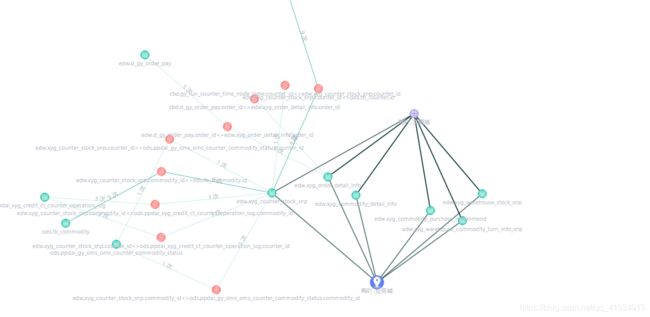
TS+React+d3.js实现数据可视化力导图
前言
基于ts+react+d3实现数据可视化关系力导图
由于第一次做相关功能,并且是在ts中使用,也是遇到了许多坑,下面记录一下实现的过程
实现过程
一、找d3.js的官网资料
目的很明确直接找网站的例子,锁定:
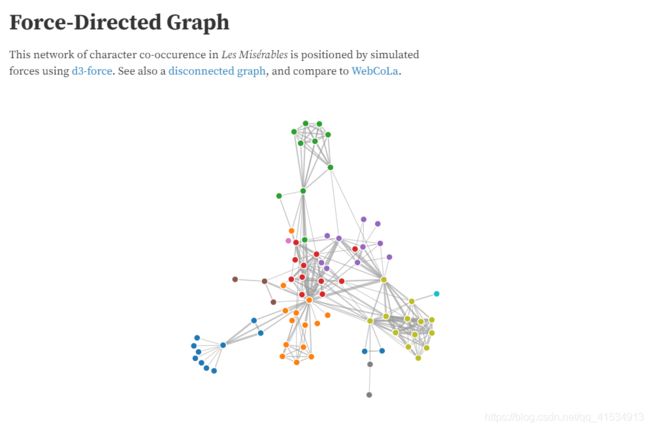
到这里,像我这种喜欢直来直去的,不得第一时间立马搬到项目里面,殊不知接下来几天的折磨也就由此而来,我先贴一下官网这个例子的原代码(网站可以直接看到的):
chart = {
const links = data.links.map(d => Object.create(d));
const nodes = data.nodes.map(d => Object.create(d));
const simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes)
.force("link", d3.forceLink(links).id(d => d.id))
.force("charge", d3.forceManyBody())
.force("center", d3.forceCenter(width / 2, height / 2));
const svg = d3.create("svg")
.attr("viewBox", [0, 0, width, height]);
const link = svg.append("g")
.attr("stroke", "#999")
.attr("stroke-opacity", 0.6)
.selectAll("line")
.data(links)
.join("line")
.attr("stroke-width", d => Math.sqrt(d.value));
const node = svg.append("g")
.attr("stroke", "#fff")
.attr("stroke-width", 1.5)
.selectAll("circle")
.data(nodes)
.join("circle")
.attr("r", 5)
.attr("fill", color)
.call(drag(simulation));
node.append("title")
.text(d => d.id);
simulation.on("tick", () => {
link
.attr("x1", d => d.source.x)
.attr("y1", d => d.source.y)
.attr("x2", d => d.target.x)
.attr("y2", d => d.target.y);
node
.attr("cx", d => d.x)
.attr("cy", d => d.y);
});
invalidation.then(() => simulation.stop());
return svg.node();
}
// 这里的data就是渲染的数据,类似{nodes:[id: "Myriel", group: 1}], links[{source: "Napoleon", target: "Myriel", value: 1}]}这样的数据
data = FileAttachment("miserables.json").json()
height = 600
color = {
const scale = d3.scaleOrdinal(d3.schemeCategory10);
return d => scale(d.group);
}
drag = simulation => {
function dragstarted(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0.3).restart();
event.subject.fx = event.subject.x;
event.subject.fy = event.subject.y;
}
function dragged(event) {
event.subject.fx = event.x;
event.subject.fy = event.y;
}
function dragended(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0);
event.subject.fx = null;
event.subject.fy = null;
}
return d3.drag()
.on("start", dragstarted)
.on("drag", dragged)
.on("end", dragended);
}
d3 = require("d3@6")
上面就是网站上这个例子给的代码
二、准备工作,让它在项目里面渲染出来
这一块过程我没有记录下来,所以只能文字描述一下我碰到的问题,\
1、话不多说直接安装引用依赖包
npm/yarn....等等都行
import * as d3 from "d3" ;这引入写法不论是官方文档还是其他文章资料都是这样用得
2、类型声明文件找不到
此时由于这里引入d3.js库,ts项目会检查有没有类型声明文件,然后鼠标移到红线上会显示一堆英文。大致意思就是找不到这个库的类型声明文件(.d.ts)结尾的,然后如果这个库有的话你可以使用安装@types/d3这样的方式安装,或者自己写一个。。。。
那我肯定直接安装一个
- 后续找到了解决办法,当安装依赖报类型声明不存在时,在项目目录下的typings.d.ts文件自己添加依赖的声明: declare module ‘XXX’';
3、整理代码
- 这时你会发现,不管是示例代码,还是网上找的实现的代码案例,翻是出现
d3.XXXX这样使用的,有一些还是会报错,大致意思就是node_modules里面的@types/d3里的 .d.ts 文件没有导出你的引用(找不见),然后我找到好多方式都没找到解决办法,就想到了直接下载d3.js库的代码,删除里面其他文件,只保留d3.js2文件,直接本地离线引入 - 这里下载的是最新版本的代码,网上的大多是教程都是基于v3版本,例如
d3.event......这种在新版本的代码里面并没有导出,所以在实现实现某些功能的时候如果是v3版本的,这里也会报错,然后我又用的很笨的办法,直接上github上找到d3V3的版本,把里面的d3.js的代码拿到本地新建了一个js放了进去(大佬别骂我,我就是奔着解决问题的) - 但是在后续实现过程中,v3版本的写法可能没用上或者换另一种写法也实现,导致我又把它给删了(
造孽啊)
上面这一大堆废话就是自己在ts中引用d3js碰到的兼容和版本问题,虽然使用笨的办法,但好在问题解决了,有其他好的方法希望各位不吝赐教
三、最终实现
不得不说一句,d3库的语法以及方式和jQuery确实很像,都是通过标签、id、class等直接选中dom然后做各种操作
但是这次的力导图本质上整体是一个svg,所以我中途也是去熟悉了下svg的属性和语法,不然我完全搞不懂我选这个,设置那个属性到底是在画猫还是画狗
直接上代码,注释也直接写在代码里面了
import { useEffect } from 'react';
// ts项目里面通过插件的方式引入d3时,会默认寻找插件的类型申明文件@types/d3,但是好多写法用的在声明文件里面并没有导出,会导致好多报错
// 网上直接下载d3库的代码,通过离线文件的方式引入使用,不过版本是v6+,学习d3库百度好多功能的时候能找到的基本上都是v3版本和js方式的写法
// 所以这里第一次使用v6+版本和ts也是踩了好多坑
// 最后实在没有好的解决办法只能去d3的github上找见v3版本的d3.js文件copy一份写在本地引用
// 不过到最后大部分功能实现的时候,某些事件、参数的取值和网上的又不太一样,到最后也是摸索避免使用d3版本的这种写法
import {
forceSimulation,
forceLink,
forceManyBody,
select,
drag,
forceCollide,
zoom,
selectAll,
} from './d3/d3.js';
// 定义四种节点颜色,线条渐变也会使用
const a = `#38CCB5`;
const b = `#FFA02D`;
const c = `#A096EA`;
const d = `#FF8988`;
export default (props: any) => {
const width = 1600;
const height = 800;
useEffect(() => {
if (props?.data?.edges?.length) {
// 调用渲染函数,渲染函数之前闲清除dom,用于条件查询之后重新渲染
select('.mySvg').remove();
chart();
}
}, [props.data]);
// 节点拖拽的方法
const drag1 = (simulation: any) => {
function dragstarted(event: any) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0.3).restart();
event.subject.fx = event.subject.x;
event.subject.fy = event.subject.y;
}
function dragged(event: any) {
event.subject.fx = event.x;
event.subject.fy = event.y;
}
function dragended(event: any) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0);
event.subject.fx = null;
event.subject.fy = null;
}
return drag().on('start', dragstarted).on('drag', dragged).on('end', dragended);
};
// 初始化
const chart = () => {
// 初始化数据
const links = props.data.edges.map((d: any) => ({
...d,
type: d.source.type,
source: d.source.label,
target: d.target.label,
}));
const nodes = props.data.nodes.map((d: any) => Object.create(d));
const simulation = forceSimulation(nodes)
// @ts-ignore
.force(
'link',
forceLink(links)
.id((d: any) => d.label)
// @ts-ignore
.distance(250),
) // 线的长度
.force('charge', forceManyBody().strength(-200))
.force('collide', forceCollide().radius(40).iterations(2)) // 节点碰撞力,不重叠
.on('tick', ticked); // 拖拽事件,更新坐标
// 获取svg
const svg = select('#myMap')
.append('svg')
.attr('class', 'mySvg')
.attr('width', 1600)
.attr('height', 650)
.attr('viewBox', `-300 ${-height / 2} ${width} ${height}`);
const defs = svg.append('defs'); // 渐变色linearGradient必须放在defs内
const g = svg.append('g');
// 缩放及平移事件
svg.call(
zoom().on('zoom', function (d: any) {
// 防止拖拽抖动和跳屏事件,将属性不要直接绑定到svg上面,所以在svg下面创建一个元素绑定
g.attr('transform', d.transform);
}),
);
// 节点线条颜色
function lineColor(y: any, i: any) {
// let color;
// 处理渐变色
const linerGradient = defs
.append('linearGradient')
.attr('id', 'linearColor')
.attr('x1', '0%')
.attr('y1', '0%')
.attr('x2', '100%')
.attr('y2', '0%');
linerGradient.append('stop').attr('offset', '0%').style('stop-color', a);
linerGradient.append('stop').attr('offset', '100%').style('stop-color', b);
const linerGradient1 = defs
.append('linearGradient')
.attr('id', 'linearColor1')
.attr('x1', '0%')
.attr('y1', '0%')
.attr('x2', '100%')
.attr('y2', '0%');
linerGradient1.append('stop').attr('offset', '0%').style('stop-color', a);
linerGradient1.append('stop').attr('offset', '100%').style('stop-color', c);
const linerGradient2 = defs
.append('linearGradient')
.attr('id', 'linearColor2')
.attr('x1', '0%')
.attr('y1', '0%')
.attr('x2', '100%')
.attr('y2', '0%');
linerGradient2.append('stop').attr('offset', '0%').style('stop-color', a);
linerGradient2.append('stop').attr('offset', '100%').style('stop-color', d);
// 这里是由于节点含义不同颜色也不同,所以根据类型渲染两个节点之间颜色渐变
if (props.data.edges[i].source.type === 'pair') {
return 'url(#' + linerGradient2.attr('id') + ')';
} else if (props.data.edges[i].source.type === 'tag') {
return 'url(#' + linerGradient.attr('id') + ')';
} else {
return 'url(#' + linerGradient1.attr('id') + ')';
}
}
// 画线
const link = g
.append('g')
.selectAll('path')
.data(links) // d3独有语法,用于给dom绑定数据
.enter()
.call((selection: any) => {
// 为连线绑定文字描述
selection
.append('svg:text')
.attr('text-anchor', 'middle')
.style('font-size', '14px')
.style('fill', '#B4B9C7')
.attr('y', 25)
.append('svg:textPath')
.attr('startOffset', '50%')
.attr('xlink:href', (d: any, i: any) => `#edgepath${i}`) // 需要和线的id绑定起来
.text((e: any) => {
if (e.properties) {
return `${e.properties.frequency} 次`;
}
return '0 次';
});
})
.append('path')
.attr('stroke', lineColor) // 颜色渐变
.style('opacity', '0.6')
.attr('fill', 'none')
.attr('stroke-width', 1)
.attr('id', function (d: any, i: any) {
return 'edgepath' + i;
});
// 画圆形节点
const node = g
.append('g')
.selectAll('circle')
.data(nodes)
.join('circle')
.attr('r', 11) // 半径
.style('fill', function (d: any) {
let color; //圆圈背景色
if (d.type === 'table') {
color = '#38CCB5';
} else if (d.type === 'tag') {
color = '#FFA02D';
} else if (d.type === 'subjectDomain') {
color = '#A096EA';
} else if (d.type === 'businessDomain') {
color = '#A096EA';
} else {
color = '#FF8988';
}
return color;
})
.call(drag1(simulation)) // 绑定事件支持拖动更新坐标
.on('click', function (d: any, i: any) {
// 节点点击切换样式,锚定右侧详细信息
props.nodeClick(i.index);
selectAll('circle').attr('r', 11).attr('stroke', 'none');
if (nodes[i.index].type === 'table') {
// @ts-ignore
select(this)
.attr('r', 16)
.attr('stroke', `rgba(56, 204, 181, 0.3)`)
.attr('stroke-width', '15px');
} else if (
nodes[i.index].type === 'businessDomain' ||
nodes[i.index].type === 'subjectDomain'
) {
// @ts-ignore
select(this)
.attr('r', 16)
.attr('stroke', `rgba(160, 150, 234, 0.3)`)
.attr('stroke-width', '15px');
} else if (nodes[i.index].type === 'tag') {
// @ts-ignore
select(this)
.attr('r', 16)
.attr('stroke', `rgba(255, 160, 45, 0.3)`)
.attr('stroke-width', '15px');
} else {
// @ts-ignore
select(this)
.attr('r', 16)
.attr('stroke', `rgba(255, 137, 136, 0.3)`)
.attr('stroke-width', '15px');
}
});
// 圆形节点的描述信息
const svg_texts = g.append('g').selectAll('text').data(nodes).enter().append('g');
svg_texts
.append('svg:text')
.attr('text-anchor', 'middle')
.attr('y', 25)
.attr('fill', '#B4B9C7')
.attr('font-size', 14)
.text(function (d: any) {
return d.label;
});
//力导图节点拖拽时的事件监听器 以实时更新坐标
function ticked() {
// 弧线
// link.attr("d", function(d) {
// var dx = d.target.x - d.source.x,//增量
// dy = d.target.y - d.source.y,
// dr = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
// return "M" + d.source.x + ","
// + d.source.y + "A" + dr + ","
// + dr + " 0 0,1 " + d.target.x + ","
// + d.target.y;
// });
link.attr('d', (d: any) => {
return d.source.x < d.target.x
? 'M' + d.source.x + ',' + d.source.y + 'L' + d.target.x + ',' + d.target.y
: 'M' + d.target.x + ',' + d.target.y + 'L' + d.source.x + ',' + d.source.y;
});
node
.attr('cx', function (d: any) {
return d.x;
})
.attr('cy', function (d: any) {
return d.y;
});
svg_texts.attr('transform', function (d: any) {
return 'translate(' + d.x + ',' + d.y + ')';
});
}
};
return <div id="myMap" style={{ position: 'absolute', overflow: 'hidden' }}></div>;
};
至此,文章开头的图,已经实现完成,本来想实现节点之间弧线连接并且保持颜色渐变的功能,弧线是实现了,但是渐变缺兼容不了,也没找到合适的方法
*
*
*
*
*
*
###############################################
后续更新版本
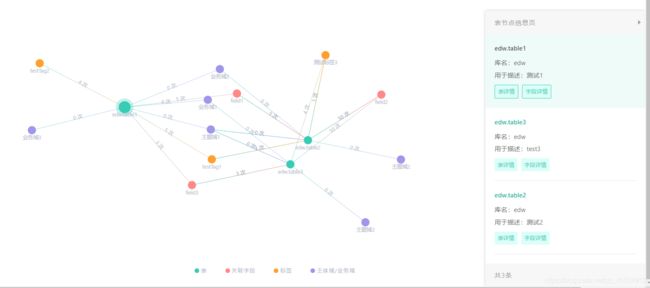
增加的功能点
- 根据节点之间关系数区分颜色粗细
- 添加节点图片
- 添加初始节点图片
- 节点点击事件穿透
下面直接贴出改动部分的代码,并附上备注说明
// 节点图片
// 通过id绑定
defs
.selectAll('pattern')
.data(nodes)
.enter()
.append('pattern')
.attr('id', function (d: any, i: any) {
return 'insect' + i;
})
.attr('width', 1)
.attr('height', 1)
.append('svg:image')
.attr('xlink:href', function (d: any, i: any) {
// 不同节点不同图片
if (nodes[i].type === 'table') {
return '图片地址';
} else if (nodes[i].type === 'businessDomain' || nodes[i].type === 'subjectDomain') {
return '图片地址';
} else if (nodes[i].type === 'tag') {
return '图片地址';
} else {
return '图片地址';
}
})
.attr('width', 22)
.attr('class', 'img');
// 节点线条颜色
// 去掉之前的渐变版本
function lineColor(y: any, i: any) {
if (y.properties) {
if (y.properties.frequency <= 5) {
return '#ADE2D8';
} else if (y.properties.frequency <= 20) {
return '#029A8F';
} else {
// @ts-ignore
select(this).attr('stroke-width', 2.5);
return '#02292B';
}
}
// @ts-ignore
select(this).attr('stroke-width', 2.5);
return '#02292B';
}
// 圆形节点的描述信息
const svg_texts = g.append('g').selectAll('text').data(nodes).enter().append('g');
svg_texts
.append('svg:text')
.attr('text-anchor', 'middle')
.attr('y', 25)
.attr('fill', '#B4B9C7')
.attr('font-size', 14)
.attr('pointer-events', 'none') // 添加事件穿透
.text(function (d: any) {
return d.label;
});