基于bp神经网络的性别预测
1背景
神经网络具有预测,拟合,分类的作用
2项目目标
通过原始数据集性别,体重与体重的对应,实验神经网络的训练。并最终完成输入体重和身高的数据,预测性别。
3数据集
4算法结构模型
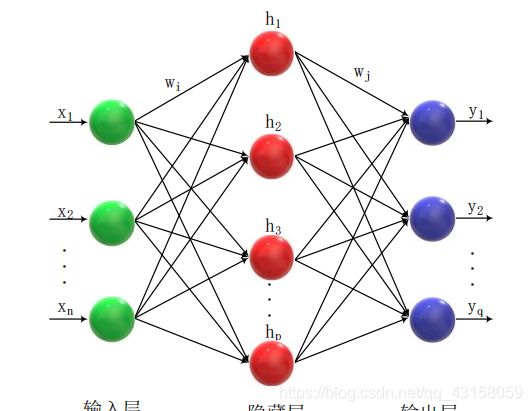
采用bp算法。建立一个bp网络,拥有输入层,隐含层,输出层。
网络的抽象图如下所示。含有中间两个权值矩阵w1,w2.
5 程序
这个matlab程序
5.1优点
1归一化数据时候使用均值平移,在使用标准差让数据在[-1,1]之间,相较于最大最小归一化,取消了不同数据之间的差异性。
2 使用了批量尺度下降算法。提高了鲁棒性,避免由于小批量或者单个数据收敛的局部最小收敛问题。
3 性别标签的处理恰到好处,通过0和1,变成二值输出。
5.2缺点
1批量尺度的训练程序思想对的,但是表述成矩阵的编程,存在编程的变量定义歧义。
5.3 函数体
直接嵌入整个函数体,原始的数据excel,处理做成封装函数。
% script: main_batch.m
% 批量方式训练BP网络,实现性别识别
%% 清理
clear all
clc
%% 读入数据
xlsfile='student.xls';
[data,label]=getdata(xlsfile);
%% 划分数据
[traind,trainl,testd,testl]=divide(data,label);
%% 设置参数
rng('default')
rng(0)
nTrainNum = 60; % 60个训练样本
nSampDim = 2; % 样本是2维的
%% 构造网络
net.nIn=2;
net.nHidden = 3; % 3个隐含层节点
net.nOut = 1; % 一个输出层节点
w = 2*(rand(net.nHidden,net.nIn)-1/2); % nHidden * 3 一行代表一个隐含层节点
b = 2*(rand(net.nHidden,1)-1/2);
net.w1 = [w,b];
W = 2*(rand(net.nOut,net.nHidden)-1/2);
B = 2*(rand(net.nOut,1)-1/2);
net.w2 = [W,B];
%% 训练数据归一化
mm=mean(traind);
% 均值平移
for i=1:2
traind_s(:,i)=traind(:,i)-mm(i);
end
% 方差标准化
ml(1) = std(traind_s(:,1));
ml(2) = std(traind_s(:,2));
for i=1:2
traind_s(:,i)=traind_s(:,i)/ml(i);
end
%% 训练
SampInEx = [traind_s';ones(1,nTrainNum)];
expectedOut=trainl;
eb = 0.0001; % 误差容限
eta = 0.001; % 学习率
mc = 0.001; % 动量因子
maxiter = 3000; % 最大迭代次数
iteration = 0; % 第一代
errRec = zeros(1,maxiter);
outRec = zeros(nTrainNum, maxiter);
NET=[]; % 记录
% 开始迭代
for i = 1 : maxiter
hid_input = net.w1 * SampInEx; % 隐含层的输入
hid_out = logsig(hid_input); % 隐含层的输出
ou_input1 = [hid_out;ones(1,nTrainNum)]; % 输出层的输入
ou_input2 = net.w2 * ou_input1;
out_out = logsig(ou_input2); % 输出层的输出
outRec(:,i) = out_out'; % 记录每次迭代的输出
err = expectedOut - out_out; % 误差
sse = sumsqr(err);
errRec(i) = sse; % 保存误差值
fprintf('第 %d 次迭代 误差: %f\n', i, sse);
iteration = iteration + 1;
% 判断是否收敛
if sse<=eb
break;
end
% 误差反向传播
% 隐含层与输出层之间的局部梯度
DELTA = err.*dlogsig(ou_input2,out_out);
% 输入层与隐含层之间的局部梯度
delta = net.w2(:,1:end-1)' * DELTA.*dlogsig(hid_input,hid_out);
% 权值修改量
dWEX = DELTA*ou_input1';
dwex = delta*SampInEx';
% 修改权值,如果不是第一次修改,则使用动量因子
if i == 1
net.w2 = net.w2 + eta * dWEX;
net.w1 = net.w1 + eta * dwex;
else
net.w2 = net.w2 + (1 - mc)*eta*dWEX + mc * dWEXOld;
net.w1 = net.w1 + (1 - mc)*eta*dwex + mc * dwexOld;
end
% 记录上一次的权值修改量
dWEXOld = dWEX;
dwexOld = dwex;
end
%% 测试
% 测试数据归一化
for i=1:2
testd_s(:,i)=testd(:,i)-mm(i);
end
for i=1:2
testd_s(:,i)=testd_s(:,i)/ml(i);
end
% 计算测试输出
InEx=[testd_s';ones(1,260-nTrainNum)];
hid_input = net.w1 * InEx;
hid_out = logsig(hid_input); % output of the hidden layer nodes
ou_input1 = [hid_out;ones(1,260-nTrainNum)];
ou_input2 = net.w2 * ou_input1;
out_out = logsig(ou_input2);
out_out1=out_out;
% 取整
out_out(out_out<0.5)=0;
out_out(out_out>=0.5)=1;
% 正确率
rate = sum(out_out == testl)/length(out_out);
%% 显示
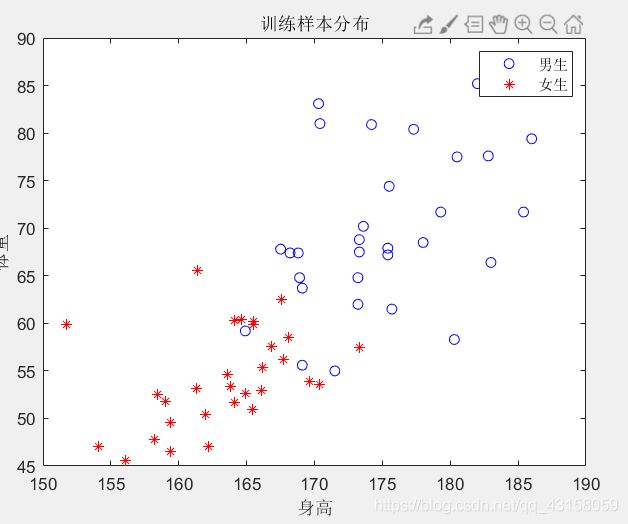
% 显示训练样本
train_m = traind(trainl==1,:);
train_m=train_m';
train_f = traind(trainl==0,:);
train_f=train_f';
figure(1)
plot(train_m(1,:),train_m(2,:),'bo');
hold on;
plot(train_f(1,:),train_f(2,:),'r*');
xlabel('身高')
ylabel('体重')
title('训练样本分布')
legend('男生','女生')
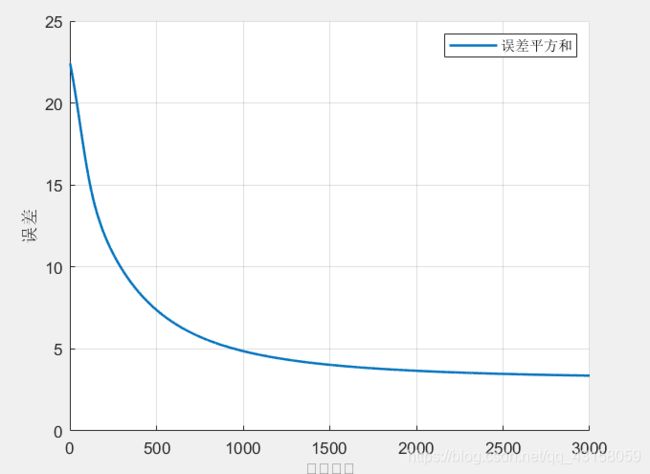
figure(2)
axis on
hold on
grid
[nRow,nCol] = size(errRec);
plot(1:nCol,errRec,'LineWidth',1.5);
legend('误差平方和');
xlabel('迭代次数','FontName','Times','FontSize',10);
ylabel('误差')
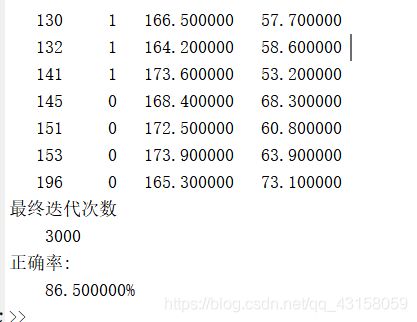
fprintf(' ----------------错误分类表----------\n')
fprintf(' 编号 标签 身高 体重\n')
ind= find(out_out ~= testl);
for i=1:length(ind)
fprintf(' %4d %4d %f %f \n', ind(i), testl(ind(i)), testd(ind(i),1), testd(ind(i),2));
end
fprintf('最终迭代次数\n %d\n', iteration);
fprintf('正确率:\n %f%%\n', rate*100);
function [traind,train1,testd,test1]=divide(data,label)
%[data,label]=getdata('student.xls')
% [traind,train1,testd,test1]=divide(data,label)
% 随机数
rng(0)
% 男女各取30个进行训练
TRAIN_NUM_M=30;
TRAIN_NUM_F=30;
% 男女分开
m_data=data(label==1,:);
f_data=data(label==0,:);
NUM_M=length(m_data); % 男生的个数
% 男
r=randperm(NUM_M);
traind(1:TRAIN_NUM_M,:)=m_data(r(1:TRAIN_NUM_M),:);
testd(1:NUM_M-TRAIN_NUM_M,:)=m_data(r(TRAIN_NUM_M+1:NUM_M),:);
NUM_F=length(f_data); % 女生的个数
% 女
r=randperm(NUM_F);
traind(TRAIN_NUM_M+1:TRAIN_NUM_M+TRAIN_NUM_F,:)=f_data(r(1:TRAIN_NUM_F),:);
testd(NUM_M-TRAIN_NUM_M+1:NUM_M-TRAIN_NUM_M+NUM_F-TRAIN_NUM_F,:)=f_data(r(TRAIN_NUM_F+1:NUM_F),:);
% 赋值
train1=zeros(1,TRAIN_NUM_M+TRAIN_NUM_F);
train1(1:TRAIN_NUM_M)=1;
test1=zeros(1,NUM_M+NUM_F-TRAIN_NUM_M-TRAIN_NUM_F);
test1(1:NUM_M-TRAIN_NUM_M)=1;
end
function [data,label]=getdata(xlsfile)
% [data,label]=getdata('student.xls')
% read height,weight and label from a xls file
[~,label]=xlsread(xlsfile,1,'B2:B261');
[height,~]=xlsread(xlsfile,'C2:C261');
[weight,~]=xlsread(xlsfile,'D2:D261');
data=[height,weight];
l=zeros(size(label));
for i=1:length(l)
if label{i}=='男'
l(i)=1;
end
end
label=l;
end
6数据集包含源程序下载地址
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_43158059/16662478