最小编辑距离 (MED)实现-Python
此帖内容是去年9月份自己做的小实验~
1. 实验目的
最小编辑距离旨在定义两个字符串之间的相似度,定义相似度可以用于拼写纠 错、计算生物学上的序列对比、机器翻译、信息提取和语音识别等。
最小编辑距离就是指将一个字符串通过插入、删除和替换的编辑操作转变为另 一个字符串所需要的最小的编辑次数。
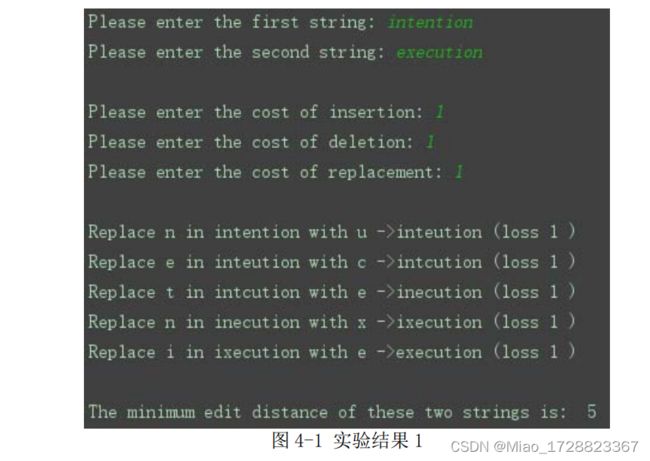
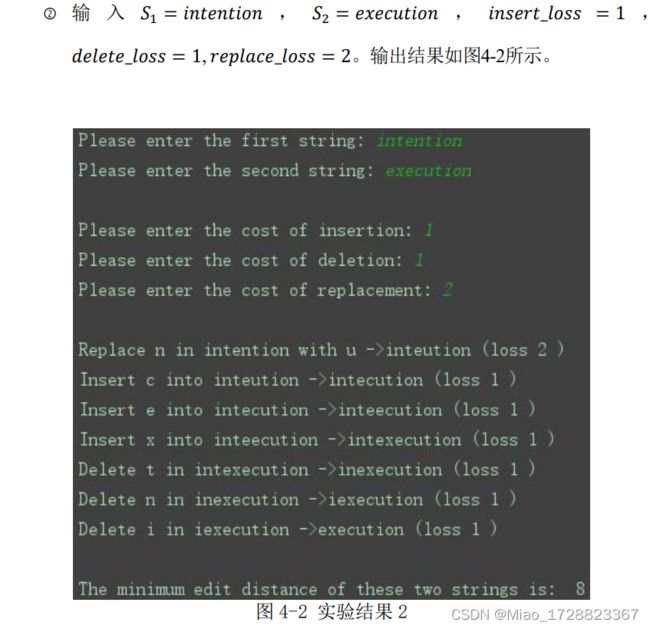
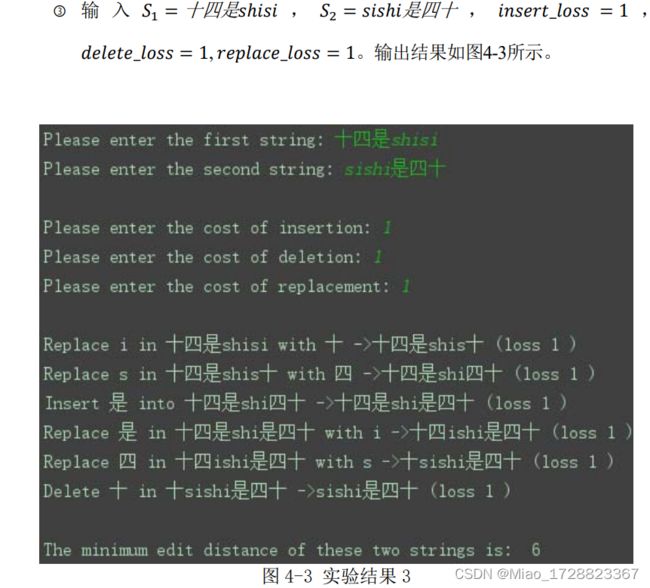
本次实验要求实现英文(及中文)字符串的最小编辑距离,计算并显示最小编辑路径;并且要求可以输入不同的字符串,以及可以同过修改操作代价来改 变最小编辑距离。
2. 实验环境
Python3.8.5。
3. 实验方法
4. 实验结果
5. 遇到问题及解决思路
在做本次实验的过程中,遇到的第一个问题是,缺乏将一个大问题转化为小 问题的能力,对dp问题不熟练,难以写出和理解动态转移方程。
在回溯并显示最小编辑路径的时候遇到困难,没有理解老师所说的回溯指针,并且最小编辑路径不止一条。我在解决这个问题时,没有使用回溯指针, 而是从D[n][m]出发,并从它的左方、下方和左下方的值中选取最小值,作为路径中的一步,以此类推直到回溯到D[0][0],此时S1已通过所有编辑操作转变为S2。
Python可以直接解析输入的汉字,不用考虑编码问题,以及中英混合的字 符串该如何区分其中的中文和英文字符,因此对于计算含有中文字符串的最小编辑距离时省了大功夫。
源代码
insert_lose = delete_lose = replace_lose = 1
def minEditDistance(s1, s2):
global insert_lose, delete_lose, replace_lose
n = len(s1)
m = len(s2)
if n * m == 0:
return n + m;
D = [[0] * (m + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(n + 1):
D[i][0] = i
for j in range(m + 1):
D[0][j] = j;
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, m + 1):
left = D[i - 1][j] + insert_lose
down = D[i][j - 1] + delete_lose
diag = D[i - 1][j - 1]
if s1[i - 1] != s2[j - 1]:
diag += replace_lose
D[i][j] = min(left, down, diag)
printPath(s1, s2, D)
return D[n][m]
def printPath(s1, s2, D):
n = len(D) - 1
m = len(D[0]) - 1
while (n != 0 or m != 0):
left = down = diag = 1e6
if (n - 1 >= 0):
if(m - 1 >= 0):
left = D[n][m - 1]
down = D[n - 1][m]
diag = D[n - 1][m - 1]
else:
down = D[n - 1][m]
else:
left = D[n][m - 1]
if (min(left, down, diag) == diag): # 往左下方回退
if(D[n][m] != diag): # 如果回退后的距离与当前距离不同,则发生置换
print("Replace", s1[n - 1], "in", s1, "with", s2[m - 1], "->",end='')
s1 = replace_char(s1, s2[m - 1], n - 1)
# s1[n - 1] = s2[m - 1]
print(s1, "(loss", replace_lose, ")")
n = n - 1
m = m - 1
elif(min(left, down, diag) == left): # 往左边回退,等价于向s1中插入字符
print("Insert", s2[m - 1], "into", s1, "->",end='')
s1 = insert_char(s1, s2[m - 1], n)
print(s1, "(loss", insert_lose, ")")
m = m - 1
else: # 往下方回退,等价于删除s1中的字符
print("Delete", s1[n - 1], "in", s1, "->",end='')
s1 = delete_char(s1, n - 1)
print(s1, "(loss", delete_lose, ")")
n = n - 1
print()
def replace_char(old_string, char, index):
# 字符串按索引位置替换字符
old_string = str(old_string)
# 新的字符串 = 老字符串[:要替换的索引位置] + 替换成的目标字符 + 老字符串[要替换的索引位置+1:]
new_string = old_string[:index] + char + old_string[index+1:]
return new_string
def insert_char(old_string, char, index):
# 按索引位置在字符串中添加字符
old_string = str(old_string)
# 新的字符串 = 老字符串[:要替换的索引位置] + 替换成的目标字符 + 老字符串[要替换的索引位置+1:]
new_string = old_string[:index] + char + old_string[index:]
return new_string
def delete_char(old_string, index):
# 按索引位置删除字符串中的字符
old_string = str(old_string)
new_string = old_string[:index] + old_string[index + 1: ]
return new_string
def main():
global insert_lose, delete_lose, replace_lose
s1 = input("Please enter the first string: ")
s2 = input("Please enter the second string: ")
print()
insert_lose = int(input("Please enter the cost of insertion: "))
delete_lose = int(input("Please enter the cost of deletion: "))
replace_lose = int(input("Please enter the cost of replacement: "))
print()
print("The minimum edit distance of these two strings is: ", minEditDistance(s1, s2))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()