【定时任务】SpringBoot多线程并发动态执行定时任务
通过读取数据库的方式来进行定时任务信息获取,再通过多线程进行并发动态执行!
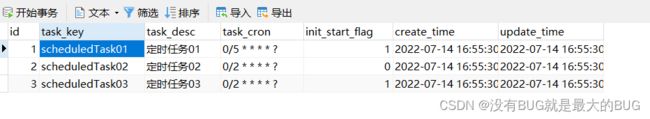
一、创建业务表
CREATE TABLE `scheduled_task` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`task_key` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '任务key值(使用bean名称)',
`task_desc` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '任务描述',
`task_cron` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '任务表达式',
`init_start_flag` int(2) DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '程序初始化是否启动 1 是 0 否',
`create_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uniqu_task_key` (`task_key`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=101 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;二、插入数据
INSERT INTO `scheduled_task`(`id`, `task_key`, `task_desc`, `task_cron`, `init_start_flag`, `create_time`, `update_time`) VALUES (1, 'scheduledTask01', '定时任务01', '0/5 * * * * ?', 1, NOW(), NOW());
INSERT INTO `scheduled_task`(`id`, `task_key`, `task_desc`, `task_cron`, `init_start_flag`, `create_time`, `update_time`) VALUES (2, 'scheduledTask02', '定时任务02', '0/2 * * * * ?', 0, NOW(), NOW());
INSERT INTO `scheduled_task`(`id`, `task_key`, `task_desc`, `task_cron`, `init_start_flag`, `create_time`, `update_time`) VALUES (3, 'scheduledTask03', '定时任务03', '0/2 * * * * ?', 1, NOW(), NOW());
三、SpringBoot启动类添加相应注解
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
/**
* @author lzw
* @create 2022-07-14-9:30
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
@MapperScan("cn.sdata.mapper")
public class SpringBootController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootController.class,args);
}
}
四、定时任务执行核心实现类
import cn.sdata.entity.LogTask;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.config.CronTask;
import org.springframework.scheduling.config.ScheduledTaskRegistrar;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
@Component
public class ScheduledTask implements SchedulingConfigurer {
private static volatile ScheduledTaskRegistrar registrar;
private static volatile ConcurrentHashMap> scheduledFutures = new ConcurrentHashMap>();
private static volatile ConcurrentHashMap cronTasks = new ConcurrentHashMap();
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar registrar) {
//设置20个线程,默认单线程
registrar.setScheduler(Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(20));
this.registrar = registrar;
}
public void refresh(List tasks){
//取消已经删除的策略任务
Set sids = scheduledFutures.keySet();
for (Integer sid : sids) {
if(!exists(tasks, sid)){
scheduledFutures.get(sid).cancel(false);
}
}
for (LogTask logTask : tasks) {
// ScheduledTaskRunnable t = new ScheduledTaskRunnable(logTask.getTask_id(), logTask.getRule_db_id());
String expression = logTask.getExpression();
//计划任务表达式为空则跳过
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(expression)){
continue;
}
//计划任务已存在并且表达式未发生变化则跳过
if(scheduledFutures.containsKey(logTask.getTask_id()) && cronTasks.get(logTask.getTask_id()).getExpression().equals(expression)){
continue;
}
//如果策略执行时间发生了变化,则取消当前策略的任务
if(scheduledFutures.containsKey(logTask.getTask_id())){
scheduledFutures.get(logTask.getTask_id()).cancel(false);
scheduledFutures.remove(logTask.getTask_id());
cronTasks.remove(logTask.getTask_id());
}
CronTask task = new CronTask(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//每个计划任务实际需要执行的具体业务逻辑
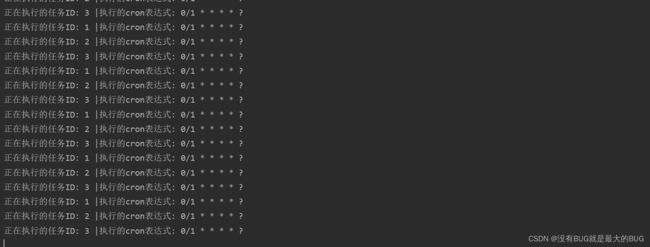
System.out.println("正在执行的任务ID: "+logTask.getTask_id()+" |执行的cron表达式: "+logTask.getExpression());
}
}, expression);
ScheduledFuture future = registrar.getScheduler().schedule(task.getRunnable(), task.getTrigger());
cronTasks.put(logTask.getTask_id(), task);
scheduledFutures.put(logTask.getTask_id(), future);
}
}
private boolean exists(List tasks, Integer tid){
for(LogTask logTask:tasks){
if(logTask.getTask_id() == tid){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
registrar.destroy();
}
} 五、定时任务相关实体类(可以根据实际业务场景进行字段添加)
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class LogTask {
private int task_id;
private String expression;
}六、进行Controller层代码编写(Service层和Mapper层代码可自己实现)
import cn.sdata.config.ScheduledTask;
import cn.sdata.entity.LogTask;
import cn.sdata.entity.Scheduled;
import cn.sdata.service.ScheduledTaskService;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.config.ScheduledTaskRegistrar;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author lzw
* @create 2022-07-14-9:35
* 定时任务相关
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("cron")
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CronController {
private final ScheduledTaskService scheduledTaskService;
@GetMapping("cron")
public void cron(){
//创建一个任务的容器
List logTasks = new ArrayList<>();
//读取数据库中的任务信息为LogTask字段进行赋值并添加进容器中
List list = scheduledTaskService.findAll();
for (Scheduled scheduled : list) {
LogTask logTask = new LogTask();
logTask.setTask_id(scheduled.getId());
logTask.setExpression(scheduled.getTaskCron());
logTasks.add(logTask);
}
//创建一个任务线程池与任务的逻辑连接纽带
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
//调用configureTasks()方法传入ScheduledTask
scheduledTask.configureTasks(new ScheduledTaskRegistrar());
//调用refresh()方法传入任务数据
scheduledTask.refresh(logTasks);
}
}
七、启动程序调用cron方法
定时任务正在并发执行
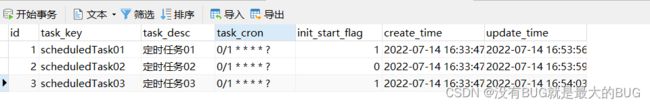
八、修改数据库中的cron数据并再次调用cron方法
当数据库中定时任务信息发生变更时可根据自己的业务场景再次调用refresh()方法
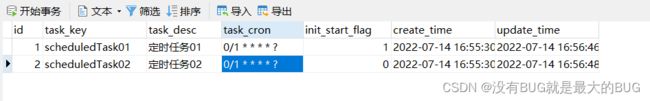
九、删除数据库中的一条cron数据并再次调用cron方法
动态多线程执行定时任务成功,并且极其灵活!