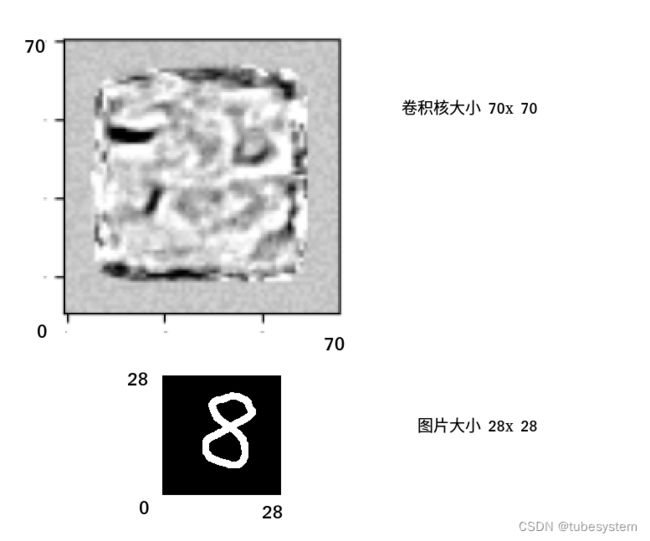
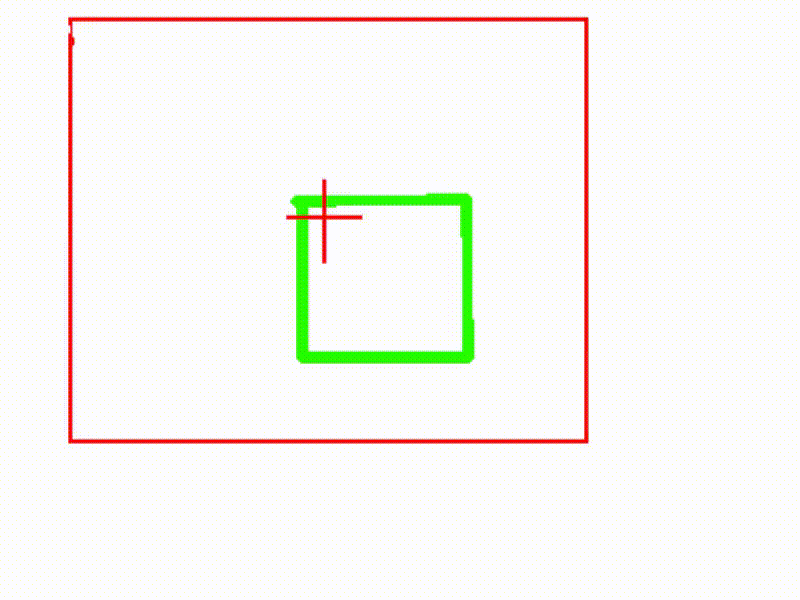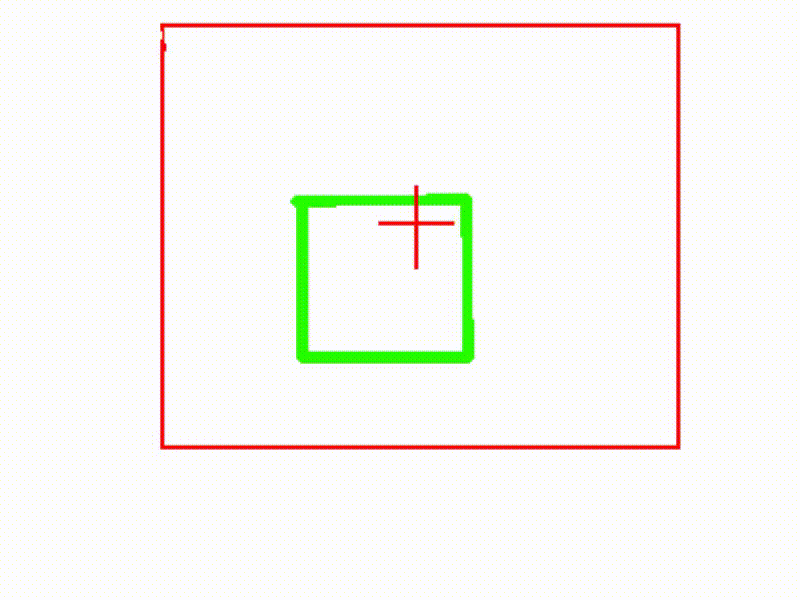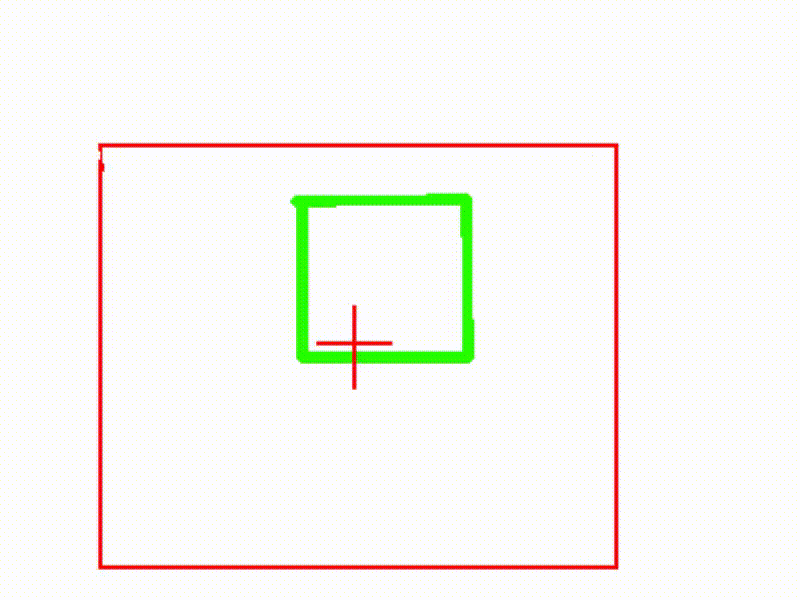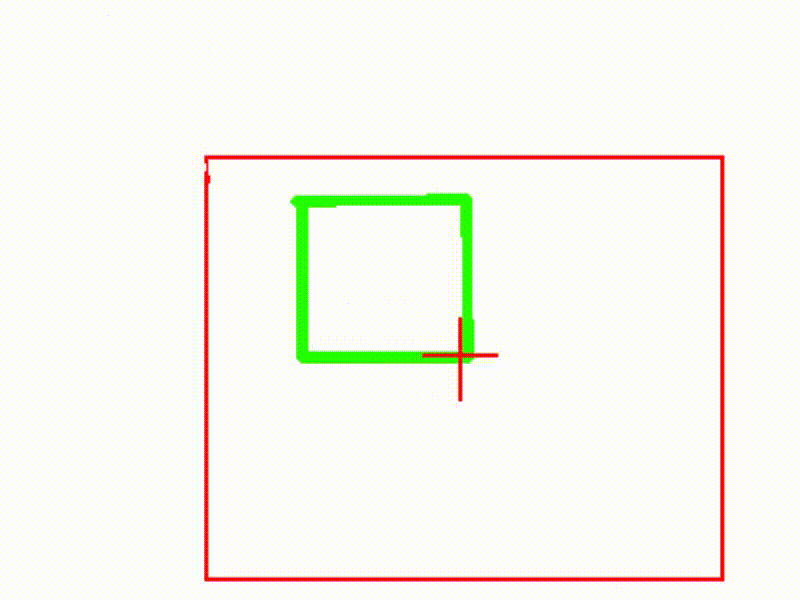
当卷积核比图片还大会发生什么?
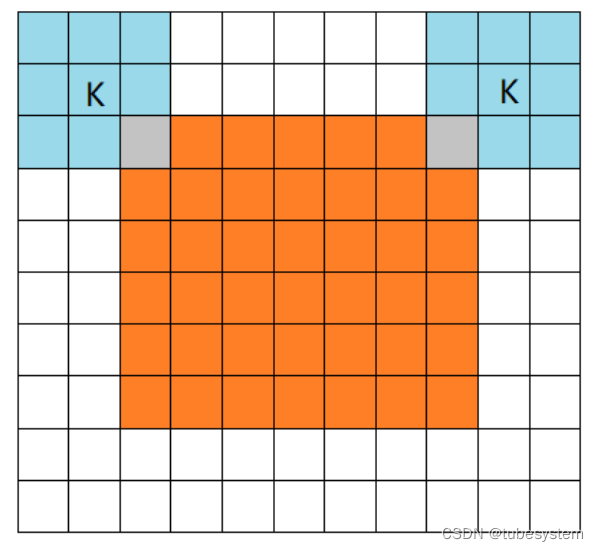
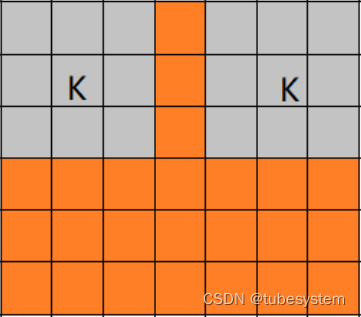
一句话答案, 卷积核里的边长大于2倍图片的部分参数空间会被浪费, 卷积核边沿参数不会更新,保持初始随机状态.就像下图中四周的灰色区域.
如果更夸张一些, 用100x 100的卷积核去卷28x28 的图片会发生下面的情形:
可以看到图像的灰色边缘扩大了,
解释一下过程
首先, fit 函数的padding参数--same,也就是补充边界,让卷积后的图片大小与卷积前的相同
其次, 卷积核的中心点与图片的左上角重合,并从左上角开始 逐行 ,逐点 做卷积. 因为卷积核太大,有一部分卷积核始终无法与图片进行重叠, 所以也不能进行参数调整,于是保持了随机噪音(灰色)
视觉化一下就是
卷积的3种模式:
full,
same,
valid
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D 属性 padding的2种模式
same,
valid
本文使用的时same. 如果使用alid,因为卷积核大于图片,会报错.
from 卷积的三种模式:full, same, valid_ _
full:
same:
valid:
# todo 测试 数组转图片,然后画图的输入范围,是否能自动map数值的上下限,是否对负数自动变为正数
# todo 用2层卷积核,拟合数据, 然后在训练完成并训练结果较好的时候, 将2层卷积核相乘,看看每一种可能性 ,看看能不能看到 1-9-0 十个数字
# todo 加入部件 输出gif 或者mp4
# todo 加入部件,看卷积核与fc层连接的权重
# todo 卷积核的初始化很重要, 看到20x20的卷积核虽然测试及表现良好,但是学习的花纹有些看不懂,也许学习的很正确,但是人类看不懂. 希望构造部件学习到类似条纹的卷积核 另外,看到20个epochs 后,花纹基本不变, 不过从初始化到第一步看不到. todo 加入部件,看最初的初始化.
# todo 如何解包, 而不是将一堆小文件存储在文件夹里 --切片??
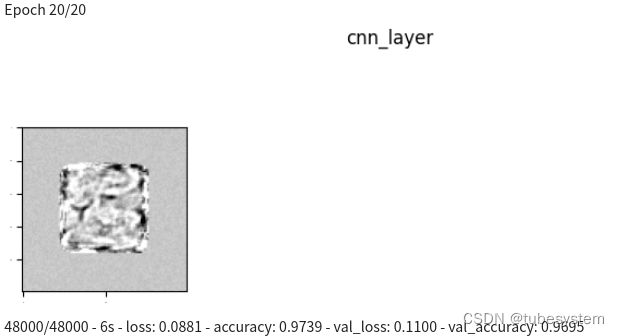
# 终于提取到卷积核的数据, 并且用图片形式表示出来(每个epoch 只画一个卷积核 ) , 并且画出全部卷积核
# https://blog.csdn.net/gaotihong/article/details/80983937 ---Python-matplotlib画图
# 控制 logs: [ p.terminate() for p in processes if p.is_alive()]
# 在model.Sequential. 里面 找卷积核数值
# xxxx 卷积核的位置从 print(model.summary()) 可以获知, 每次运行 卷积核的序列号加2
# 可以用命名的方式,指定每层的名称。 from https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras/sequential_model
# (因为每个层都是一个类,所以返回的层本质上是一个类)
#导入模块
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import LambdaCallback
from PIL import Image
################################################################
# 没有gpu的计算机不需要本段
# 这一段的作用是在用gpu计算时,debug gpu内存报错 UnknownError: Failed to get convolution algorithm.
# This is probably because cuDNN failed to initialize, so try looking to see if a warning log message was printed above.
# [[node sequential/cnn_layer/Conv2D (defined at tmp/ipykernel_13733/2736373417.py:104) ]] [Op:__inference_distributed_function_799]
from tensorflow.compat.v1.keras.backend import set_session
config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
sess=tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config)
set_session(sess)
tf.keras.backend.clear_session() #清理session
###############################################################
#导入数据集
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
#数据预处理
#Reshape
x_train4D = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],28,28,1).astype('float32')
x_test4D = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],28,28,1).astype('float32')
#像素标准化
x_train, x_test = x_train4D / 255.0, x_test4D / 255.0
#模型搭建
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=1 , kernel_size=(50,50), padding='same',input_shape=(28,28,1), activation='relu',name="cnn_layer"), # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<卷积核大小 数量
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(), # 卷积层输出二维数据,而全连接层接收一维数据,faltten降维数据
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10,activation='softmax')
])
#打印模型
print(model.summary()) # print 模型
#训练配置
model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
#开始训练
class plot_kernel(keras.callbacks.Callback): # 定义class
"""
def on_train_begin(self, logs={}):
self.losses = []
"""
def on_epoch_end(self, batch, logs={}):
#img = Image.fromarray(model.get_layer(name="cnn_layer").kernel.numpy ()[:, :, :, :])
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 9)) #设置窗口大小
plt.suptitle('cnn_layer') # 图片名称
for i in range(0,1 ): #<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< 绘图 ,设定卷积核个数
img = Image.fromarray(model.get_layer(name="cnn_layer").kernel.numpy ()[:,:,0,i] *500+200 )
plt.subplot(4,4, (i+1) )
plt.title(' ')
plt.imshow(img)
#plt.axis('off') # plt.imshow(gray,cmap='gray'), plt.axis('off') #这里显示灰度图要加cmap
plt.xticks(fontsize=0)
plt.yticks(fontsize=0)
plt.show()
pltKernel = plot_kernel() # class 实例化
model.fit(
x=x_train, y=y_train,
callbacks=[pltKernel],
validation_split=0.2,
epochs=20 , batch_size=300, verbose=2) # verbose = 2 为每个epoch输出一行记录 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<,<<< epochs
#print("model.get_layer(index=0).output_shape============", model.get_layer(index=0).output_shape) # 这个是第一层(cnn)的输出图片.维度
print("model.cnn_layer.kernel=============", model.get_layer(name="cnn_layer").kernel)
print("model.cnn_layer.kernel.shape=========", model.get_layer(name="cnn_layer").kernel.shape) # 这个是第一层 卷积核图片.维度
# callbacks