【运筹优化】结合天际线启发式的禁忌搜索算法求解二维矩形装箱问题 + Java代码实现
文章目录
- 一、天际线启发式
- 二、禁忌搜索算法结合天际线启发式
-
- 2.1 初始解构造
- 2.2 邻域动作
- 三、Java代码实现
-
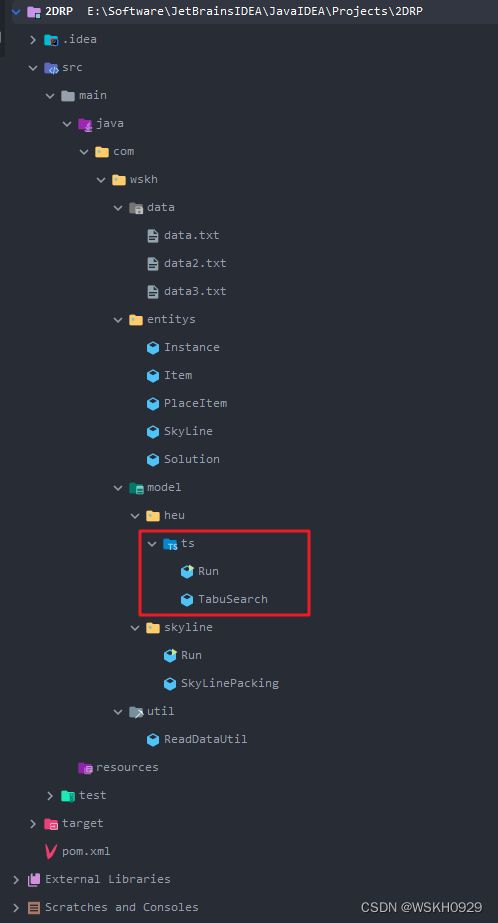
- 3.1 项目结构
- 3.2 TabuSearch
- 3.3 Run
- 3.4 运行结果展示
【运筹优化】求解二维矩形装箱问题的算法合辑(Java代码实现)
一、天际线启发式
关于天际线启发式的介绍请看我的另一篇博客:【运筹优化】基于堆优化的天际线启发式算法和复杂的评分策略求解二维矩形装箱问题 + Java代码实现
二、禁忌搜索算法结合天际线启发式
禁忌搜索算法结合天际线启发式其实很简单,只需要将序列对应成一个矩形集合,传给天际线启发式算法进行求解即可。
也就是说,天际线启发式其实就是禁忌搜索这类启发式算法的解码器(评价函数)。
2.1 初始解构造
我使用按照面积降序的顺序构造初始序列,然后调用天际线启发式算法进行求解,获得初始解
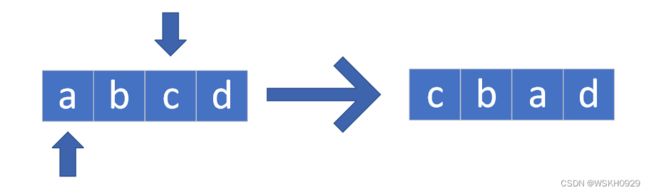
2.2 邻域动作
采用两两互换的方式,构造新序列
三、Java代码实现
3.1 项目结构
红框以外的代码文件在上面说的博客里有,本博客只给 Run 和 TabuSearch 的代码
3.2 TabuSearch
/**
* @Author:WSKH
* @ClassName:TabuSearch
* @ClassType:
* @Description:禁忌搜索算法结合天际线算法求解二维矩形装箱问题
* @Date:2022/11/7/11:32
* @Email:[email protected]
* @Blog:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51545953?type=blog
*/
public class TabuSearch {
// 迭代次数(提高这个值可以稳定地提高解质量,但是会增加求解时间)
private int MAX_GEN;
// 局部搜索的次数(这个值不要太大,太大的话搜索效率会降低)
public int N;
// 禁忌长度
private int tabuSize;
// 禁忌表
private int[][] tabuList;
// 最佳的迭代次数*
public int bestT = -1;
// 随机函数对象
public Random random;
// 当前禁忌表长度
public int l = 0;
// 边界的宽
private double W;
// 边界的高
private double H;
// 矩形数组
Item[] items;
// 是否可以旋转
private boolean isRotateEnable;
/**
* @param MAX_GEN 迭代次数(提高这个值可以稳定地提高解质量,但是会增加求解时间)
* @param N 局部搜索的次数(这个值不要太大,太大的话搜索效率会降低)
* @param tabuSize 禁忌表最大长度
* @param instance 实例对象
* @param seed 随机数种子,如果传入null则不设置随机数种子,否则按照传入的种子进行设置,方便复现结果
* @Description 构造函数
*/
public TabuSearch(int MAX_GEN, int N, int tabuSize, Instance instance, Long seed) {
this.MAX_GEN = MAX_GEN;
this.N = N;
this.tabuSize = tabuSize;
this.W = instance.getW();
this.H = instance.getH();
this.isRotateEnable = instance.isRotateEnable();
this.items = Item.copy(instance.getItemList().toArray(new Item[0]));
this.random = seed == null ? new Random() : new Random(seed);
}
/**
* @return 最佳装载结果对象Solution
* @Description 禁忌搜索主函数
*/
public Solution solve() {
// 初始化禁忌表
tabuList = new int[tabuSize][items.length];
// 讲矩形按照面积降序排列
Arrays.sort(items, (o1, o2) -> {
// 由于是降序,所以要加个负号
return -compareDouble(o1.getW() * o1.getH(), o2.getW() * o2.getH());
});
// 获取初始解 [ 0, 1, 2, 3,... ,n ]
int[] sequence = new int[items.length];
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
sequence[i] = i;
}
// 初始解就是当前最优解
Solution bestSolution = evaluate(sequence);
int[] bestSequence = sequence.clone();
System.out.println("初始解:" + bestSolution.getRate());
// 开始迭代,停止条件为达到指定迭代次数
for (int t = 0; t < MAX_GEN; t++) {
// 当前领域搜索次数
int n = 0;
Solution LocalSolution = null;
int[] LocalSequence = null;
while (n <= N) {
// 两两交换,得到当前序列的邻居序列
int[] tempSequence = generateNewSequence(sequence);
// 判断其是否在禁忌表中
if (!isInTabuList(tempSequence)) {
// 如果不在
Solution tempSolution = evaluate(tempSequence);
if (LocalSolution == null || compareDouble(tempSolution.getTotalS(), LocalSolution.getTotalS()) == 1) {
// 如果临时解优于本次领域搜索的最优解
// 那么就将临时解替换本次领域搜索的最优解
LocalSequence = tempSequence.clone();
LocalSolution = tempSolution;
}
n++;
}
}
// 如果局部搜索到了其他序列,则进行下面的流程
if (LocalSequence != null) {
if (compareDouble(LocalSolution.getTotalS(), bestSolution.getTotalS()) == 1) {
// 如果本次搜索的最优解优于全局最优解
// 那么领域最优解替换全局最优解
bestT = t;
bestSequence = LocalSequence.clone();
bestSolution = evaluate(bestSequence);
System.out.println("找到更优解: t = " + t + " , " + bestSolution.getRate());
}
sequence = LocalSequence.clone();
// 加入禁忌表
enterTabuList(LocalSequence);
}
}
// 返回结果
return bestSolution;
}
/**
* @param sequence 序列
* @return void
* @Description 将序列加入禁忌表
*/
public void enterTabuList(int[] sequence) {
if (l < tabuSize) {
// 如果当前禁忌表还有空位,则直接加入即可
tabuList[l] = sequence.clone();
l++;
} else {
// 如果禁忌表已经满了,则移除第一个进表的路径,添加新的路径到禁忌表末尾
// 后面的禁忌序列全部向前移动一位,覆盖掉当前第一个禁忌序列
for (int i = 0; i < tabuList.length - 1; i++) {
tabuList[i] = tabuList[i + 1].clone();
}
// 将sequence加入到禁忌队列的最后
tabuList[tabuList.length - 1] = sequence.clone();
}
}
/**
* @param sequence 序列
* @return 如序列是否存在于禁忌表中则返回true,反之返回false
* @Description 判断序列是否存在于禁忌表中
*/
public boolean isInTabuList(int[] sequence) {
int count = 0;
for (int[] ints : tabuList) {
for (int j = 0; j < ints.length; j++) {
if (sequence[j] != ints[j]) {
count++;
break;
}
}
}
return count != tabuList.length;
}
/**
* @param sequence 旧序列
* @return 新序列
* @Description 两两互换,根据旧序列生成新序列
*/
public int[] generateNewSequence(int[] sequence) {
//将 sequence 复制到 tempSequence
int[] tempSequence = sequence.clone();
// 获取两个不同的随机索引
int r1 = random.nextInt(items.length);
int r2 = random.nextInt(items.length);
while (r1 == r2) {
r2 = random.nextInt(items.length);
}
// 交换
int temp = tempSequence[r1];
tempSequence[r1] = tempSequence[r2];
tempSequence[r2] = temp;
return tempSequence;
}
/**
* @param sequence 序列
* @return 装载结果对象Solution
* @Description 评价序列的函数:传入一个序列,以该顺序的矩形集合传入天际线算法进行装载
*/
public Solution evaluate(int[] sequence) {
Item[] items = new Item[this.items.length];
for (int i = 0; i < sequence.length; i++) {
items[i] = this.items[sequence[i]];
}
return new SkyLinePacking(isRotateEnable, W, H, items).packing();
}
/**
* @param d1 双精度浮点型变量1
* @param d2 双精度浮点型变量2
* @return 返回0代表两个数相等,返回1代表前者大于后者,返回-1代表前者小于后者,
* @Description 判断两个双精度浮点型变量的大小关系
*/
private int compareDouble(double d1, double d2) {
// 定义一个误差范围,如果两个数相差小于这个误差,则认为他们是相等的 1e-06 = 0.000001
double error = 1e-06;
if (Math.abs(d1 - d2) < error) {
return 0;
} else if (d1 < d2) {
return -1;
} else if (d1 > d2) {
return 1;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("d1 = " + d1 + " , d2 = " + d2);
}
}
}
3.3 Run
/**
* @Author:WSKH
* @ClassName:Application
* @ClassType:
* @Description:运行程序的主类
* @Date:2022/11/6/19:39
* @Email:[email protected]
* @Blog:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51545953?type=blog
*/
public class Run extends javafx.application.Application {
private int counter = 0;
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
// 数据地址
String path = "src/main/java/com/wskh/data/data.txt";
// 根据txt文件获取实例对象
Instance instance = new ReadDataUtil().getInstance(path);
// 记录算法开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 实例化禁忌搜索对象
TabuSearch tabuSearch = new TabuSearch(500, 100, 50, instance, null);
// 调用禁忌搜索对象进行求解
Solution solution = tabuSearch.solve();
// 输出相关信息
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("求解用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000.0 + " s");
System.out.println("共放置了矩形" + solution.getPlaceItemList().size() + "个");
System.out.println("最佳利用率为:" + solution.getRate());
// 输出画图数据
String[] strings1 = new String[solution.getPlaceItemList().size()];
String[] strings2 = new String[solution.getPlaceItemList().size()];
for (int i = 0; i < solution.getPlaceItemList().size(); i++) {
PlaceItem placeItem = solution.getPlaceItemList().get(i);
strings1[i] = "{x:" + placeItem.getX() + ",y:" + placeItem.getY() + ",l:" + placeItem.getH() + ",w:" + placeItem.getW() + "}";
strings2[i] = placeItem.isRotate() ? "1" : "0";
}
System.out.println("data:" + Arrays.toString(strings1) + ",");
System.out.println("isRotate:" + Arrays.toString(strings2) + ",");
// --------------------------------- 后面这些都是画图相关的代码,可以不用管 ---------------------------------------------
AnchorPane pane = new AnchorPane();
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(instance.getW(), instance.getH());
pane.getChildren().add(canvas);
canvas.relocate(100, 100);
// 绘制最外层的矩形
canvas = draw(canvas, 0, 0, instance.getW(), instance.getH(), true);
// 添加按钮
Button nextButton = new Button("Next +1");
Canvas finalCanvas = canvas;
nextButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
try {
PlaceItem placeItem = solution.getPlaceItemList().get(counter);
draw(finalCanvas, placeItem.getX(), placeItem.getY(), placeItem.getW(), placeItem.getH(), false);
counter++;
} catch (Exception e) {
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.WARNING);
alert.setContentText("已经没有可以放置的矩形了!");
alert.showAndWait();
}
}
});
//
pane.getChildren().add(nextButton);
primaryStage.setTitle("二维矩形装箱可视化");
primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(pane, 1000, 1000, Color.AQUA));
primaryStage.show();
}
private Canvas draw(Canvas canvas, double x, double y, double l, double w, boolean isBound) {
GraphicsContext gc = canvas.getGraphicsContext2D();
// 边框
gc.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
gc.setLineWidth(2);
gc.strokeRect(x, y, l, w);
// 填充
if (!isBound) {
gc.setFill(new Color(new Random().nextDouble(), new Random().nextDouble(), new Random().nextDouble(), new Random().nextDouble()));
} else {
gc.setFill(new Color(1, 1, 1, 1));
}
gc.fillRect(x, y, l, w);
return canvas;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
3.4 运行结果展示
输出(最后两行是在前端画图用的,可以忽略):
可以看到,通过禁忌搜索算法的迭代过程,利用率不断上升
初始解:0.9877375
找到更优解: t = 1 , 0.98985
找到更优解: t = 2 , 0.99114375
找到更优解: t = 3 , 0.9915375
找到更优解: t = 5 , 0.99273125
找到更优解: t = 80 , 0.99508125
找到更优解: t = 366 , 0.99644375
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
求解用时:4.217 s
共放置了矩形25个
最佳利用率为:0.99644375
data:[{x:0.0,y:0.0,l:116.0,w:113.0}, {x:113.0,y:0.0,l:116.0,w:99.0}, {x:212.0,y:0.0,l:116.0,w:111.0}, {x:323.0,y:0.0,l:116.0,w:20.0}, {x:343.0,y:0.0,l:89.0,w:57.0}, {x:343.0,y:89.0,l:95.0,w:57.0}, {x:0.0,y:116.0,l:100.0,w:113.0}, {x:113.0,y:116.0,l:88.0,w:99.0}, {x:212.0,y:116.0,l:79.0,w:111.0}, {x:323.0,y:116.0,l:58.0,w:20.0}, {x:332.0,y:184.0,l:42.0,w:68.0}, {x:230.0,y:195.0,l:31.0,w:102.0}, {x:113.0,y:204.0,l:71.0,w:117.0}, {x:0.0,y:216.0,l:88.0,w:113.0}, {x:230.0,y:226.0,l:81.0,w:102.0}, {x:332.0,y:226.0,l:97.0,w:68.0}, {x:113.0,y:275.0,l:29.0,w:117.0}, {x:0.0,y:304.0,l:96.0,w:98.0}, {x:98.0,y:304.0,l:96.0,w:84.0}, {x:182.0,y:304.0,l:50.0,w:48.0}, {x:230.0,y:307.0,l:53.0,w:102.0}, {x:332.0,y:323.0,l:37.0,w:68.0}, {x:182.0,y:354.0,l:46.0,w:30.0}, {x:212.0,y:360.0,l:40.0,w:106.0}, {x:318.0,y:360.0,l:40.0,w:82.0}],
isRotate:[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
可视化展示(利用率 99.64%)