阿里天池:小样本商标检测(baseline0.50)
阿里天池:小样本商标检测(baseline0.50)
在学会YOLO目标检测后第一次参加这样的比赛,特此做个记录,此处也提出一些改进的方案。比赛链接:ICME-2022 安全AI挑战者计划第九期:小样本商标检测挑战赛-天池大赛-阿里云天池 (aliyun.com)。比赛规则比较严格,首先只能使用Image 1K的预训练模型,但YOLO自身只提供基于COCO的预训练模型;且不允许使用模型融合,即使用多个模型的预测结果做并集,冲排名的话需要注意。本文需要掌握一定的yolo检测基础,具体的训练命令和检测命令省略。
数据集分析
首先比赛提供的是COCO格式的数据标注结果,初赛按理说是提供50类商品的每类50张图片,但实际只有2476张,可以参考这篇文章做数据集的分析,具体分析结果如下:
图中可以看出数据集所有图片的宽高和宽高比,大多还是以淘宝商品页的800*800为主,实现代码如下:
import os.path as osp
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import glob
root = "数据集根目录"
img_dir = osp.join(root, 'images')
img_paths = glob.glob(img_dir + '/*')
def get_img_size(img_path):
image = Image.open(img_path)
w, h = image.size
return w, h
w_list, h_list, rat_list = [], [], []
for img in img_paths:
w, h = get_img_size(img)
w_list.append(w)
h_list.append(h)
f, ax = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(16,4))
sns.histplot(w_list, ax=ax[0], palette=sns.light_palette("seagreen", as_cmap=True)).set_title('Width')
sns.histplot(h_list, ax=ax[1], palette=sns.color_palette("RdPu", 10)).set_title('Height')
sns.histplot(np.array(w_list)/np.array(h_list), ax=ax[2], palette=sns.color_palette("RdPu", 10)).set_title('W&H Ratio')
plt.show()
对于数据标注的结果分析如下,重点考察bbox的宽高比和小目标占比:
bbox 小目标(area<%3)占比 统计
+------------------------+---------------------+
| class | small object ratio |
+------------------------+---------------------+
| 冰墩墩 | 0.35398230088495575 |
| Sanyo/三洋 | 1.0 |
| Eifini/伊芙丽 | 1.0 |
| PSALTER/诗篇 | 0.9636363636363636 |
| Beaster | 0.84375 |
| ON/昂跑 | 0.9878048780487805 |
| BYREDO/柏芮朵 | 0.9568965517241379 |
| Ubras | 0.98 |
| Eternelle | 0.6326530612244898 |
| PERFECT DIARY/完美日记 | 0.8918918918918919 |
| 花西子 | 0.9897959183673469 |
| Clarins/娇韵诗 | 0.9734513274336283 |
| L'occitane/欧舒丹 | 0.9716312056737588 |
| Versace/范思哲 | 0.8235294117647058 |
| Mizuno/美津浓 | 0.7520661157024794 |
| Lining/李宁 | 0.95 |
| DOUBLE STAR/双星 | 0.5416666666666666 |
| YONEX/尤尼克斯 | 0.8475609756097561 |
| Tory Burch/汤丽柏琦 | 0.9105691056910569 |
| Gucci/古驰 | 0.9432624113475178 |
| Louis Vuitton/路易威登 | 0.9702970297029703 |
| CARTELO/卡帝乐鳄鱼 | 0.7894736842105263 |
| JORDAN | 0.828125 |
| KENZO | 0.8148148148148148 |
| UNDEFEATED | 0.8936170212765957 |
| BOY LONDON | 0.6715328467153284 |
| TREYO/雀友 | 0.9081632653061225 |
| carhartt | 0.9514563106796117 |
| 洁柔 | 0.9771241830065359 |
| Blancpain/宝珀 | 1.0 |
| GXG | 1.0 |
| 乐町 | 1.0 |
| Diadora/迪亚多纳 | 0.38271604938271603 |
| TUCANO/啄木鸟 | 0.6031746031746031 |
| Loewe | 0.9120879120879121 |
| Granite Gear | 0.9813084112149533 |
| DESCENTE/迪桑特 | 1.0 |
| OSPREY | 0.8968253968253969 |
| Swatch/斯沃琪 | 0.9466666666666667 |
| erke/鸿星尔克 | 0.8674698795180723 |
| Massimo Dutti | 0.9807692307692307 |
| PINKO | 0.8390804597701149 |
| PALLADIUM | 0.9441624365482234 |
| origins/悦木之源 | 0.9767441860465116 |
| Trendiano | 1.0 |
| 音儿 | 1.0 |
| Monster Guardians | 0.9891304347826086 |
| 敷尔佳 | 0.8620689655172413 |
| IPSA/茵芙莎 | 0.9777777777777777 |
| Schwarzkopf/施华蔻 | 0.954954954954955 |
| all | 0.8899438093392753 |
+------------------------+---------------------+
具体实现代码如下:
# refer: https://github.com/CarryHJR/LogDet/blob/master/LogDetMini/eda/eda.ipynb
import os.path as osp
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
import pandas as pd
root = "json文件所在的根目录"
json_path = osp.join(root, 'instances_train2017.json')
coco = COCO(json_path) # 此处可能会报错,需要再coco的jsonload语句下添加encoding='utf-8'
print('bbox 小目标(area<%3)占比 统计')
class_names = []
wh_ratios_cls = []
for cat_id in coco.cats:
wh_ratios = []
for ann_id in coco.getAnnIds(catIds=[cat_id]):
ann = coco.anns[ann_id]
image_id = ann['image_id']
w_ratio = ann['bbox'][2] / coco.imgs[image_id]['width']
h_ratio = ann['bbox'][3] / coco.imgs[image_id]['height']
wh_ratios.append([w_ratio, h_ratio])
wh_ratios = np.array(wh_ratios)
wh_ratios[:, -1] = wh_ratios[:, 0] * wh_ratios[:, 1]
class_names.append(coco.cats[cat_id]['name'])
wh_ratios_cls.append((wh_ratios[:,-1]<0.03).sum() / wh_ratios.shape[0]) # 此处可以调整阈值
wh_ratios = []
for _, ann in coco.anns.items():
image_id = ann['image_id']
w_ratio = ann['bbox'][2] / coco.imgs[image_id]['width']
h_ratio = ann['bbox'][3] / coco.imgs[image_id]['height']
wh_ratios.append([w_ratio, h_ratio])
wh_ratios = np.array(wh_ratios)
wh_ratios[:, -1] = wh_ratios[:, 0] * wh_ratios[:, 1]
class_names.append('all')
wh_ratios_cls.append((wh_ratios[:,-1]<0.03).sum() / wh_ratios.shape[0])
# 生成面积占比表格
from prettytable import PrettyTable
table_data = PrettyTable()
table_data.add_column('class', class_names)
table_data.add_column('small object ratio', wh_ratios_cls)
print(table_data.get_string())
# 生成宽高比例图
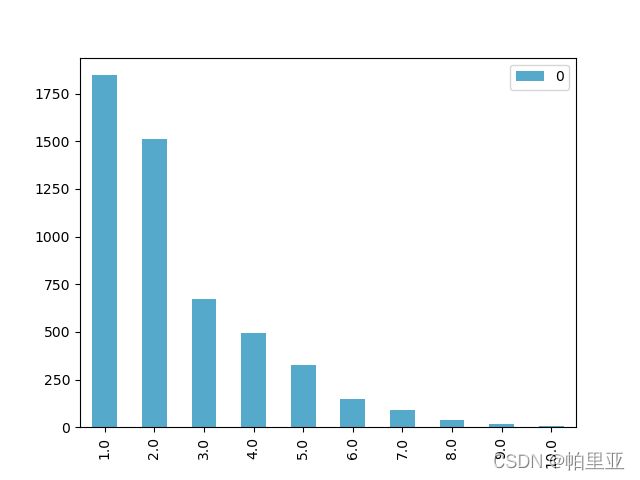
bbox_wh = [round(max(ann['bbox'][2], ann['bbox'][3]) / min(ann['bbox'][2], ann['bbox'][3]), 0) for _, ann in coco.anns.items()]
bbox_wh_unique = list(set(bbox_wh))
bbox_wh_count=[bbox_wh.count(i) for i in bbox_wh_unique]
k = 10
wh_df = pd.DataFrame(bbox_wh_count[:k], index=bbox_wh_unique[:k])
wh_df.plot(kind='bar',color="#55aacc")
plt.show()
JSON2YOLO
YOLOv5的源码对数据集的要求时txt格式,源码的团队也有写转换的方法ultralytics/JSON2YOLO: Convert JSON annotations into YOLO format. (github.com),此处我实现的代码如下:
#COCO 格式的数据集转化为 YOLO 格式的数据集
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
json_path = 'json文件的地址'
save_path = 'txt文件保存地址'
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = box[0] + box[2] / 2.0
y = box[1] + box[3] / 2.0
w = box[2]
h = box[3]
# round函数确定(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)的小数位数
x = round(x * dw, 6)
w = round(w * dw, 6)
y = round(y * dh, 6)
h = round(h * dh, 6)
return (x, y, w, h)
if __name__ == '__main__':
json_file = json_path # COCO Object Instance 类型的标注
ana_txt_save_path = save_path # 保存的路径
data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8'))
if not os.path.exists(ana_txt_save_path):
os.makedirs(ana_txt_save_path)
# 因为json文件的类别id从1开始,所以此处做了一下重映射,并将类别存入了classes.txt文件下,当然也可以不保存文件;同样的也可以不做重映射,那样类别数量为51,因为id0为空
id_map = {}
with open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'classes.txt'), 'w') as f:
for i, category in enumerate(data['categories']):
f.write(f"{category['name']}\n")
id_map[category['id']] = i
print(id_map)
for img in tqdm(data['images']):
filename = img["file_name"]
img_width = img["width"]
img_height = img["height"]
img_id = img["id"]
head, tail = os.path.splitext(filename)
ana_txt_name = head + ".txt" # 对应的txt名字,与jpg一致
f_txt = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, ana_txt_name), 'w')
for ann in data['annotations']:
if ann['image_id'] == img_id:
box = convert((img_width, img_height), ann["bbox"])
f_txt.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (id_map[ann["category_id"]], box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]))
f_txt.close()
最后提交检测结果的json文件时需要注意自己的类别id和比赛要求是否对应的上,否则会导致提交结果的成绩错误。
数据集离线增强
小样本很容易就想到了数据增强,包括但不限于添加噪点、图片的旋转平移、mosaic、copy_paste等等,yolov5本身自带了数据集的在线增强,但缺少了数据扩充,因此姑且是做了旋转的增强,且将图片按照类别名做了重命名。实现的方法代码如下:
# 需要对训练集进行增强,将train和val
import cv2
import os
import random
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy as np
root_path = "数据集根目录"
image_p = "images"
label_p = "labels"
image_path = os.path.join(root_path, image_p)
label_path = os.path.join(root_path, label_p)
# 获得对应类别的图片以及便签名
def find_same_class(label_path, id):
label = os.listdir(label_path)
result = []
for l in label:
with open(os.path.join(label_path, l), "r") as f:
temp = f.read().split(' ')
if temp[0] == id:
result.append(l.split('.')[0])
f.close()
else:
f.close()
return result
# 将文件名重新按(类别_编号)的形式命名
def change_file_name():
class_list = []
for i in tqdm(range(50)):
class_list.append(find_same_class(os.path.join(root_path, label_p), i.__str__()))
k = 0
for j in tqdm(class_list):
n = 0
for temp in j:
os.rename(os.path.join(image_path, temp + ".jpg"), os.path.join(image_path, "{}_{}.jpg".format(k, n)))
os.rename(os.path.join(label_path, temp + ".txt"), os.path.join(label_path, "{}_{}.txt".format(k, n)))
n += 1
k += 1
# 图片旋转,此处只做了90、180和270的旋转
def image_rotation(path=image_path, angle=90):
image_list = os.listdir(path)
for img in tqdm(image_list):
if img.split('_').__len__() != 2:
continue
img_p = os.path.join(path, img)
res_name = img.split('.')[0] + "_rot{}.jpg".format(angle)
temp = cv2.imread(img_p)
if angle == 90:
result = cv2.rotate(temp, cv2.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE)
elif angle == 180:
result = cv2.rotate(temp, cv2.ROTATE_180)
elif angle == 270:
result = cv2.rotate(temp, cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(path, res_name), result)
def rotation(x, y, angle):
# x, y坐标变成图片中心点,标准坐标轴
x = x - 0.5
y = -1 * (y - 0.5)
pt = np.array([x, y])
ang = np.pi * angle/180
# 设定旋转矩阵
M = np.zeros((2, 2), dtype=float)
# 设定旋转角度
alpha = np.cos(ang)
beta = np.sin(ang)
# 初始化旋转矩阵
M[0, 0] = alpha
M[1, 1] = alpha
M[0, 1] = beta
M[1, 0] = -beta
[nx, ny] = M @ pt
# 还原x, y到图片坐标系
nx = nx + 0.5
ny = -1 * ny + 0.5
return str(nx), str(ny)
# 旋转90度和270度时需要交换w和h
def switch_p(w, h):
return h, w
# 标签的坐标旋转,x、y、w、h
def label_rotation(path=label_path, angle=90):
label_list = os.listdir(path)
for lab in tqdm(label_list):
if lab.split('_').__len__() != 2:
continue
save_name = lab.split('.')[0]
with open(os.path.join(path, lab), 'r') as f:
write_label = []
label = f.readlines()
for i in label:
temp = i.split(' ')
temp[4] = temp[4].split('\n')[0]
temp[1] , temp[2] = rotation(float(temp[1]), float(temp[2]), angle)
if angle != 180:
temp[3] , temp[4] = switch_p(temp[3], temp[4])
s = str.join(' ', temp)
write_label.append(s)
with open(os.path.join(path, "{}_rot{}.txt".format(save_name, angle)), 'w') as nf:
for line in write_label:
nf.write(line+"\n")
print("{}_rot{}.txt,done".format(save_name, angle))
数据分割
由于做了数据增强,感觉yolov5的autosplit有点不够看了,很容易造成过拟合,即测试集和训练集部分重合,因此我做了一个特殊的分割,按照每类进行划分,得益于文件重命名的原因,这个方法写的非常简单。
import os
import random
from tqdm import tqdm
root_path = '数据集根目录'
image_path = os.path.join(root_path, "images")
# 单个类下的图片总数为num,weights为train和val的分割,此处偷懒将所有类别的图片均设置为50张,实际可以根据上面的find_same_class方法读取每一类的图片数量
def random_id(num=50, weights=(0.8, 0.2)):
len = num * weights[0]
num_list = []
val_list = []
while num_list.__len__() < len:
random_num = int(num * random.random())
if num_list.count(random_num) == 0:
num_list.append(random_num)
num_list.sort()
for i in range(num):
if num_list.count(i) == 0:
val_list.append(i)
return num_list, val_list
# 根据重命名的图片文件,使得样本均衡
def random_split(path=image_path, weights=(0.8, 0.2)):
train_list = []
val_list = []
for i in tqdm(range(50)):
t, v = random_id(50, weights)
for k in t:
train_list.append("{}_{}.jpg".format(i, k))
train_list.append("{}_{}_rot90.jpg".format(i, k))
train_list.append("{}_{}_rot180.jpg".format(i, k))
train_list.append("{}_{}_rot270.jpg".format(i, k))
for m in v:
val_list.append("{}_{}.jpg".format(i, m))
val_list.append("{}_{}_rot90.jpg".format(i, m))
val_list.append("{}_{}_rot180.jpg".format(i, m))
val_list.append("{}_{}_rot270.jpg".format(i, m))
txt = ['train.txt', 'val.txt']
with open(os.path.join(root_path, txt[0]), 'w') as f:
for n in range(train_list.__len__()):
f.write('./images/{}\n'.format(train_list[n])) # add image to txt file
with open(os.path.join(root_path, txt[1]), 'w') as f:
for n in range(val_list.__len__()):
f.write('./images/{}\n'.format(val_list[n])) # add image to txt file
模型训练
YOLO源码需要编写一个yaml文件指向数据集,文件内容如下:
train: E:\Document\tianchi\dataset\ali_train\train\train.txt # train images
val: E:\Document\tianchi\dataset\ali_train\train\val.txt # val images
nc: 50 # number of classes 如果没有做重映射,即id从1开始的话,nc=51,在names前加一个空类''
names: ['冰墩墩', 'Sanyo/三洋', 'Eifini/伊芙丽', 'PSALTER/诗篇', 'Beaster', 'ON/昂跑', 'BYREDO/柏芮朵',
'Ubras', 'Eternelle', 'PERFECT DIARY/完美日记', '花西子', 'Clarins/娇韵诗', "L'occitane/欧舒丹",
'Versace/范思哲', 'Mizuno/美津浓', 'Lining/李宁', 'DOUBLE STAR/双星', 'YONEX/尤尼克斯', 'Tory Burch/汤丽柏琦',
'Gucci/古驰', 'Louis Vuitton/路易威登', 'CARTELO/卡帝乐鳄鱼', 'JORDAN', 'KENZO', 'UNDEFEATED',
'BOY LONDON', 'TREYO/雀友', 'carhartt', '洁柔', 'Blancpain/宝珀', 'GXG', '乐町', 'Diadora/迪亚多纳',
'TUCANO/啄木鸟', 'Loewe', 'Granite Gear', 'DESCENTE/迪桑特', 'OSPREY', 'Swatch/斯沃琪', 'erke/鸿星尔克',
'Massimo Dutti', 'PINKO', 'PALLADIUM', 'origins/悦木之源', 'Trendiano', '音儿', 'Monster Guardians',
'敷尔佳', 'IPSA/茵芙莎', 'Schwarzkopf/施华蔻'] # class names
做完上述内容后,就可以进行YOLOv5模型的训练了,本文使用了YOLOv5s和YOLOv5m6两种,优点是官方都提供了基于COCO的预训练模型,且yolov5m6设计了4个检测框,理论上会有一定的提升,实验结果也确实如此。本文使用官方的yolov5m6作为baseline,本地测试mAP为0.56,线上测试mAP为0.50,而yolov5s的线上成绩只有0.48。
更进一步的改进可以参考对于小目标检测的遥感方向的目标检测方案,如TPH-YOLO在检测头上引入了Transformer增强,还有YOLO-Z使用了Bi-FPN等,但由于没有预训练模型,因此直接训练的效果可能会不及yolov5m6。由于这次比赛不考虑检测时间,因此应该是Transformer大放异彩的时刻,此外RCNN的效果应该也会更好。
结果提交
比赛是提交json文件进行考核,使用val.py自带的save-json方法生成即可,但需要对图片的id进行重映射。参考官方的提交规范可知,image-id需要从测试集的json文件中读取,本文直接采取暴力的重命名方法,重映射的方法如下:
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
json_path = 'json文件路径'
img_path = '测试集图片根目录'
if __name__ == '__main__':
json_file = json_path
data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8'))
id_map = {} # id和图片的映射
for category in enumerate(data['images']):
file_name = category[1]['file_name']
id = category[1]['id']
id_map[id] = file_name
# 对图片进行重命名
for i in id_map:
img_path = os.path.join(img_path, id_map[i])
output_path = os.path.join(img_path, "{}.jpg".format(i))
os.rename(img_path, output_path)
此外还需要准备一个yaml指向测试集图片,即更改yaml文件下的val地址,这样就可以使用val.py直接进行结果的生成了。需要注意的是如果做了重映射会导致类别id对应不上,需要对val.py下的save_one_json方法进行修改,保证检测结果的有效性。
def save_one_json(predn, jdict, path, class_map):
# Save one JSON result {"image_id": 42, "category_id": 18, "bbox": [258.15, 41.29, 348.26, 243.78], "score": 0.236}
image_id = int(path.stem) if path.stem.isnumeric() else path.stem
box = xyxy2xywh(predn[:, :4]) # xywh
box[:, :2] -= box[:, 2:] / 2 # xy center to top-left corner
for p, b in zip(predn.tolist(), box.tolist()):
jdict.append({'image_id': image_id,
'category_id': class_map[int(p[5])+1], # 如果做了重映射id编号为0-49,但实际结果需求是1-50,因此让id+1即可。
'bbox': [round(x, 3) for x in b],
'score': round(p[4], 5)})
总结
本次比赛算是一次对于之前学习成果的检验,并发现自身的不足。受限于算力不足,许多网络模型甚至没有办法运行,采用大的网络则需要减少batch的大小,十分影响效率和结果,且本文是基于yolov5源码做的比赛,实在是费劲,且只能做消融实验,确实有些不够用了。这里推荐学习官方使用的mmdetection,不仅可以直接使用RCNN、SDD等网络进行检测,修改特征提取的主干网络也比较容易,后续我也会对学习mmdetection做出自己的总结。