【Neural-Symbolic】方向的研究工作核心思想一览
【Neural-Symbolic】方向的研究工作核心思想一览
Neural-Symbolic可以认为是将人工智能中原本对立的连接主义和符号主义结合的一个新兴研究方向(实际上最早相关工作可追至1978年),先对其相关研究工作典型的十篇论文做出总结。
Neural-Symbolic的本质是什么
Neural-Symbolic意指神经符号主义,但是更本质地讲,实际上是将现代数学中的分析学和代数学结合,分析学擅长处理数值、函数、逼近等问题,代数学擅长处理推演、抽象、结构等问题;因此如果能适当结合,威力必然可观.
Neural-Symbolic研究工作思路
根据选定的这十篇论文,可以总结其基本研究思路如下:
- 研究问题:即研究定位的推理问题是什么,如视觉推理问题数据集CLEVER,知识图谱数据集Freebase,或者分类问题数据集Fashion等等;介绍研究任务和意义,随后简介面向这个任务的已有方法,接着说明已有方法面临的关键挑战,针对这些挑战,本文提出什么创新思路和具体方法;
- 逻辑范式:即给出本文需要使用的符号逻辑的公理化描述,如谓词逻辑 ( e 1 , p , e 2 ) ∈ E × P × E \left(e_{1}, p, e_{2}\right) \in \mathcal{E} \times \mathcal{P} \times \mathcal{E} (e1,p,e2)∈E×P×E,蕴含逻辑 α ⊨ β \alpha \models \beta α⊨β,规则逻辑 C l e a r ( x ) ← ∀ y ¬ O n ( y , x ) \mathrm{Clear}(x) \leftarrow \forall y \neg \mathrm{On}(y, x) Clear(x)←∀y¬On(y,x)等等.这些描述一般和研究问题紧密相关,也是下面的逻辑数值表示学习的基础架构.
- 逻辑表示学习:如同NLP的第一步永远是如何将自然语言映射到特征向量空间一样,逻辑表示学习是如何将符号逻辑的先验知识映射到数值向量空间.可以说,逻辑表示学习是连接分析和代数的纽带.具体的方法比如同NLP一样用神经网络做embedding[10]:
e i F , h i F = LSTM ( Φ E ( x i ) , h i − 1 F ) e_{i}^{F}, h_{i}^{F}=\operatorname{LSTM}(\Phi_{E}(x_{i}), h_{i-1}^{F}) eiF,hiF=LSTM(ΦE(xi),hi−1F)
又比如利用Markov模型的逻辑知识信息导出[3]:
P ( X = x ) = 1 Z exp ( ∑ i = 1 n w i f i ( x { i } ) ) P(X=x)=\frac{1}{Z} \exp (\sum_{i=1}^{n} w_{i} f_{i}(x_{\{i\}})) P(X=x)=Z1exp(i=1∑nwifi(x{i}))
- 提出目标函数:通常需要考虑逻辑推理的结构(如谓词结构)和神经网络的效率结合功能模块的设计(如视觉、语义信息的扒取)等,设计一个可供参数优化(最大似然或者最小误差)的目标函数.具体的比如知识图谱补全任务的目标函数[2]:
f ( s , p , o ) = ∥ s + p − o ∥ 2 2 f(s, p, o)=\|\mathbf{s}+\mathbf{p}-\mathbf{o}\|_{2}^{2} f(s,p,o)=∥s+p−o∥22
又比如语义损失函数[6]:
L s ( α , p ) ∝ − log ∑ x ⊨ α ∏ i : x ⊨ X i p i ∏ i : x ⊨ ¬ X i ( 1 − p i ) L^{s}(\alpha, p) \propto-\log \sum_{\mathbf{x} \models \alpha} \prod_{i:\mathbf{x} \models X_{i}} p_i \prod_{i : \mathbf{x} \models \neg X_{i}} (1-p_i) Ls(α,p)∝−logx⊨α∑i:x⊨Xi∏pii:x⊨¬Xi∏(1−pi)
- 优化、实验、评估:这和其他的计算机论文如出一辙不再赘述;
Neural-Symbolic研究工作亮点
在这里总结一些可以说超越了上述一般套路思维的亮点思维.
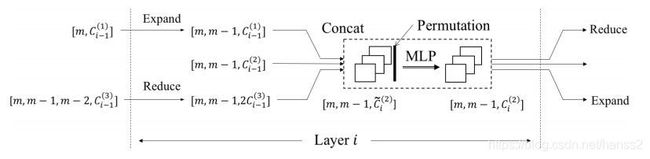
- 融合不规则信息:文章[4]展示了如何将不规则信息先整合为规则的信息,然后再进行学习.即使用:
I i ( r ) = Concat ( Expand ( O i − 1 ( r − 1 ) ) , O i − 1 ( r ) , Reduce ( O i − 1 ( r + 1 ) ) ) I_{i}^{(r)}=\text{ Concat }\left(\text{ Expand }(O_{i-1}^{(r-1)}\right), O_{i-1}^{(r)}, \text{ Reduce }(O_{i-1}^{(r+1)})) Ii(r)= Concat ( Expand (Oi−1(r−1)),Oi−1(r), Reduce (Oi−1(r+1)))
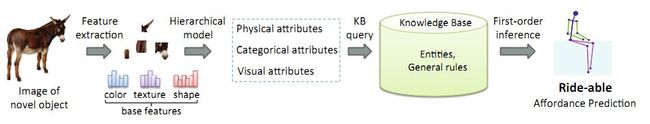
- 使用Neural-Symbolic来实现zero-shot learning:加入了逻辑先验知识,实现零样本学习似乎变得理所应当.文章[3]中,借由一个排序函数 R k ( I ) = w k T ϕ ( I ) R_{k}(I)=w_{k}^{T} \phi(I) Rk(I)=wkTϕ(I)的帮助来实现.
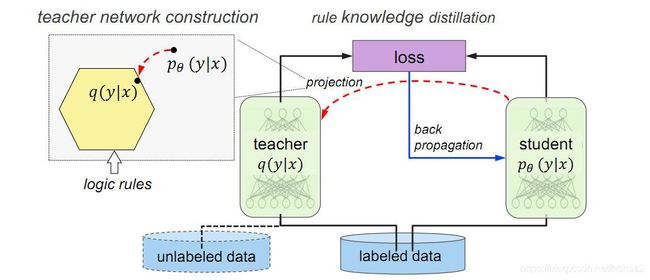
- 借符号先验知识实现teacher-student模式:teacher-student模式更符合人类学习方式,因而逐渐成为一种流行范式,现在文章[7]将符号先验知识作为teacher的信息源,并且约束teacher和student的差异来实现学习:
min q , ξ ≥ 0 KL ( q ( Y ∣ X ) ∥ p θ ( Y ∣ X ) ) + C ∑ l , g l ξ l , g l \min _{q, \xi \geq 0} \operatorname{KL}(q(\boldsymbol{Y} | \boldsymbol{X}) \| p_{\theta}(\boldsymbol{Y} | \boldsymbol{X}))+C \sum_{l, g_{l}} \xi_{l, g_{l}} q,ξ≥0minKL(q(Y∣X)∥pθ(Y∣X))+Cl,gl∑ξl,gl
总结
人类是以神经元为基础的生物,但却最终用符号的语言来交流信息,因此从学习机制上,结合Neural-Symbolic来探究人工智能是合理的.从数学上来说,分析学分支和代数学分支的结合是Neural-Symbolic的理论本质.
到目前为止,已有的关于Neural-Symbolic只能说算将神经网络方法和逻辑符号的一些概念有所结合,还处于比较初级的应用层面,无论在neural还是symbolic方向,都亟待加深,否则难以做出有深度的研究.
- neural方向可深入:脑认知机制的数学模型、泛函分析关于映射的理论、融入了测度论的随机过程等等;
- symbolic方向可深入:抽象代数的群论、哲学和逻辑学、符号计算(数学机械化理论)等等;
Neural-Symbolic研究的十篇代表性论文
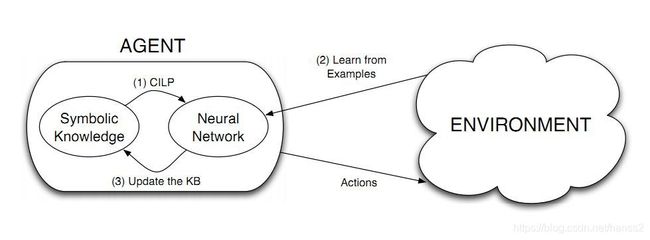
[1] Boella, Guido , et al. “Learning and reasoning about norms using neural-symbolic systems.” Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems - Volume 2 2012.
[2] Zhang, Xiangling , et al. “Knowledge Graph Completion via Local Semantic Contexts.” International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications Springer International Publishing, 2016.
[3] Zhu, Yuke , A. Fathi , and L. Fei-Fei . “Reasoning about Object Affordances in a Knowledge Base Representation.” European Conference on Computer Vision Springer International Publishing, 2014.
[4] Dong, Honghua , et al. “Neural Logic Machines.”,2019.
[5] Ramakrishna Vedantam , et al. “Probabilistic Neural-symbolic Models for Interpretable Visual Question Answering.” ,2018.
[6] Xu, Jingyi , et al. “A Semantic Loss Function for Deep Learning with Symbolic Knowledge.” (2017).
[7] Hu, Zhiting , et al. “Harnessing Deep Neural Networks with Logic Rules.” Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) 2016.
[8] Socher, Richard , et al. “Reasoning With Neural Tensor Networks for Knowledge Base Completion.” International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Curran Associates Inc. 2013.
[9] Liang, Chen , et al. “Neural Symbolic Machines: Learning Semantic Parsers on Freebase with Weak Supervision.” (2016).
[10] Yi, Kexin,Wu, Jiajun , et al. “Neural-Symbolic VQA: Disentangling Reasoning from Vision and Language Understanding.” ,2019.