python开发桌面软件实例-Python开发的第一步:利用Python开发一个桌面小程序
前言
当使用桌面应用程序的时候,有没有那么一瞬间,想学习一下桌面应用程序开发?建议此次课程大家稍作了解不要浪费太多时间,因为没有哪家公司会招聘以为Python程序员开发桌面程序吧?
开发环境:
Python 3.6
Pycharm
代码
界面设置
1.导入模块
import tkinter as tk
2.实例化一个窗体对象
root = tk.Tk()
3.标题
root.title('计算器')
4.大小以及出现的位置
root.geometry("295x280+150+150")
5.透明度
root.attributes("-alpha", 0.9)
6.背景
root["background"] = "#ffffff"
7.标签
lable1 = tk.Label(root, textvariable=result_num, width=20, height=2, font=('宋体', 20), justify='left', background='#ffffff', anchor='se')
8.布局
lable1.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
9.按钮
button_clear = tk.Button(root, text='C', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: clear())
button_back = tk.Button(root, text='←', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: back())
button_division = tk.Button(root, text='/', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: operator('/'))
button_multiplication = tk.Button(root, text='x', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: operator('*'))
button_clear .grid(padx=4, row=1, column=0)
button_back .grid(padx=4, row=1, column=1)
button_division .grid(padx=4, row=1, column=2)
button_multiplication .grid(padx=4, row=1, column=3)
button_seven = tk.Button(root, text='7', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('7'))
button_eight = tk.Button(root, text='8', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('8'))
button_nine = tk.Button(root, text='9', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('9'))
button_subtraction = tk.Button(root, text='—', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: operator('-'))
button_seven .grid(padx=4, row=2, column=0)
button_eight .grid(padx=4, row=2, column=1)
button_nine .grid(padx=4, row=2, column=2)
button_subtraction .grid(padx=4, row=2, column=3)
button_four = tk.Button(root, text='4', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('4'))
button_four.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=3, column=0)
button_five = tk.Button(root, text='5', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('5'))
button_five.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=1)
button_six = tk.Button(root, text='6', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('6'))
button_six.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=2)
button_addition = tk.Button(root, text='+', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: operator('+'))
button_addition.grid(padx=4, row=3, column=3)
button_one = tk.Button(root, text='1', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('1'))
button_one.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=0)
button_two = tk.Button(root, text='2', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('2'))
button_two.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=1)
button_three = tk.Button(root, text='3', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('3'))
button_three.grid(padx=4, row=4, column=2)
button_equal = tk.Button(root, text='=', width=5, height=3, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: equal())
button_equal.grid(padx=4, row=4, rowspan=5, column=3)
button_zero = tk.Button(root, text='0', width=12, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('0'))
button_zero.grid(padx=4, pady=4, row=5, column=0, columnspan=2)
button_decimal = tk.Button(root, text='.', width=5, font=('宋体', 16), relief='flat', background='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: append_num('.'))
button_decimal.grid(padx=4, row=5, column=2)
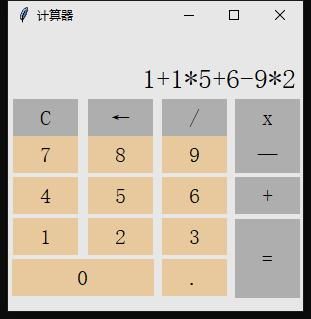
现在得出界面效果
功能
添加数字
def append_num(i):
lists.append(i)
result_num.set(''.join(lists))
选择运算符号
def operator(i):
if len(lists) > 0:
if lists[-1] in ['+', '-', '*', '/']:
lists[-1] = i
else:
lists.append(i)
result_num.set(''.join(lists))
清零
def clear():
lists.clear()
result_num.set(0)
退格
def back():
del lists[-1]
result_num.set(lists)
等号
def equal():
a = ''.join(lists)
end_num = eval(a)
result_num.set(end_num)
lists.clear()
lists.append(str(end_num))
定义一个列表收集输入的内容
lists = []
result_num = tk.StringVar()
result_num.set(0)
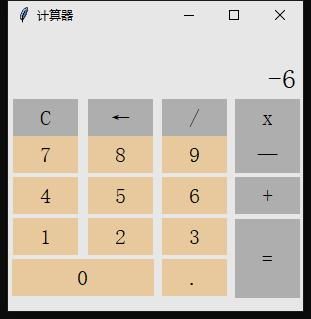
最后运行代码,效果如下图
先试试
运算得出结果
PS:如有需要Python学习资料的小伙伴可以加下方的群去找免费管理员领取
可以免费领取源码、项目实战视频、PDF文件等
![]()