【花书笔记|PyTorch版】手动学深度学习6:多层感知机
4 多层感知机
2022.11.10
- 感知机模型 详见:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/563472789
- 感知机算法过程、收敛性:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/564294975
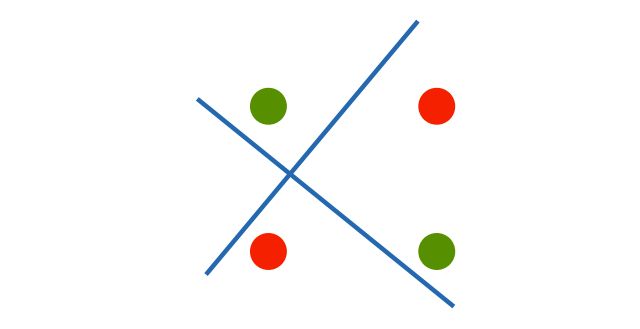
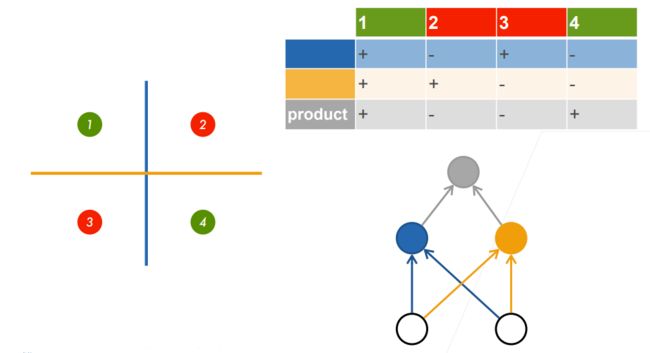
感知机的问题:线性无法解决XOR问题!!
解决:引出了多层感知机!!
4.1 多层感知机
4.1.1 单层感知机
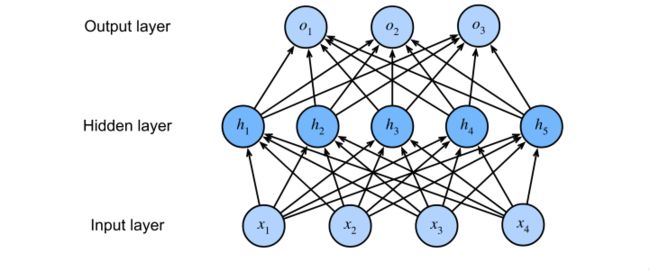
h = σ ( W 1 x + b 1 ) o = W 2 T H + b 2 h= \sigma(W_1x+b_1)\\ o= W_2^TH+b_2 h=σ(W1x+b1)o=W2TH+b2
σ 是 激 活 函 数 \sigma是激活函数 σ是激活函数
4.1.2 激活函数
【问题1】为什么要用激活函数都是非线性的?
因为当激活函数是线性时,相当于没用,原函数还是线性的,多层感知机相当于还是1层,有些无法解决的问题依旧没法解决
【问题2】常用的激活函数
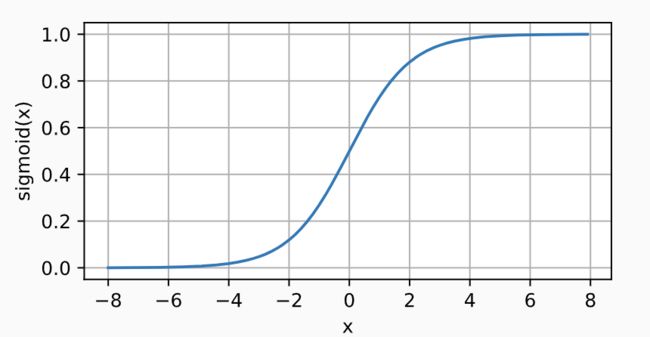
- ① sigmoid激活函数:讲输入投到(0,1)
s i g m o i d ( x ) = 1 1 + e x p ( − x ) sigmoid(x)=\frac{1}{1+exp(-x)} sigmoid(x)=1+exp(−x)1
y = torch.sigmoid(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(), 'x', 'sigmoid(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))
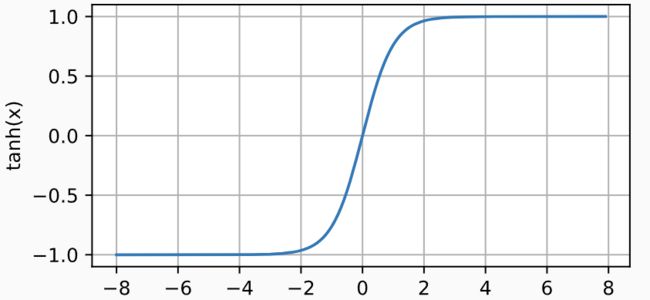
- ② tanh激活函数:与sigmoid函数类似, tanh(双曲正切)函数也能将其输入压缩转换到区间(-1, 1)上
t a n h ( x ) = 1 − e x p ( − 2 x ) 1 + e x p ( − 2 x ) tanh(x)=\frac{1-exp(-2x)}{1+exp(-2x)} tanh(x)=1+exp(−2x)1−exp(−2x)
y = torch.tanh(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(), 'x', 'tanh(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))
- ③ ReLU激活函数:最常用的激活函数,因为简单,计算成本低。(指数计算成本很高)
R e L U ( x ) = m a x ( 0 , x ) ReLU(x)=max(0,x) ReLU(x)=max(0,x)
x = torch.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.relu(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(), 'x', 'relu(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))
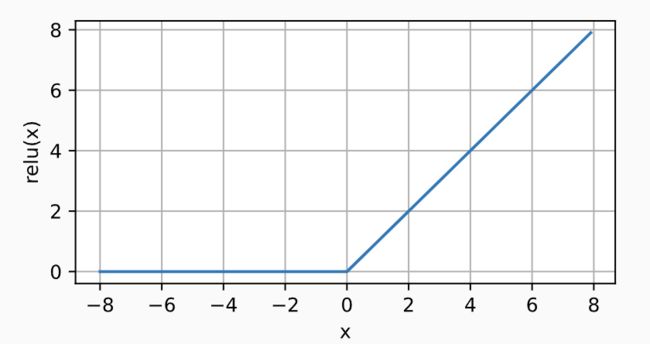
它求导表现得特别好:要么让参数消失(导数为0),要么让参数通过。 这使得优化表现得更好,并且ReLU减轻了困扰以往神经网络的梯度消失问题
4.1.3 多分类模型
h = σ ( W 1 x + b 1 ) o = W 2 T H + b 2 y = s o f t m a x ( o ) h= \sigma(W_1x+b_1)\\ o= W_2^TH+b_2\\y=softmax(o) h=σ(W1x+b1)o=W2TH+b2y=softmax(o)
4.2 多层感知机的从零开始实现
导入数据
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
4.2.1. 初始化模型参数
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens = 784, 10, 256
W1 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(
num_inputs, num_hiddens, requires_grad=True) * 0.01)
b1 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens, requires_grad=True))
W2 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(
num_hiddens, num_outputs, requires_grad=True) * 0.01)
b2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True))
params = [W1, b1, W2, b2]
- 传入的照片是
28*28=784,我们处理的时候要拉成一条张量,输入就是784 - 随机产生
X同型的参数(行数、列数)w和列数相同的b
4.2.2. 激活函数
选用ReLU激活函数
def relu(X):
a = torch.zeros_like(X)
return torch.max(X, a)
4.2.3. 模型
def net(X):
X = X.reshape((-1, num_inputs))
H = relu(X@W1 + b1) # 这里“@”代表矩阵乘法
return (H@W2 + b2)
4.2.4. 损失函数
交叉熵损失,定义可看上一章
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
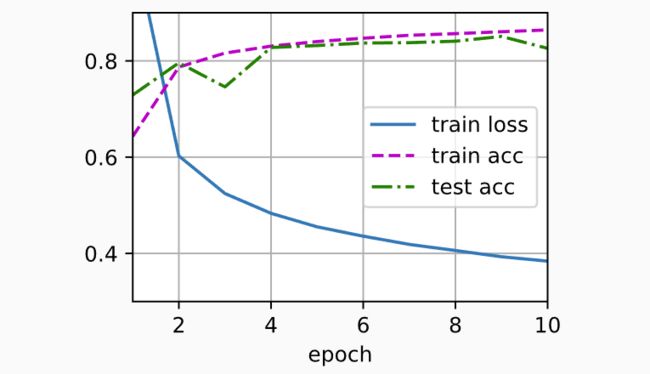
4.2.5. 训练
将迭代周期数设置为10,并将学习率设置为0.1
num_epochs, lr = 10, 0.1
updater = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=lr)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater)
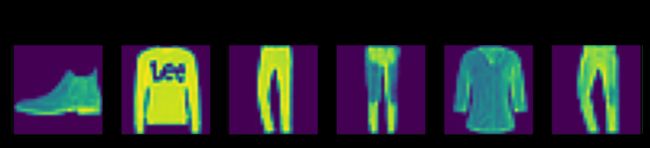
d2l.predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
4.3. 多层感知机的简洁实现
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
4.3.1 网络
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(784, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 10))
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights);
- 我们在线性层前定义了展平层(flatten),来调整网络输入的形状,也就是拉成了一条784的直线
init_weights(m)初始化权重,看这个模型是不是现行的:nn.Linear(784, 256)这里是的,那么初始化参数net.apply(init_weights)将参数组层加入到网络.
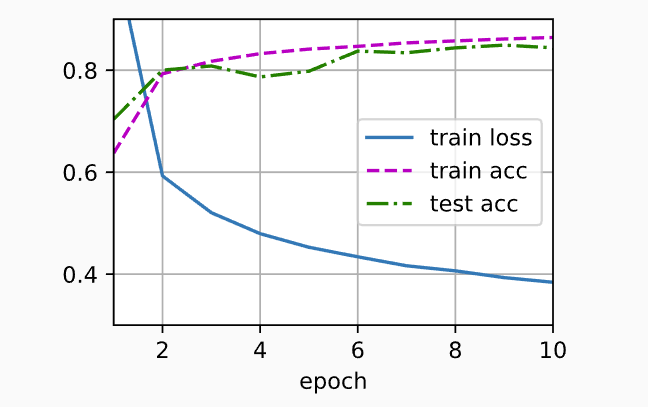
4.3.2 训练
训练过程的实现与我们实现softmax回归时完全相同(注释可看上章)
batch_size, lr, num_epochs = 256, 0.1, 10
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
课后提问重点:与SVM区别
SVM比较常用是因为 不需要特别调参,同时有比较完美的数学推理逻辑;缺点也是没法调参,跳来跳去作用不大;
感知机优势是在改动时候,只需改动相应需要改的几行,SVM需要较大改动,。但是如果参数非常多那么不适合
神经网络比较好的特点是可以特征分离,支持大参数,巨量参数和数据