西瓜书第五章习题及答案
![]()
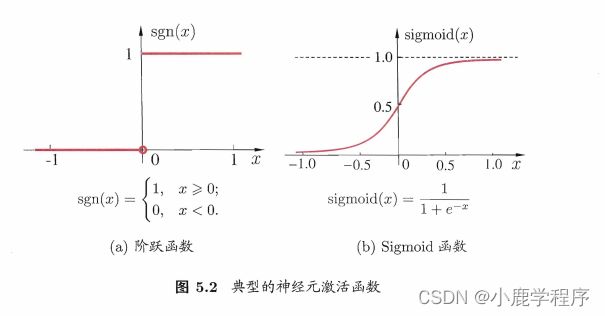
如果神经网络只使用一个sigmoid函数,此时的神经网络等同于对数几率回归,但是不同的是,对数几率回归通常用于一个二分类问题,对于输出的结果通常需要跟一个阈值进行比较(比如大于0.5时归类为正例,小于0.5时归类为反例)
![]()
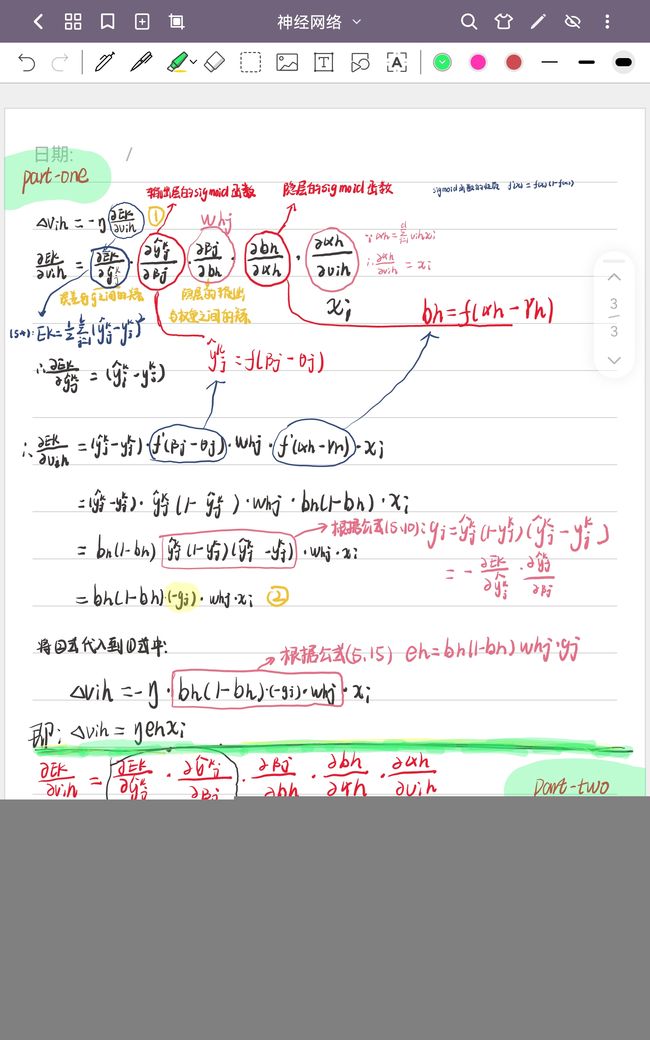
本题证明中所用到的公式是书上P101-P104上所给的,下面的图片由两部分组成,基础差的看part-one部分,基础好的,并且对书上公式很了解的可以直接看part-two部分,当然大家都可以先看part-two部分,这样可以有助于理解part-one部分的详细推导过程。
(如果觉得字太丑了,推荐大家阅读这篇文章,这篇文章的最后几个过程有些错误,大家注意一下。)
这张图,我写了好久、好久、好久。虽然推导出来了,但是我觉得我对神经网络还是不懂,咋整???(呜呜,太难了!!!)
![]()
学习率 η太小,则每次的更新量会太小,这使得迭代次数增多;反之,如果学习率 η太大,则会出现震荡情况,即在最小值附近来回波动,导致算法无法收敛。(参考链接)

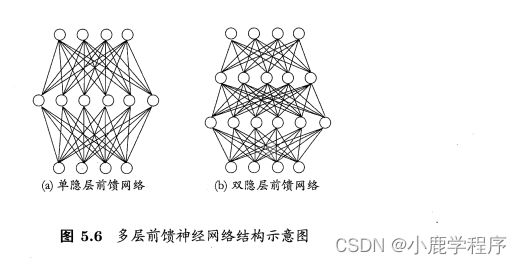
BP算法(error BackPropagation):误差逆传播算法,而BP网络通常是指用BP算法训练的多层前馈神经网络
,多层前馈神经网络是指-每层神经元与下层神经元全互连,神经元之间不存在同层连接,也不存在跨层连接。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
dataset = pd.read_csv('F:\\python\\dataset\\chapter5\\watermelon_3a.csv', delimiter=",")
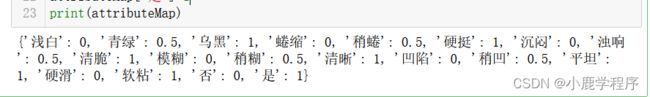
对数据经行处理:
#according to P54--3.2
#process the dataset
attributeMap={}
attributeMap['浅白']=0
attributeMap['青绿']=0.5
attributeMap['乌黑']=1
attributeMap['蜷缩']=0
attributeMap['稍蜷']=0.5
attributeMap['硬挺']=1
attributeMap['沉闷']=0
attributeMap['浊响']=0.5
attributeMap['清脆']=1
attributeMap['模糊']=0
attributeMap['稍糊']=0.5
attributeMap['清晰']=1
attributeMap['凹陷']=0
attributeMap['稍凹']=0.5
attributeMap['平坦']=1
attributeMap['硬滑']=0
attributeMap['软粘']=1
attributeMap['否']=0
attributeMap['是']=1
print(attributeMap)
del dataset['编号']
print(dataset)
#转化成数组
dataset=np.array(dataset)
print(dataset)
m,n=np.shape(dataset)
print(m, n)
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if dataset[i,j] in attributeMap: #将离散属性数字化--按照字典键值对
dataset[i,j]=attributeMap[dataset[i,j]]
dataset[i,j]=round(dataset[i,j],3) #将连续的属性值保留三位
print('处理之后的数据集:\n',dataset)
print('---------------分割线---------------')
trueY=dataset[:,n-1]
print('数据的真实标签类别:\n',trueY)
X=dataset[:,:n-1] #去除了最后一列
m,n=np.shape(X)
print('---------------分割线---------------')
print("去除了最后一列的数据集:\n",X)
print(m, n)
import math
def sigmoid(iX,dimension):#iX is a matrix with a dimension
if dimension==1:
for i in range(len(iX)):
iX[i] = 1 / (1 + math.exp(-iX[i]))
else:
for i in range(len(iX)):
iX[i] = sigmoid(iX[i],dimension-1)
return iX
标准BP算法与累计BP算法(将其中一个注释一下就好了):
# do the repeat----standard BP
#m = 17 17行数据
while(maxIter>0):
maxIter-=1
sumE=0
for i in range(m):
alpha = np.dot(X[i],v)#p101 line 2 from bottom, shape=1*q
b=sigmoid(alpha-gamma,1)#隐层使用sigmoid函数,#b=f(alpha-gamma), shape=1*q
beta=np.dot(b,w)#shape=(1*q)*(q*l)=1*l
predictY=sigmoid(beta-theta,1)#输出层使用sigmoid函数(得到输出结果)#shape=1*l ,p102--5.3
E = sum((predictY-trueY[i])*(predictY-trueY[i]))/2 #5.4
sumE+=E#5.16
#p104
g=predictY*(1-predictY)*(trueY[i]-predictY)#shape=1*l p103--5.10
e=b*(1-b)*((np.dot(w,g.T)).T) #shape=1*q , p104--5.15
w+=eta*np.dot(b.reshape((q,1)),g.reshape((1,l)))#5.11
theta-=eta*g#5.12
v+=eta*np.dot(X[i].reshape((d,1)),e.reshape((1,q)))#5.13
gamma-=eta*e#5.14
print(sumE)
# #accumulated BP
# trueY=trueY.reshape((m,l))
# while(maxIter>0):
# maxIter-=1
# sumE=0
# alpha = np.dot(X, v)#p101 line 2 from bottom, shape=m*q
# b = sigmoid(alpha - gamma,2) # b=f(alpha-gamma), shape=m*q
# beta = np.dot(b, w) # shape=(m*q)*(q*l)=m*l
# predictY = sigmoid(beta - theta,2) # shape=m*l ,p102--5.3
# E = sum(sum((predictY - trueY) * (predictY - trueY))) / 2 # 5.4
# print(round(E,5))
# g = predictY * (1 - predictY) * (trueY - predictY) # shape=m*l p103--5.10
# e = b * (1 - b) * ((np.dot(w, g.T)).T) # shape=m*q , p104--5.15
# w += eta * np.dot(b.T, g) # 5.11 shape (q*l)=(q*m) * (m*l)
# theta -= eta * g # 5.12
# v += eta * np.dot(X.T, e) # 5.13 (d,q)=(d,m)*(m,q)
# gamma -= eta * e # 5.14
# print(sumE)
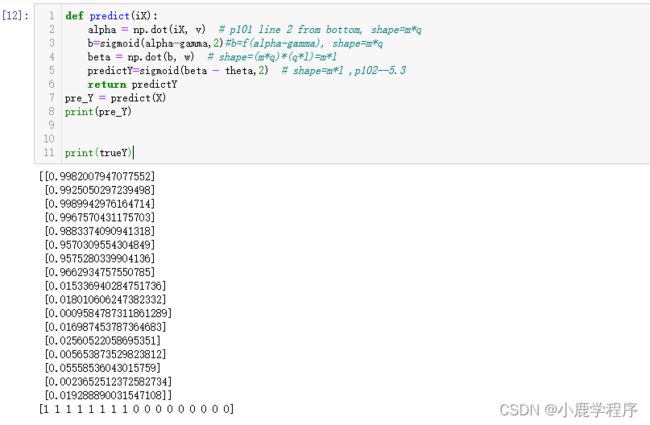
最后的预测函数:
def predict(iX):
alpha = np.dot(iX, v) # p101 line 2 from bottom, shape=m*q
b=sigmoid(alpha-gamma,2)#b=f(alpha-gamma), shape=m*q
beta = np.dot(b, w) # shape=(m*q)*(q*l)=m*l
predictY=sigmoid(beta - theta,2) # shape=m*l ,p102--5.3
return predictY
pre_Y = predict(X)
print(pre_Y)
print(trueY)
结果图,从结果可以看出,预测的很准(标准BP算法的结果)
说明:本代码不是本人书写,好吧,我就是一个搬运工。原文章作者写的很好,让我们一起膜拜大佬吧。原文章链接。需要数据集的可以留言哈。