深度学习的不确定性(Uncertainty/confidence score)与校准(Calibration)
目录
- 不确定性估计(uncertainty estimates)
-
- 什么是不确定性(uncertainty )
-
- 不确定性的统计学定义
- 不确定性分类
- 什么是不确定性估计值(uncertainty estimates:名词,表示估计值)
- 为何不确定性估计重要
- 怎么生成不确定性估计(Uncertainty Estimation或者Estimating the predictive uncertainty)
- 评价不确定性估计的指标(UNCERTAINTY MEASURES AND QUALITY)
- 容易混淆的术语
-
-
- uncertainty = probability = Confidence
- uncertainty estimates、uncertainty estimation、uncertainty measure
-
- 相关论文
- 模型校准的概念与原理
-
-
-
- calibration的概念、定义与例子
- 如何评估uncertanty estimates的好坏(是否well-calibrated)
-
-
- 常用的校准方法(Calibration Methods/有时也称recalibration methods)
-
-
- 校准方法的分析和对比
-
- 不确定性校准程度的评价指标
-
-
- 论文:On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks
- 朴素贝叶斯:概率类模型的评估指标
-
- birer score 与brier kill score
- 多分类的评价指标
- 可靠性图与Expected Calibration Error (ECE)
- 一个好的github评价指标实现
-
- 与不确定性(置信度)相关的研究
不确定性估计(uncertainty estimates)
什么是不确定性(uncertainty )
不确定性的统计学定义
如何创造可信任的机器学习模型?先要理解不确定性
那「不确定性」究竟是什么?
不确定性度量反映的是一个随机变量的离散程度(dispersion)。换句话说,这是一个标量,反应了一个随机变量有多「随机」。在金融领域,这通常被称为「风险」。
不确定性不是某种单一形式,因为衡量离散程度的方法有很多:标准差、方差、风险值(VaR)和熵都是合适的度量。但是,要记住一点:单个标量数值不能描绘「随机性」的整体图景,因为这需要传递整个随机变量本身才行!
尽管如此,为了优化和比较,将随机性压缩成单个数值仍然是有用的。总之要记住,「越高的不确定性」往往被视为「更糟糕」(除了在模拟强化学习实验中)。
- xys:在深度分类模型中,随机变量就是模型预测所得的类别,不确定性就是模型给出的盘位该类别的置信度(softmax输出的概率分布里最大的那个值)。
监督学习中的不确定性(uncertainty quantification):笔记1
什么是不确定性(uncertianty)
关于如何定义各种不确定性,文献中的说法普遍比较模糊。关于data uncertainty,model uncertainty,distributional uncertainty 的准确描述也有争论。这里尝试从头整理。
(1)首先,data uncertainty的定义是清晰且确定的。由于系统自身和数据收集中产生的随机性,输出所服从的概率分布对应的预测极限,就是data uncertainty
(2)第二,关于model/distributional uncertainty的定义。我们这里还是介绍文献中主流的model/ditributional uncertainty 定义。
Model uncertainty 定义为,给定模型所输出条件概率分布的mode的不确定性。mode是指条件概率最大处所对应的随即变量的值(xys:置信度的不确定性)
distributional uncertainty 一般定义为,给定模型所输出条件概率分布的方差的不确定性。
不确定性分类
不确定估计学习小结
一般而言,不确定性可以分类两种[2]:
- 1.数据的不确定性:也被称为偶然(Aleatoric)不确定性,它描述的是数据中内在的噪声,即无法避免的误差,这个现象不能通过增加采样数据来削弱。例如有时候拍照的手稍微颤抖画面便会模糊,这种数据是不能通过增加拍照次数来消除的。因此解决这个问题的方法一般是提升数据采集时候的稳定性,或者提升衡量指标的精度以囊括各类客观影响因素。
- 2.模型的不确定性:也被称为认知(Epistemic)不确定性。它指出,模型自身对输入数据的估计可能因为训练不佳、训练数据不够等原因而不准确,与某一单独的数据无关。因此,认知不确定性测量的,是训练过程本身所估计的模型参数的不确定性。这种不确定性是可以通过有针对性的调整(增加训练数据等方式)来缓解甚至解决的。
如何创造可信任的机器学习模型?先要理解不确定性
该文阐述了三种不确定性:
- 偶然不确定性
- 认知不确定性
超出分布的不确定性
用模型不确定性理解模型
1、模型不确定性,又称认知不确定性(epistemic uncertainty):假设你有一个单一数据点,想知道哪种线性模型是最适合数据的。但是没有数据的话,我们根本无法判断,所以需要更多数据!
认知不确定性是由于模型的参数不确定。我们不知道模型的哪个权重能最好地表现数据,但是数据越多,不确定性越低。这种类型的不确定性在数据较少的高风险应用中很重要。
再比如,你想搭建一个模型,要在一系列动物图片中预测哪种动物会吃掉你。假设你在训练时给模型提供的都是狮子和长颈鹿的照片,现在模型看到了一张僵尸照片。由于之前它没有见过僵尸,所以这里的不确定性就非常高。如果在训练时能提供足够的僵尸照片,那么模型的不确定性会随之减少。
(xys:模型不确定性与数据量的关系)
2、数据不确定性
3、测量不确定性
4、噪声标签
《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks》
These factors are mainly based on an uncertainty already included in the data (data uncertainty) or a lack of knowledgeof the neural network (model uncertainty)--------------------------《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks.》
不确定性包括:(1)数据不确定性:事先存在于数据中的不确定性,(2)模型不确定性:神经网络知识的缺乏(模型没有训练好,模型能力不够)
什么是不确定性估计值(uncertainty estimates:名词,表示估计值)
Estimating the predictive uncertainty is not sufficient for safe decision-making. Furthermore, it is crucialto assure that the uncertainty estimates are reliable.To this end,the calibration property (the degree of reliability) of DNNs has been investigated and re-calibration methods have been proposed [15], [47], [48] to obtain reliable (well-calibrated)uncertainty estimates.--------------------------《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks.》
- Estimating the predictive uncertainty:动词,指的是产生不确定性值的过程和方法
- the uncertainty estimates:名词,指的是不确定性估计值(不确定性值)。例如,在分类问题中,用softmax输出的概率分布、或者softmax输出的概率分布中的最大值(置信度)作为不确定性估计值。
- reliable (well-calibrated)uncertainty estimates:可靠的(well-calibrated)不确定性估计值
- calibration property:可靠性程度,一般用calibration error来衡量。
- re-calibration methods:使不确定性值更加可靠的方法
Through a series of experiments on classification and regression benchmarks, we demonstrate that our method produces well-calibrated uncertainty estimates which are as good or better than approximate Bayesian NNs-----《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- well-calibrated uncertainty estimates,明显可以看出uncertainty estimates指的是模型输出的预测概率值。(estimate可以作为名词)
- Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles,可以看出Uncertainty Estimation指的是通过某种方法产生不确定性估计值(产生uncertainty estimates)。
不确定估计学习小结(笔者认为其理解并不太好)
(1)以人脸识别为例,输入一张人脸图像,得到一个特征向量embedding,将此特征向量与底库中的特征向量计算相似度,从而根据此相似度来判断两张人脸图像是否属于同一个ID。假设相似度很高(95%),则认为这两张人脸图像属于同一个人。这种将一张输入图像x映射到高维空间中的一个点embedding的方式,可以被称为确定性预测(deterministic prediction)。
但以同样的人脸系统、相同的底库来看,假设我们输入一张很模糊的人脸或者一张猫的图片,此时系统可能会给出同样是95%的相似度。然而,在这种情形下,这种相似度得分并不能反映出两张图片是属于同一ID的,即这个相似度结果不可信。因此,我们不仅需要一个相似度得分,还需要一个能判断此相似度是否可信的得分。具体而言,假设在此种情形下,即使两种图片的相似度得分是95%,但只有10%的得分认为该相似度得分可行,那么做出判断就需要更加谨慎。
(2)再举一个例子,假设我们使用了cifar100来训练了一个分类模型,现在用户随意找了张不属于此100类的图片(例如猫),输入到该分类模型中,那么这个“猫”必然会分类到cifar100中的其中一个类别,例如认为是飞机。从模型来看,这个分类置信度得分可能很高,坚定认为这个“猫”就是“飞机”;从人的认识来看,此次分类结果是失败的。面对这种情况,我们希望模型不仅能给出分类的置信度得分,还希望模型能给出一个判断此次置信度得分是否可信的判断。(xys认为更好的说法:我们希望模型不仅能给出分类的置信度得分,还希望模型能给出的置信度能恰好等于模型真实的预测准确率。因为分类问题中模型的最终输出是类别,而置信度是模型对判断为该类别的信心程度,已经是对模型给出的此次决策的可信程度的判断了)
(3)从上面几个案例来看,无论是相似度得分还是置信度得分,都不一定可信,即模型对于给出的判断具有一定程度的“不确定性”。那么,我们就希望知道模型对于此次判断有多少把握,对于“不确定性”得分高的判断(即把握度低),我们可以进行额外的处理操作。(xys:要使模型给出的不确定性估计是可靠的,就需要对模型进行校准,使得模型达到well-calibrated的状态。)
- xys—对模型给出的得分或置信度等进行可靠性的估计(是否可信,以及可信任的程度),即为不确定性估计。也可认为:不确定性估计 = 计算置信度与真实准确率之间的误差程度。(该解释是笔者对上述引文的直接理解,但实际上笔者认为深度学习领域很少这样理解"uncertainty estimates")
- xys—如果模型给出的得分或置信度正好能准确地表示预测结果的可信任程度(即置信度恰好等于样本的准确率),那么就说模型是well-calibrated的。
- xys—然而,在深度学习中,很多时候会将“模型输出的置信度”与“uncertainty estimates”两个词混用。意思是:模型输出的置信度(通常为一个表示类别概率的小数)就表示了最终预测类别的不确定性(可能性)。即uncertainty esimates= uncertainty= probability = Confidence。例如:We propose an alternative to Bayesian neural networks, that is simple to implement, readily parallelisable and yields high quality predictive uncertainty estimates.--------《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
这里,“uncertainty estimates”指的是模型输出的置信度,而不是“计算置信度与真实准确率之间的误差程度”。
为何不确定性估计重要
R TALK | 旷视危夷晨:不确定性学习在视觉识别中的应用
上面介绍完之后,我们再来谈谈它为什么重要。简单来讲,不确定性估计在深度学习之中有着广泛的应用场景,为其落地发挥着不可替代的重要作用,下面讲一些比较要代表性的场景:
- 高风险应用场景。这类场景需要非常精确的估计,因为一旦估计错误,可能出现严重的后果,例如医疗图像诊断、自动驾驶。
- 大量机器学习场景。比如,在主动学习(Active Learning)这种技术框架中,模型需要确定哪些样本更值得被打标签。这也涉及到系统对于估计样本“价值程度”不确定性。同时,的研究人员往往也会发现单纯使用机器学习系统进行判断时,会存在少量样本系统无法做出很好的判断,因此这时人们会邀请专家来标记这部分困难样本,以训练模型。
- 强化学习。强化学习由于经常要权衡exploration和exploitation操作,因此如何确定每一台机器的概率分布是否被准确估计,就是对这台机器模型参数的不确定性估计。
- 对处于训练数据分布之外情况的检测。由于很多时候测试数据并不在训练数据中,因此如果测试数据超出了训练数据的数据分布,那这样的预测是没有准确度可言的,这时候就需要一个额外的不确定性估计来确认对当前的预测有多大把握。
如何创造可信任的机器学习模型?先要理解不确定性
校准:下一件大事?
警告:只是因为一个模型能够确定一个预测结果的置信区间,并不意味着该置信区间能真正反映结果在现实中的实际概率!
展望未来,如果我们要信任部署在现实世界中的机器学习系统(机器人、医疗系统等),我认为「证明我们的模型能够正确理解世界」的一种远远更为强大方法是针对统计校准测试它们。优良的校准也意味着优良的准确度,所以这是一个更严格的更高的优化指标。
用模型不确定性理解模型
你为什么应该关注不确定性?
1、一个重要的例子就是高风险的应用,假设你正在创建一个模型,可以帮助医生判断病人的严重程度。在这种情况下,我们不应该仅仅关心模型的精确度,更要关注模型对其预测结果有多大程度的肯定。如果不确定性太高,医生需要谨慎决策。
2、自动驾驶汽车是另外一个有趣的例子。如果模型不确定是否有行人在马路上,我们可以利用这一信息让车子减速,或者发出警报让驾驶员手动操作。
3、不确定性还可以在缺乏数据样本的情况下帮助我们。如果模型不是在与样本相似的数据上训练的,它可能无法输出想要的结果。谷歌照片曾经将黑种人错误地认成了大猩猩,就是由于这个原因,种类单一的训练集可能导致令人尴尬的结果。
4、不确定性的最大用途,也是本文的主要目的,就是为模型排除错误。
怎么生成不确定性估计(Uncertainty Estimation或者Estimating the predictive uncertainty)
《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks.》第三部分:
- Single deterministic methods give the prediction basedon one single forward pass within a deterministic network. The uncertainty quantification is either derivedby using additional (external) methods or is directly predicted by the network(xys:就是将模型直接输出的某个值(如softmax或置信度)当做不确定性估计值)
- Bayesian methods cover all kinds of stochastic DNNs,i.e. DNNs where two forward passes of the same samplegenerally lead to different results.
- Ensemble methods combine the predictions of severaldifferent deterministic networks at inference.(集成方法)
- Test-time augmentation methods give the predictionbased on one single deterministic network but augmentthe input data at test-time in order to generate several predictions that are used to evaluate the certainty of the prediction.(测试时,将数据多次增广,分别输入模型获得多个预测,然后据此来计算预测的不确定性)
评价不确定性估计的指标(UNCERTAINTY MEASURES AND QUALITY)
《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks.》第四部分:UNCERTAINTY MEASURES AND QUALITY
uncertainty estimation与uncertaity measures/quality有区别:
- uncertainty estimation:产生表示不确定性的概率值或者置信度的过程或方法(=Estimating the predictive uncertainty)。
- uncertaity measures/quality:对各种uncertainty estimation的测量/质量,即定量计算这些uncertainty estimation的好坏。主要是采用一些指标如softmax的最大值、熵、互信息、KL散度、softmax的均值和方差等等)
容易混淆的术语
uncertainty = probability = Confidence
Confidence calibration – the problem of predicting probability estimates representative of the true correctness likelihood – is important forclassification models in many applications.----《On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks》
- uncertainty = probability = Confidence , 不确定性=概率=置信度
- Confidence calibration = uncertainty calibration,
- predicting probability estimates,这里的estimate意为“估计值”(其实就是指这个probability)
有时会见到术语predicting uncertainty estimates ,其实也就是"不确定性(概率)估计值"。
所以predicting uncertainty estimates = predicting probability estimates(这里estimate作为名词, estimate=Estimation)
a network should provide a calibrated confidence measure in addition to its prediction.
Calibrated confidence estimates are also important for model interpretability
----------《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- uncertainty = probability = Confidence , 不确定性=概率=置信度
- estimate =measure(xys:这里measure不太规范,在《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks》中,estimate 和measure有区别:
— --uncertainty estimate :模型输出的表示不确定性的概率值或者置信度。
------uncertaity measures/quality:对各种uncertainty estimate 的测量/质量,即定量计算这些uncertainty estimation的好坏。主要是采用一些指标如softmax的最大值、熵、互信息、KL散度、softmax的均值和方差等等)
uncertainty estimates、uncertainty estimation、uncertainty measure
参见论文:《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks.》
- predictive uncertainty estimates:指的是模型输出的预测概率值。(estimate可以作为名词)
- uncertainty estimation:产生表示不确定性的概率值或者置信度的过程或方法(=Estimating the predictive uncertainty)。
- uncertaity measures/quality:对各种uncertainty estimation的测量/质量,即定量计算这些uncertainty estimation的好坏。主要是采用一些指标如softmax的最大值、熵、互信息、KL散度、softmax的均值和方差等等)
相关论文
Uncertainty 相关论文
模型校准的概念与原理
Calibration: 一个工业价值极大,学术界却鲜有研究的问题!(原论文:On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks,论文中有一些基本的校准方法,包括温度缩放Temperature Scaling)
在大多情况下,我们只关心类别的预测 有多准,根本不 care 置信度是怎样的。然而,在一些实际应用场景下,置信度的度量也同样重要。
例如 对于自动驾驶中的目标识别任务,车辆的前方出现了一个人,神经网络会将其识别成塑料袋,此时输出的置信度为50%(低于阈值),则可通过其它传感器进行二次的正确识别(识别为人)。但想想看,若神经网络对塑料袋预测的置信度为90%会怎样?
再例如,使用 Resnet 模型简单的对一些图片任务进行训练,收敛后的模型对测试集的平均置信度高达80%-85%,然而只有将近70%的图片能被正确分对(红色代表分错,绿色代表分对)。这意味着啥?训练好的模型好像有点盲目自信,即出现 overconfidence 现象,或者可以称为模型的准确率和置信度不匹配(miscalibration)。
Expected Calibration Error (ECE)模型校准原理解析
- 什么是模型校准?
模型校准就是要让模型结果预测概率和真实的经验概率保持一致。说人话也就是,在一个二分类任务中取出大量(M个)模型预测概率为0.6的样本,其中有0.6M个样本真实的标签是1。总结一下,就是模型在预测的时候说某一个样本的概率为0.6,这个样本就真的有0.6的概率是标签为1。
上面是一个正面的例子,下面我再来举一个反面的例子说明模型校准的重要性。还是在一个二分类任务中取出大量(M个)模型预测概率为0.6的样本,而这些样本的真实标签全部都是1。虽然从accuracy的角度来考察,模型预测样本概率为0.6最后输出时会被赋予的标签就是1,即accuracy是100%。但是从置信度的角度来考察,这个模型明显不够自信,本来这些全部都是标签为1的样本,我们肯定希望这个模型自信一点,输出预测概率的时候也是1。
如何创造可信任的机器学习模型?先要理解不确定性
Hinton等人最新研究:大幅提升模型准确率,标签平滑技术到底怎么用?
本文通过实验证明,标签平滑不仅能够提升模型的泛化能力,还能够提升模型的修正能力,并进一步提高模型的集束搜索能力。
calibration的概念、定义与例子
所谓校准:预测置信度与事件发生的真实概率的匹配程度,二者相等即为well-calibrated,否则就存在calobration error。
Firstly, we shall examine calibration [12, 13], a frequentist notion of uncertainty which measures the discrepancy between subjective forecasts and(empirical) long-run frequencies.
The quality of calibration can be measured by proper scoring rules[17] such as log predictive probabilities and the Brier score [9]. Note that calibration is an orthogonal concern to accuracy: a network’s predictions may be accurate and yet miscalibrated, and vice versa
------《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- calibration的定义和参考文献
- The quality of calibration 校准的质量可以通过布里尔分数等来测量
The probability that a system outputs for an event should reflect the true frequency of that event: ifan automated diagnosis system says 1,000 patients have cancer with probability 0.1, approximately100 of them should indeed have cancer. In this case, we say the model is uncertainty calibrated.------《Verified Uncertainty Calibration》
a network should provide a calibrated confidence measure in addition to its prediction. In other words, the probability associated with the predicted class label should reflect its ground truth correctness likelihood. -------《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- 什么是一个校准好的confidence measure
Let h be a neural network with h ( X ) = ( ˆ Y , ˆ P ) h(X) =( ˆY , ˆP) h(X)=(ˆY,ˆP), where ˆY is a class prediction and ˆP is its associated confidence, i.e. probability of correctness. We wouldlike the confidence estimate ˆP to be calibrated, which in-tuitively means that ˆP represents a true probability. Forexample, given 100 predictions, each with confidence of 0.8, we expect that 80 should be correctly classified. Moreformally, we define perfect calibration as ----《On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks》
- calibration的公式定义,举例
如何评估uncertanty estimates的好坏(是否well-calibrated)
NLL is a proper scoring rule and a popular metric for evaluating predictive uncertainty [49]. For classification we additionally measure classification accuracy andthe Brier score-----《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- evaluating predictive uncertainty:评估不确定性,即对不确定性的校准情况(校准:置信度与真实概率的匹配情况)进行评估。它与uncertainty estimates是两个概念。
A clas-sifier is well-calibrated, if the probability associated withthe predicted class label matches the probability of suchprediction being correct (Br ̈ocker, 2009; Dawid, 1982)
- well-calibrated的参考文献
More formally, we define perfect calibration(well-calibrated) as: ------------《On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks》
- perfect calibration或well-calibrated的公式化定义
Definition 2.1. The classifier f is perfectly calibrated, if for any input instances x ∈X, the prediction and the canonical calibration probabilities match: z = π(z) (Dawid, 1982)----------《Mix-n-Match : Ensemble and Compositional Methods for Uncertainty Calibration in Deep Learning》
Definition 2.3 (Top-label calibration error). The top-label calibration error examines the difference between the model’s probability for its top prediction and the true probability of that prediction given the model’s output:-----------------《Verified Uncertainty Calibration》
- 多分类情况下,calobration error的公式化定义
常用的校准方法(Calibration Methods/有时也称recalibration methods)
《A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks》
- Regularization methods applied during the training phase(如lable smooth,mixup等)
- Post-processing methods applied after the training pro-cess of the DNN(后处理,如temperature scaling)
- Neural network uncertainty estimation methods(如集成学习、贝叶斯方法)
《On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks 》的calibration methods一节有大量的校准方法。
Uncertainty Calibration Library----对应文章:Verified Uncertainty Calibration
深度学习模型不确定性校准方法对比
(NeurIPS 2019 的 Can You Trust Your Model’s Uncertainty? Evaluating
Predictive Uncertainty Under Dataset Shift 论文为主线,回顾近年顶级机器学习会议对于
dataset shift 和 out-of-distribution dataset 问题相关的论文,包括了 Temperature
scaling [1],DeepEnsemble [2],Monte-Carlo Dropout [3] 等方法)
pytorch神经网络_使用pytorch进行神经网络校准(温度缩放Temperature Scaling)
https://github-dotcom.gateway.web.tr/gpleiss/temperature_scaling(基于pytorch的模型校准:temperature_scaling)
A simple way to calibrate your neural network. The temperature_scaling.py module can be easily used to calibrated any trained model.
Based on results from On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks.
Learning Confidence for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Neural Networks
《在神经网络中计算置信度用于域外检测》阅读笔记

校准方法的分析和对比
《Verified Uncertainty Calibration》----分析了scaling系列方法(Plattscaling [12], isotonic regression [13], and temperature scaling)和histogram binning方法的优缺点
《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》分析了贝叶斯方法、MC-dropout方法的优缺点
《Mix-n-Match : Ensemble and Compositional Methods for Uncertainty Calibration in Deep Learning
》-----
- introduction部分将校准方法进行了分类:后验校准(post-hoc manner.),前置校准(ab-initio well calibrated model)
- introduction部分介绍了深度学习的校准方法(也属于后验方法):Recently, calibra-tion methods for multi-class deep neural network classifiershave been developed, which include: temperature, vector& matrix scaling (Guo et al., 2017), Dirichlet scaling (Kullet al., 2019), intra order-preserving method (Rahimi et al.,2020) and Gaussian processes based calibration methods(Milios et al., 2018; Wenger et al., 2020)
- 2.1节将校准方法分为:参数化方法、非参数化方法
不确定性校准程度的评价指标
论文:On Calibration of Modern Neural Networks
有四个指标的公式化定义:
- Reliability Diagrams
- Expected Calibration Error (ECE)
- Maximum Calibration Error (MCE)
- Negative log likelihood
In the case ofmulti-class K-way classification, the popular softmax cross entropy loss is equivalent to the log likelihood and is a proper scoring rule. Interestingly, L(θ) = −S(pθ,(y,x)) = K−1 ∑Kk=1(δk=y −pθ(y = k|x))2, i.e., minimizing the squared error between the predictive probability of a label and one-hot encoding of the correct label, is also a proper scoring rule known as the Brier score [9].-----《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- 对多分类问题,softmax交叉熵=对数似然
- 布里尔分数=预测概率与one-hot标签之间的平方误差
朴素贝叶斯:概率类模型的评估指标
内容包括(基于sklearn的代码):
1.布里尔分数Brier Score
2.对数似然函数Log Loss
3.可靠性曲线Reliability Curve
4.预测概率的直方图
5.校准可靠性曲线
birer score 与brier kill score
Brier Score – How to measure accuracy of probablistic predictions
What is a Brier Score?
While the Brier Score (BS) tells you how good a model is, it is still not a relative metric. That is, it does not tell you how good a model is compared to others. A useful metric to compare the performance of one more in comparison with another is the ‘Brier Skill Score’.
Brier Skill Score = (BSE – BSN) / BSE
where: BSE = Brier Score of existing model
BSN = Brier Score of new model
If a Brier Skill Score is positive, then the new model makes more accurate predictions. If the Brier Skill Score is negative, then the new model makes worse predictions. And if the Brier Skill Score is equal to zero, then the new model offers no improvement over the existing model.
For example,
suppose our existing model has a Brier Score of BSE = 0.4221 and our new model has a Brier Score of BSN = 0.3352. The Brier Skill Score of our new model can be calculated as:
Brier Skill Score = (0.4421 – 0.3352) / (0.4421) = 0.2418.
Since this number is positive, it’s an indication that our new model provides more accurate forecasts relative to the existing model.
The higher the Brier Skill Score, the bigger the improvement is in the new model compared to the existing model.
多分类的评价指标
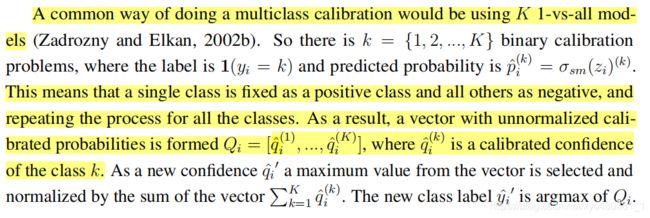
摘自:(Calibration of Convolutional Neural Networks)
多分类的布里尔分数Brier Score计算
briercalc: Brier Scores (and decompositions) for multiple classes(代码)
In the case ofmulti-class K-way classification, the popular softmax cross entropy loss is equivalent to the log likelihood and is a proper scoring rule. Interestingly, L(θ) = −S(pθ,(y,x)) = K−1 ∑Kk=1(δk=y −pθ(y = k|x))2, i.e., minimizing the squared error between the predictive probability of a label and one-hot encoding of the correct label, is also a proper scoring rule known as the Brier score [9].-----《Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles》
- 对多分类问题,softmax交叉熵=对数似然
- 布里尔分数=预测概率与one-hot标签之间的平方误差
可靠性图与Expected Calibration Error (ECE)
marcoromanelli-github/ReliabilityDiagrams(从模型输出的softmaxt开始进行计算,又详细的注释)
hollance/reliability-diagrams(对图形有详细的解释,论文中可以借鉴)
zygmuntz/classifier-calibration(包含两种校准方法)
ECE的计算公式参照:Expected Calibration Error (ECE)模型校准原理解析(ECE公式是基于可靠性图的bin分区的)
一个好的github评价指标实现
https://github.com/markus93/NN_calibration/tree/master/scripts/calibration
(对应的文章:Calibration of Convolutional Neural Networks)
与不确定性(置信度)相关的研究
- 对置信度不高的分类结果进行后处理:
CAN:借助先验分布提升分类性能的简单后处理技巧
CAN: 借助数据分布提升分类性能
模型训练Tricks——后处理:利用训练集先验类别提升分类预测效果