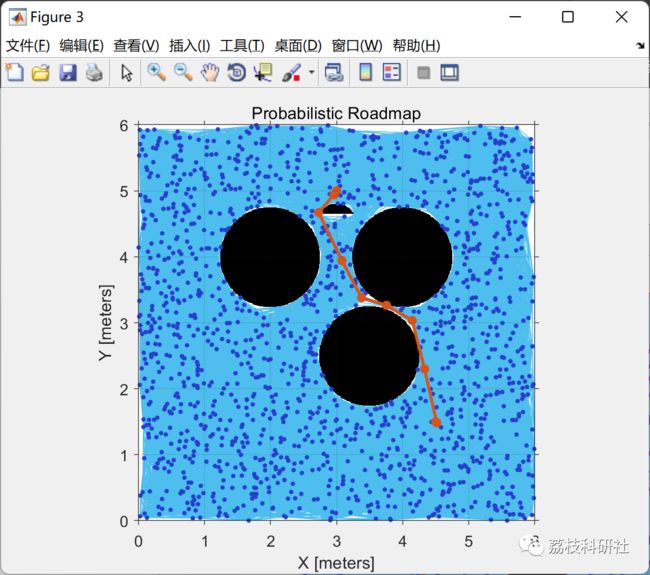
path2 = findpath(planner,goal_1,goal_2);
figure()
show(planner)
print('prm_ptB_ptC','-dpng');
grid on
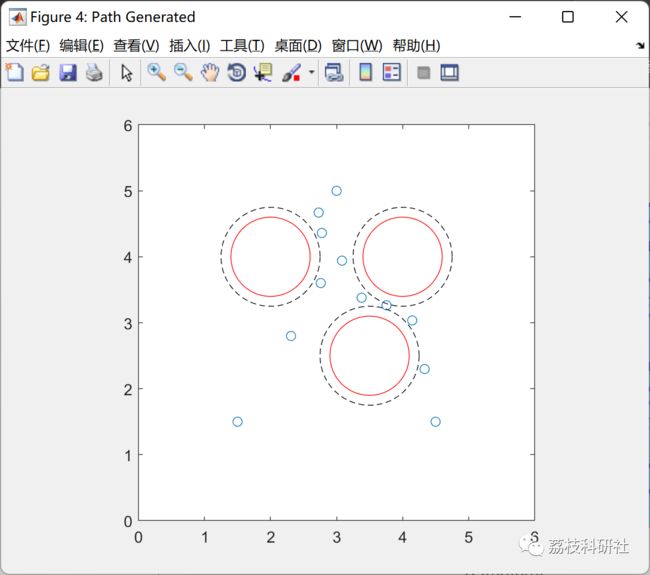
path = vertcat(start,path1(4:end-2,1:end),goal_1,path2(3:end-2,1:end),goal_2);
figure('Name', 'Path Generated');
plot(path(:,1),path(:,2), 'o'); hold on;
for i = 1: num_obs
plot(obs(1,i)+xp_ext,obs(2,i)+yp_ext,'--k');
plot(obs(1,i)+xp_int,obs(2,i)+yp_int,'-r');
end;
axis([0 6 0 6])
pbaspect([1 1 1])
print('path_generated','-dpng');
hold off ;
% find the index of point b
for i=1:length(path)
if (path(i,:) == goal_1)
ptb_idx = i ;
end
end
%%
%------------------------------------------------------------------
%Path Point Reduction
%------------------------------------------------------------------
if (reduce_path_generated == false)
clearvars -except map_check path obs num_obs ptb_idx
return;
end
tol = 0.1 ;
i = 1 ; % index of first path
j = 3 ; % index of path two ahead
distance_ok = true ;
while (distance_ok)
if (j > length(path))
path(i+1:j-2,:) = [] ;
distance_ok = false ;
elseif ((max(max(point_to_line_distance([path(i+1:j-1, :), zeros(j-i-1,1)], ...
[path(i,:), 0], [path(j,:), 0] )))>tol )... % check point to line
|| min(path(j-1,:) == goal_1)... % don't remove if it's point B
|| check_path_collision(map_check, path(i,:), path(j-1,:))) % check for collision
path(i+1:j-2,:) = [] ;
i = i+1 ;
j = i+2 ;
else
j = j+1 ;
end
end
% update the index of point b
for i=1:length(path)
if (path(i,:) == goal_1)
ptb_idx = i ;
end
end
figure('Name', 'Path Reduced')
plot(path(:,1),path(:,2), 'o'); hold on;
for i = 1: num_obs
plot(obs(1,i)+xp_ext,obs(2,i)+yp_ext,'--k');
plot(obs(1,i)+xp_int,obs(2,i)+yp_int,'-r');
end;
axis([0 6 0 6])
pbaspect([1 1 1])
print('path_reduced','-dpng');
hold off ;
clearvars -except map_check path obs num_obs ptb_idx
3 参考文献
[1]王小璐,黄辰,于远航,陈福豪,胡蝶,陆琪,崔曦予.基于适应度值优劣粒子群算法的无人机路径规划[J].电子制作,2022,30(16):16-19.DOI:10.16589/j.cnki.cn11-3571/tn.2022.16.005.
[2]赵志,段炼,路东林,张杨,邱雪.基于蚁群算法的无人机三维路径规划与冲突解脱[J].航空计算技术,2022,52(04):33-37.