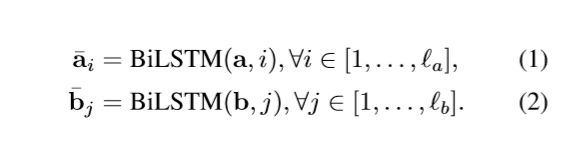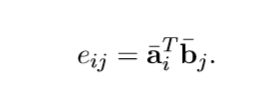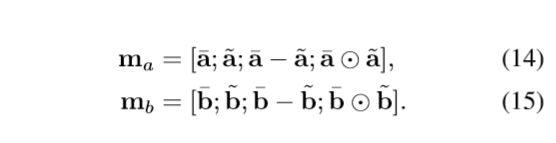《Enhanced LSTM for Natural Language Inference》论文总结
ESIM,简称 “Enhanced LSTM for Natural Language Inference“。顾名思义,一种专为自然语言推断而生的加强版 LSTM。至于它是如何加强 LSTM,请继续往下看:
Unlike the previous top models that use very complicated network architectures, we first demonstrate that carefully designing sequential inference models based on chain LSTMs can outperform all previous models.Based on this, we further show that by explicitly considering recursive architectures in both local inference modeling and inference composition,we achieve additional improvement.
上面一段话我摘选自ESIM论文的摘要,总结来说,ESIM 能比其他短文本分类算法牛逼主要在于两点:
- 精细的设计序列式的推断结构。
- 考虑局部推断和全局推断。
作者主要是用句子间的注意力机制(intra-sentence attention),来实现局部的推断,进一步实现全局的推断。
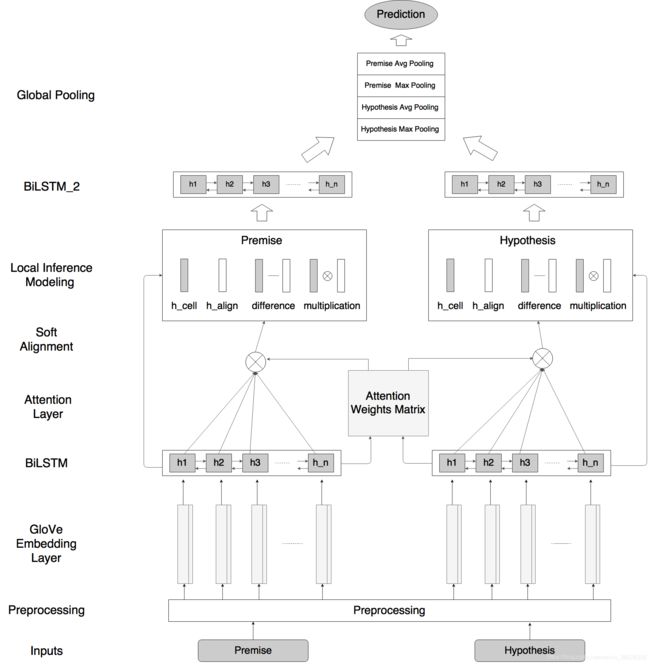
ESIM主要分为三部分:input encoding,local inference modeling 和 inference composition。如下图所示,ESIM 是左边一部分。
input encoding
没啥可说的,就是输入两句话分别接 embeding + BiLSTM。这里为什么不用最近流行的 BiGRU,作者解释是实验效果不好。这里作者也额外提了一句,如果可以做句子的语法分析的话,那么也可以 使用 TreeLSTM,原始的 ESIM 没有这一部分。
使用 BiLSTM 可以学习如何表示一句话中的 word 和它上下文的关系,我们也可以理解成这是 在 word embedding 之后,在当前的语境下重新编码,得到新的 embeding 向量。这部分的代码如下,比较直观。
def forward(self, *input):
# batch_size * seq_len
sent1, sent2 = input[0], input[1]
mask1, mask2 = sent1.eq(0), sent2.eq(0)
# embeds: batch_size * seq_len => batch_size * seq_len * embeds_dim
x1 = self.bn_embeds(self.embeds(sent1).transpose(1, 2).contiguous()).transpose(1, 2)
x2 = self.bn_embeds(self.embeds(sent2).transpose(1, 2).contiguous()).transpose(1, 2)
# batch_size * seq_len * embeds_dim => batch_size * seq_len * hidden_size
o1, _ = self.lstm1(x1)
o2, _ = self.lstm1(x2) local inference modeling
local inference 之前需要将两句话进行 alignment,这里是使用 soft_align_attention。
怎么做呢,首先计算两个句子 word 之间的相似度,得到2维的相似度矩阵,这里会用到 torch.matmul。
然后才进行两句话的 local inference。用之前得到的相似度矩阵,结合 a,b 两句话,互相生成彼此相似性加权后的句子,维度保持不变。这里有点绕,用下面的代码解释吧。
在 local inference 之后,进行 Enhancement of local inference information。这里的 enhancement 就是计算 a 和 align 之后的 a 的差和点积, 体现了一种差异性吧,更利于后面的学习。
def soft_align_attention(self, x1, x2, mask1, mask2):
'''
x1: batch_size * seq_len * hidden_size
x2: batch_size * seq_len * hidden_size
'''
# attention: batch_size * seq_len * seq_len
attention = torch.matmul(x1, x2.transpose(1, 2))
mask1 = mask1.float().masked_fill_(mask1, float('-inf'))
mask2 = mask2.float().masked_fill_(mask2, float('-inf'))
# weight: batch_size * seq_len * seq_len
weight1 = F.softmax(attention + mask2.unsqueeze(1), dim=-1)
x1_align = torch.matmul(weight1, x2)
weight2 = F.softmax(attention.transpose(1, 2) + mask1.unsqueeze(1), dim=-1)
x2_align = torch.matmul(weight2, x1)
# x_align: batch_size * seq_len * hidden_size
return x1_align, x2_align
def submul(self, x1, x2):
mul = x1 * x2
sub = x1 - x2
return torch.cat([sub, mul], -1)
def forward(self, *input):
···
# Attention
# output: batch_size * seq_len * hidden_size
q1_align, q2_align = self.soft_align_attention(o1, o2, mask1, mask2)
# Enhancement of local inference information
# batch_size * seq_len * (8 * hidden_size)
q1_combined = torch.cat([o1, q1_align, self.submul(o1, q1_align)], -1)
q2_combined = torch.cat([o2, q2_align, self.submul(o2, q2_align)], -1)
...inference composition
最后一步了,比较简单。
再一次用 BiLSTM 提前上下文信息,同时使用 MaxPooling 和 AvgPooling 进行池化操作, 最后接一个全连接层。这里倒是比较传统。没啥可说的。
def apply_multiple(self, x):
# input: batch_size * seq_len * (2 * hidden_size)
p1 = F.avg_pool1d(x.transpose(1, 2), x.size(1)).squeeze(-1)
p2 = F.max_pool1d(x.transpose(1, 2), x.size(1)).squeeze(-1)
# output: batch_size * (4 * hidden_size)
return torch.cat([p1, p2], 1)
def forward(self, *input):
...
# inference composition
# batch_size * seq_len * (2 * hidden_size)
q1_compose, _ = self.lstm2(q1_combined)
q2_compose, _ = self.lstm2(q2_combined)
# Aggregate
# input: batch_size * seq_len * (2 * hidden_size)
# output: batch_size * (4 * hidden_size)
q1_rep = self.apply_multiple(q1_compose)
q2_rep = self.apply_multiple(q2_compose)
# Classifier
x = torch.cat([q1_rep, q2_rep], -1)
sim = self.fc(x)
return sim
思考
为啥 ESIM 效果会这么好呢?这里我提几个自己的想法,我觉得 ESIM 牛逼在它的 inter-sentence attention,就是上面代码中的 soft_align_attention,这一步中让要比较的两句话产生了交互。以前我见到的类似 Siamese 网络的结构,往往中间都没有交互,只是在最后一层求个余弦距离或者其他距离。
最后放一张细节图
参考文献: Enhanced LSTM for Natural Language Inference