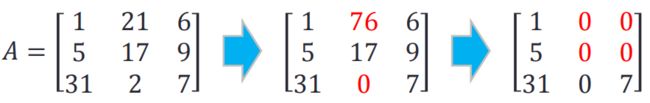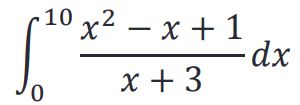国立台湾大学_郭彦甫老师_MATLAB课程练习
国立台湾大学_郭彦甫老师_MATLAB课程课程链接
【Bilibili链接】
【最近在自学郭彦甫老师MATLAB的相关课程,课程中有些许小练习在此记录下来,如果各位也学习了老师的相关课程,或是有更好的方法,欢迎交流】
01 Array_Operation
- 1.Calculate:
• cos( sqrt((1+2+3+4)3/5) )
• sin( sqrt() ) + ln( tan(1) ) )
• 23.5×1.7
• sin(10)
cos( sqrt((1+2+3+4)^3/5) )
sin( sqrt(pi) + log( tan(1) ))
2^(3.5*1.7)
exp(sin(10))
- 2.Calculate:
3/13 +4/14 +5/15=
format long
3/13 +4/14 +5/15
format rat
3/13 +4/14 +5/15
- 3.Change the following elements in the matrix:
A=[1 21 6;5 17 9;31 2 7];
A(1,2)=76;A(3,2)=0;
A([1:2],[2:3])=0;
- 4.try the expression:
A=[1 0 0;5 0 0;31 0 7];
>A(3,:)
>A(3,:) = [ ]
>>A(3,:)
ans =
31 0 7
>>A(3,:)=[]
A =
1 0 0
5 0 0
- 5.Create matrices A, B, C, and D and concatenate them into F:
A=[1 2;3 4];B=[9 9;9 9];
C=[5 6 7 8];D=[-2 -1 0 1];
F=[A B;C;D]
02 Structured_Programming_&_Function
- 1.Use while loop to calculate the summation of the series 1+2+3+…+999
n=1;
s=0;
while n<=999
s=s+n;
n=n+1;
end
disp(s)
- 2.Use structured programming to:
1.Find the entries in matrix A that are negative
2.Store these entries’ position in a matrix B
3.Change the values of these entries to zero
A =[0 −1 4;9 −14 25;−34 49 64]
A=[0 -1 4;9 -14 25;-34 49 64];
[x, y]=size(A);
B=zeros(x,y);
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
B(i,j)=A(i,j);
if B(i,j)<0
B(i,j)=0;
end
end
end
disp([A;B]);
- 3.Exercise:
Write a function that asks for a temperature in degrees Fahrenheit
• Compute the equivalent temperature in degrees Celsius
• Show the converted temperature in degrees Celsius
• The script should keep running until no number is provided to convert
function test()
H=input('→→请求输入温度(华氏度):');
while ~isempty(H)
C=(H-32).*(5/9);
disp(['转化为摄氏度为:',num2str(C)]);
test();
break;
end
03 Data_Structure_&_File_Access
- 1.Write a script that inverts any given string
s1=‘I like the letter E’
s2=‘E rettel eht ekil I’
s1=input('请输入待转换的字符串:','s');
n=length(s1);
s2=zeros(1,n);
for i=1:n
s2(i)=s1(n-i+1);
end
disp(['转换前:',s1]); %%s2=(end:-1:1);
disp(['转换后:',s2]); %%s2=reverse(s1);
- 2.Create a cell array B that has the following structure
B={'This is the first cell' [5+j*6 4+j*5];...
[1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] {'Tim','Chris'}}
B{1,1}='This is the first cell'
B{1,2}=[5+j*6 4+j*5];
B{2,1}=[1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9];
B{2,2}='Tim','Chris';
- 3.How do we write both the text and number into an Excel file?
data=xlsread('example1.xlsx');
z=mean(data')';
xlswrite('example1.xlsx',z,1,'E2:E4');%%写数值内容
xlswrite('example1.xlsx',{'AVERAGE'},1,'E1');%%写标题
std_1=sqrt(sum((data-z).^2))./length(data);
xlswrite('example1.xlsx',std_1',1,'F2:F4');
xlswrite('example1.xlsx',{'标准差'},1,'F1');
[numeric, title_01]=xlsread('example1.xlsx');
numeric_cell=num2cell(numeric);
title_01(2:4,2:6)=numeric_cell(1:3,1:5);
xlswrite('example1.xlsx',title_01,1,"n1:s4");
04 Basic_Plotting
- 1.Plot 1
•Plot as a black line and as a series of red circles for the range t = 1 to 2 in one figure:
= 2 and = sin(2)
•Label each axis, and add title and legend
t=linspace(1,2);
h=plot(t,t.^2,'k-',t,sin(2*pi*t),'ro');
title('Mini Assignment #1');
legend('t^2','sin(2\pit)','location','northwest');
xlabel('Time (ms)'); %%x坐标标签
ylabel('f(t)'); %%y坐标标签
- 2.Plot 2
t=linspace(1,2);
h=plot(t,t.^2,'k-',t,sin(2*pi*t),'ro');
title('Mini Assignment #1');
legend('t^2','sin(2\pit)','location','northwest');
xlabel('Time (ms)'); %%x坐标标签
ylabel('f(t)'); %%y坐标标签
set(gca,'FontSize',16)
set(h(1),'LineWidth',2);
set(h(2),'MarkerEdgeColor','r','MarkerFaceColor','b','LineWidth',1);
05 Advanced_Plotting
- 1.Stack the horizontal bar chart
x = [1 2 5 4 8];
y = [x;1:5];
subplot(1,3,1);
bar(y,'stacked');title('Stacked');
subplot(1,3,2);
barh(y);title('Horizontal');
subplot(1,3,3);
barh(y,'stacked');
- 2.Separate all the pieces in the pie chart
a = [10 5 20 30];
subplot(2,3,1); pie(a);title('饼图');
subplot(2,3,2); pie(a, [0,0,0,1]);title('饼图散');
subplot(2,3,3); pie3(a, [0,0,0,1]);title('饼图立体');
subplot(2,3,4); pie(a);
subplot(2,3,5); pie(a, [1,1,1,1]);
subplot(2,3,6); pie3(a, [1,1,1,1]);
- 3.Plot a hexagon on a polar chart
theta=linspace(0,2*pi,7);
r=ones(1,length(theta)); %%1行n列
h=polar(theta,r,'r-');
set(h,'LineWidth',1)
- 4.Exercise
• Plot a function: () = sin(2/4)
• Add the points sampled at 5 Hz using stem()
t1=0:0.01:10;
y1=sin(pi.*t1.^2./4);
plot(t1,y1,'b');hold on;
t2=0:0.2:10;
y2=sin(pi.*t2.^2./4);
stem(t2,y2,'r');hold off;
- 5.Plot a wait sign
t =[0:pi/2:2*pi]; x = cos(t);y=sin(t);
h=fill(x,y,'y'); axis square off;
set(h,'LineWidth',3);
text(0,0,'WAIT','Color', 'K','FontSize', 66, ...
'FontWeight','bold','HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
- 6.‘Gold’, ‘Silver’ and 'Bronze
G = [46 38 29 24 13]; S = [29 27 17 26 8];
B = [29 23 19 32 7]; h = bar(1:5, [G' S' B']);
set(h(1),'FaceColor',[hex2dec('FF')/255 hex2dec('FF')/255 hex2dec('00')/255])
set(h(2),'FaceColor',[hex2dec('cc')/255 hex2dec('cc')/255 hex2dec('cc')/255])
set(h(3),'FaceColor',[hex2dec('FF')/255 hex2dec('99')/255 hex2dec('00')/255])
get(gca);
set(gca, 'XTickLabel',{'USA','CHN','GBR','RUS','KOR'})
title('Medal count for top 5 countries in 2012 Olympics');
ylabel('Number of medals'); xlabel('Country');
legend('Gold', 'Silver', 'Bronze')
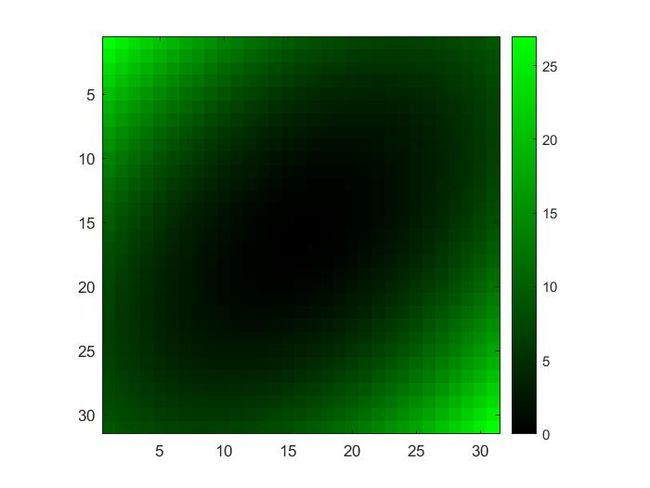
- 7.Create a custom green color map such that the output of the script below looks like:
green=[zeros(255,1) linspace(0,1,255)' zeros(255,1)];
colormap(green);
colorbar;
- 8.Combine the contour techniques to generate a figure as shown below
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
% subplot(1,3,1); contour(Z,[-.45:.05:.45]); axis square;
% subplot(1,3,2); [C,h] = contour(Z);clabel(C,h); axis square;
% subplot(1,3,3); contourf(Z); axis square;
[Ex,el]=contourf(Z,[-.45:.05:.45]);
clabel(Ex,el);
06 Graphical_User_Interface
% --- Executes on slider movement.
function slider1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
handles.a=get(handles.slider1,'Value');guidata(hObject, handles);
handles.b=get(handles.slider2,'Value');guidata(hObject, handles);
c=num2str(int16(handles.a+handles.b));
set(handles.text2,'String',['A+B=',c]);
% Hints: get(hObject,'Value') returns position of slider
% get(hObject,'Min') and get(hObject,'Max') to determine range of slider
% --- Executes on slider movement.
function slider2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to slider2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
handles.a=get(handles.slider1,'Value');guidata(hObject, handles);
handles.b=get(handles.slider2,'Value');guidata(hObject, handles);
c=num2str(int16(handles.a+handles.b));
set(handles.text2,'String',['A+B=',c]);
% Hints: get(hObject,'Value') returns position of slider
% get(hObject,'Min') and get(hObject,'Max') to determine range of slider
%%%%其他部分保持默认即可
07 Image_Processing I
- 1.Adjust the “brightness” and “contrast” of rice.png and display it on the screen
• Plot the histograms of the images before and after the “brightness” and “contrast” adjustment for rice.png
I=imread('rice.png');
J=immultiply(I,0.5);
K=immultiply(I,1.5);
subplot(2,3,1);imshow(I);
subplot(2,3,2);imshow(K);
subplot(2,3,3);imshow(J);
subplot(2,3,4);imhist(I);
subplot(2,3,5);imhist(J);
subplot(2,3,6);imhist(K);
- 2.Write your own equalization function, try it on pout.tif, and display it on the screen
I=imread('pout.tif');
N=double(255/(max(max(I))-min(min(I)))*1.5);
IEQ=immultiply(imsubtract(I,double(min(min(I)))),N);
subplot(2,3,1);imshow(I);title('原图');
subplot(2,3,2);imshow(IEQ);title('自制');
subplot(2,3,3);imshow(histeq(I));title('系统');
subplot(2,3,4);imhist(I);
subplot(2,3,5);imhist(IEQ);
subplot(2,3,6);imhist(histeq(I));
08 Image_Processing II
- 1.Practice 1
• Write a program to convert the image rice.png into a binary image using a threshold
• Do NOT use im2bw()
• Try different threshold values to see if your program works
I=imread('rice.png');
[x,y]=size(I);
I1=zeros(x,y);
thre=sum(sum(I))/(x*y);
thre_1=max(max(I))-min(min(I))*0.5;
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
if I(i,j)>(thre+thre_1)*0.5
I1(i,j)=255;
end
end
end
subplot(1,3,1);imshow(I);title('原图');
subplot(1,3,2);imshow(I1);title('自制');
level=graythresh(I);
I2=im2bw(I,level);
subplot(1,3,3);imshow(I2);title('im2bw');
- 2.Practice
• Plot the histogram of grain size
• Identify all the grains in the image by painting them in red
%%%%读取图像并进行二值化
I=imread('rice.png'); %%读取图像
BG=imopen(I,strel('disk',15)); %%生成背景图
I_1=imsubtract(I,BG); %%图像相减
level=graythresh(I_1); %%分界线
I_2=im2bw(I_1,level); %%新的二值化
[labeled,numObjects]=bwlabel(I_2,8);
RGB_label=label2rgb(labeled);
imshow(RGB_label);title('RGB\_label');
[x, y, z]=size(RGB_label);
%%%%Paint red
redim=labeled;
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
if redim(i,j)>0
redim(i,j)=255;
end
end
end
gr=zeros(x,y);bl=zeros(x,y);
redim(:,:,2)=gr;
redim(:,:,3)=bl;
figure;imshow(redim);title('Red Painted');
%%%%数米的数量绘制直方图
h=zeros(1,numObjects);
for n=1:numObjects
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
if labeled(i,j)==n
h(n)=h(n)+1;
end
end
end
end
figure;hist(h,20);title('The Grain Size');
09 Integration_&_Differentiation
- 1.Plot the polynomial and its derivative for −2 ≤ ≤ 1
f(x)=(5x3-7x2+5x+10)(4x2+12x-3)
y1=[5 -7 5 10];
y2=[4 12 -3];
y3=conv(y1,y2); %%返回向量 u 和 v 的卷积。如果 u 和 v 是多项式系数的向量,对其卷积与将这两个多项式相乘等效
x=linspace(-2,1);
plot(x,polyval(y3,x),'--b','LineWidth',1.6);hold on;
plot(x,polyval(polyder(y3),x),'-r','LineWidth',1.6);hold off;
legend({'f (x)','f''(x)'},'FontSize',12);
set(gca,'FontSize',12);
- 2.Given () = sin(), write a script to find the error of ′(0) at 0 = /2 using various ℎ
n=1:7;
x0=pi/2;
for i=1:n
x=[x0 x0+power(10,-n)];
y=[sin(x0) sin(x0+power(10,-n))];
m(n)=diff(y)./diff(x);
end
disp(m);
- 3.Given () = −sin(2/2), plot the approximate derivatives ′ of ℎ = 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001
g = colormap(lines); hold on;
for i=1:3
x = 0:power(10, -i):2*pi;
y = exp(-x).*sin(x.^2./2);
m = diff(y)./diff(x);
plot(x(1:end-1), m, 'Color', g(i,:));
end
hold off;
set(gca,'XLim', [0, 2*pi]); set(gca,'YLim', [-0.25,0.25]);
set(gca,'FontSize', 18); set(gca,'FontName', '宋体');
set(gca,'XTick', 0:pi/2:2*pi);
set(gca,'XTickLabel', {'0', '\pi/2', '\pi','3\pi/2','2\pi'});
h = legend('h=0.1','h=0.01','h=0.001');
set(h,'FontName', '宋体'); box on;
10 Root_Finding
- 1.Find the roots for:
cos(x) 2 − sin(x)2 = 0;
cos(x) 2 + sin(x)2 = 0
syms x;
y1=cos(x).^2-sin(x).^2;
y2=cos(x).^2+sin(x).^2;
solve(y1,x)
solve(y2,x)
- 2.Solve this equation for x using symbolic approach
(x − a)2 + (y − b )2 = r2
syms x y a b r; %%不能有逗号
y1=(x-a)^2+(y-b)^2-r^2;
x0=solve(y1)
Find the matrix inverse using symbolic approach [a b;c d]
syms a b c d a1 b1 c1 d1;
y1=a*a1+b*c1-1;
y2=a*b1+b*d1-1;
y3=c*a1+d*c1-1;
y4=c*b1+d*d1-1;
A=solve(y1,y2,y3,y4,a1,b1,c1,d1)
- 3.求偏导
syms x y
y1=exp(x^2)/(x^3-x+3);
y2=(x^2+x*y-1)/(y^3+x+3);
y1p=diff(y1)
y2p=diff(y2) %%对y求偏导y2p=diff(y2,y)
- 4.求积分
syms x;
y=(x^2-x+1)/(x+3);
z=int(y,[0 10])
- 5.Exercise
% % z1=@(x,y) (2*x-y-exp(-x));
% % z2=@(x,y) (-x+2*y-exp(-y));fsolve不能同时解两个
f=@(x)[2*x(1)-x(2)-exp(-x(1));-x(1)+2*x(2)-exp(-x(2))];
x=fsolve(f,[-5 -5]) %%不会的时候去help吧。fsolve牛顿法斜率、fzero二分法
11 Linear_Equations
- 1.Write a function to solve 1 … 5 for given 1, 2, and 1 … 5
syms R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 V1 V2;
A=[R1 0 0 R4 0;
0 R2 0 -R4 R5;
0 0 -R3 0 R5;
1 -1 0 -1 0;
0 1 -1 0 -1];
b=[V1 0 V2 0 0];
x=A\b
- 2.Plot the planes in 3D
x=0:40;
y=0:40;
[X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y);
z1=-X-Y;
z2=-X+Y;
z3=-X./3;
hold on;surf(X,Y,z1);
surf(X,Y,z2);
surf(X,Y,z3);grid on;
hold off;
xlabel('这是x轴');ylabel('这是y轴');zlabel('这是z轴');
set(gca,'XLim',[0 40]);
set(gca,'YLim',[0 40]);
set(gca,'ZLim',[-20 20]); %%这个和老师PPT上的好像不太一样@_@
12 Statistics_&_Data_Analysis
- 1.Find the following properties of the variable x4
1 Mean, median, mode, and quartile
2 Range and interquartile range
3 Variance and standard deviation
load stockreturns;
x4=stocks(:,4);
Mean=mean(x4)
Median=median(x4)
Mode=mode(x4)
Quartile=quantile(x4,0.25)
Range=max(x4)-min(x4)
Variance=var(x4)
Standa_d=std(x4)
- 2.Plot the histograms:
x = [1 3 5 5 5 5 7 9 9 9 10 13 14];
fre=zeros(1,max(x));
for i=1:length(x)
for j=1:length(fre)
if x(i)==j
fre(j)=fre(j)+1;
end
end
end
subplot(1,3,1);bar(1:14,fre);xlim([0 15]);
subplot(1,3,2);area(1:14,fre);xlim([0 15]);
subplot(1,3,3);stem(1:14,fre);xlim([0 15]);
- 3.Plot the boxplot of the variable stocks
Find the skewness and kurtosis for each column of the variable stocks
load stockreturns;
boxplot(stocks);
prctile(stocks,[25 50 75]);
y = skewness(stocks);
plot(y)
13 Curve_Fitting_&_Interpolation
- 1.Given the table below
1.Find the 0 and 1 of the regression line
2 Plot the figure
TC=[0.025 0.035 0.050 0.060 0.080];
TE=[20 30 40 50 60];
fit=polyfit(TE,TC,1);
x=[TE(1):0.1:TE(end)];
yfit=fit(1)*x+fit(2);
plot(TE,TC,'ko',x,yfit,'-r','LineWidth',1);grid on;
set(gca,'FontSize',12);
xlabel('Temperature (\circC)');
ylabel('TC Output (mV)');
- 2.Find the 4th, 5th, and 6th-order polynomials
x =[-1.2 -0.5 0.3 0.9 1.8 2.6 3.0 3.5];
y =[-15.6 -8.5 2.2 4.5 6.6 8.2 8.9 10.0];
x =[-1.2 -0.5 0.3 0.9 1.8 2.6 3.0 3.5];
y =[-15.6 -8.5 2.2 4.5 6.6 8.2 8.9 10.0];
figure('Position', [50 50 1500 400]);
for i=4:6
subplot(1,3,i-3); p = polyfit(x,y,i);
xfit = x(1):0.1:x(end);
yfit = polyval(p,xfit);
plot(x,y,'ro',xfit,yfit);
set(gca,'FontSize',14);ylim([-17, 11]);
legend('Data points','Fitted curve','Location','southeast');
end
- 3.Fit the data using the formulation:
= 0 + 11 + 22 + 312 + 422 + 512
load carsmall;
y = MPG;
x1 = Weight;
x2 = Horsepower;
X = [ones(length(x1),1) x1 x2 x1.^2 x2.^2 x1.*x2];
b = regress(y,X);
x1fit = min(x1):100:max(x1);
x2fit = min(x2):10:max(x2);
[X1FIT,X2FIT]=meshgrid(x1fit,x2fit);
YFIT=b(1)+b(2)*X1FIT+b(3)*X2FIT+b(4)*X1FIT.^2+b(5)*X2FIT.^2+b(6)*X1FIT.*X2FIT;
scatter3(x1,x2,y,'filled'); hold on;
surf(X1FIT,X2FIT,YFIT); hold off;
xlabel('Weight');
ylabel('Horsepower');
zlabel('MPG'); view(50,10)
- 4.Fit the data using linear lines and cubic splines
x=[0 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.75 2.0 2.25];
y=[1.2 1.18 1.1 1 0.92 0.8 0.7 0.55 0.35 0];
n=length(x);
xfit=x(1):0.01:x(end);
yfit_1=interp1(x,y,xfit);
yfit_2=spline(x,y,xfit);
hold on;
plot(x,y,'-bo',xfit,yfit_1,'r-','LineWidth',1);
plot(xfit,yfit_2,'g','LineWidth',1);
hold off;
legend('Original','Linear','Spline');