轻量级实时语义分割:ENet & ERFNet
ENet: A Deep Neural Network Architecture for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation 发表在CVPR2016。
ERFNet: Efficient Residual Factorized ConvNet for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation 发表在2018年1月的IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems。
两者任务均为轻量级实时性语义分割。ENet和ERFNet在实时性语义分割算法中算是早期比较优秀的算法。 在Cityscapes数据集上,ENet的IoU达到了58.3,而ERFNet的IoU则达到了69.7,精度提升10个点。参数方面,根据RRFNet里的实验数据,ERFNet的参数量比ENet大十倍,速度方面是ENet的将近一半。 总的来说,虽然ERFNet参数量较大,运行较慢,但精度也提升大,实时性和精度确实都在可接受的范围。两篇论文都在Resnet基础上进行了改进,比较值得注意的是ERFNet中ResNet的Low-rank approximation的操作,后面经常会使用到。
一、Enet网络结构及代码实现
1. 网络特点【0】
1、Feature map resolution:
语义分割中的图像下采样有两个主要缺点:一是降低特征图的分辨率意味着丢失精确边缘形状等空间信息;二是全像素分割要求输出与输入具有相同的分辨率。这意味着进行了多少次下采样将需要同样次数的上采样,这将增加模型尺寸和计算成本。第一个问题在FCN中通过编码器生成的特征映射之间的add得到了解决(FPN),在SegNet中通过保存在max pooling层中选择的元素的索引,并使用它们在解码器中生成稀疏的上采样映射得到了解决。作者遵循SegNet方法,因为它减少了对内存需求。尽管如此,还是发现下采样会损害准确性,需要尽可能的限制下采样。当然,下采样能够扩大感受野,学习到更多的上下文特征用于逐像素的分类。
2、Early downsampling:
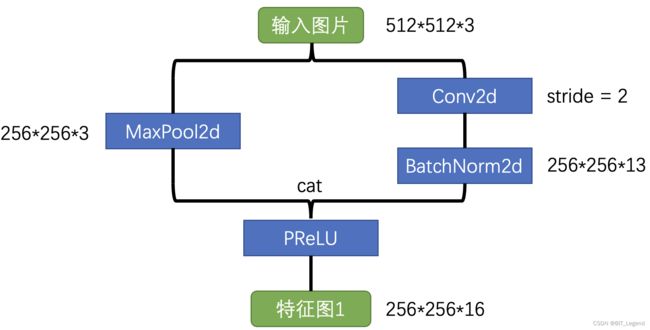
高分辨率的输入会耗费大量计算资源,ENet的初始化模块会大大减少输入图像的大小,并且只使用了少量的feature maps,初始化模块充当良好的特性提取器,并且只对网络稍后部分的输入进行预处理。
3、Decoder size:
ENet的Encoder和Decoder不对称,由一个较大的Encoder和一个较小的Decoder组成,作者认为Encoder和分类模型相似,主要进行特征信息的处理和过滤,而decoder主要是对encoder的输出做上采样,对细节做细微调。
4、Nonlinear operations:
作者发现ENet上使用ReLU却降低了精度。相反,删除网络初始层中的大多数ReLU可以改善结果。用PReLU替换了网络中的所有ReLU,对每个特征映射PReLU有一个附加参数,目的是学习非线性的负斜率。
5、Information-preserving dimensionality changes:
选择在使用步长2的卷积的同时并行执行池化操作,并将得到的特征图拼接(concatenate)起来。这种技术可以将初始块的推理时间提高10倍。此外,在原始ResNet架构中发现了一个问题。下采样时,卷积分支中的第一个1×1卷积在两个维度上以2的步长滑动,直接丢弃了75%的输入。而ENet将卷积核的大小增加到了2×2,这样可以让整个输入都参与下采样,从而提高信息流和精度。虽然这使得这些层的计算成本增加了4倍,但是在ENET中这些层的数量很少,开销并不明显。
6、Factorizing filters:
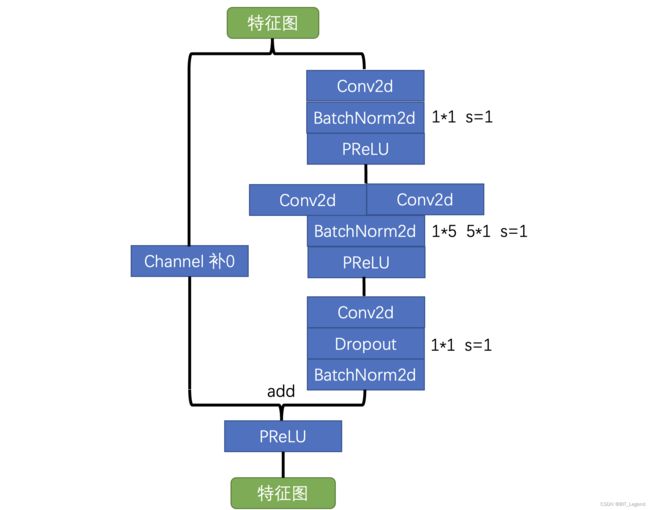
卷积权重存在大量冗余,并且每个n x n卷积可以分解成一个n x 1滤波和一个1 x n滤波,称为非对称卷积。本文采用n = 5的非对称卷积,它的操作相当于一个5 x 5的卷积,增加了模块的学习能力并增加了感受野,更重要的是,在瓶颈模块中使用的一系列操作(投影、卷积、投影)可以被视为将一个大卷积层分解为一系列更小和更简单的操作,即其低阶近似。这样的因子分解可以极大地减少参数的数量,从而减少冗余。此外,由于在层之间插入的非线性操作,特征也变得更丰富了。
7、Dilated convolutions:
大的感受野对分割任务也是非常重要的,可以参考更多的上下文特征对像素进行分类,为了避免对特征图进行过度的下采样,使用空洞卷积,在最小分辨率下运行的阶段中,几个瓶颈模块内的主要卷积层都使用了空洞卷积。在没有增加额外计算开销的情况下,便提高了准确度。当作者将空洞卷积与其他bottleneck(常规和非对称卷积)交织时,即不是按顺序排列它们,获得了最佳效果。
8、Regularization:
为了防止过拟合,把Spatial Dropout放在卷积分支的末端,就在加法之前
2. 网络结构和代码
整个网络模型由下面5种block,分别组成encoder和decoder,进而组成整个模型,encoder包含3个子层,decoder包含2个子层,模型输入输出尺寸相同
Block1: 初始降采样模块
class InitialBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__ (self, in_channels=3, out_channels=13):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.batchnorm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)
self.prelu = nn.PReLU(16)
def forward(self, x):
main = self.conv(x)
main = self.batchnorm(main)
side = self.maxpool(x)
x = torch.cat((main, side), dim=1)
x = self.prelu(x)
return xBlock2: 通用降采样模块 + Block3: 通用特征提取模块
class RDDNeck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dilation, in_channels, out_channels, down_flag, relu=False, projection_ratio=4, p=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.dilation = dilation # 孔洞卷积size
self.down_flag = down_flag # 降采样标识
if down_flag:
self.stride = 2
self.reduced_depth = int(in_channels // projection_ratio)
else:
self.stride = 1
self.reduced_depth = int(out_channels // projection_ratio)
if relu:
activation = nn.ReLU()
else:
activation = nn.PReLU()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, return_indices=True)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False, dilation=1)
self.batchnorm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu1 = activation
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=3, stride=self.stride, padding=self.dilation, bias=False, dilation=self.dilation)
self.batchnorm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu2 = activation
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0,bias=False, dilation=1)
self.batchnorm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=p)
self.prelu3 = activation
def forward(self, x):
bs = x.size()[0]
x_copy = x
# Side Branch
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.batchnorm1(x)
x = self.prelu1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.batchnorm2(x)
x = self.prelu2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.batchnorm3(x)
x = self.dropout(x) # dropout是解决过拟合的,maxpool不会导致过拟合,所以dropout加在side branch
# Main Branch
if self.down_flag: # indice是下采样的索引,可用于后面的上采样
x_copy, indices = self.maxpool(x_copy)
if self.in_channels != self.out_channels:
out_shape = self.out_channels - self.in_channels
extras = torch.zeros((bs, out_shape, x.shape[2], x.shape[3]))
if torch.cuda.is_available():
extras = extras.cuda()
x_copy = torch.cat((x_copy, extras), dim = 1)
# Sum of main and side branches
x = x + x_copy
x = self.prelu3(x)
if self.down_flag:
return x, indices
else:
return xBlock4: 特殊特征提取模块,采用空间可分离卷积 5*5 -> 1*5 and 5*1
class ASNeck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, projection_ratio=4):
super().__init__()
# Define class variables
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.reduced_depth = int(in_channels / projection_ratio)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.batchnorm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu1 = nn.PReLU()
self.conv21 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=(1, 5), stride=1, padding=(0, 2), bias=False)
self.conv22 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=(5, 1), stride=1, padding=(2, 0), bias=False)
self.batchnorm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu2 = nn.PReLU()
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=0.1)
self.batchnorm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels)
self.prelu3 = nn.PReLU()
def forward(self, x):
bs = x.size()[0]
x_copy = x
# Side Branch
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.batchnorm1(x)
x = self.prelu1(x)
x = self.conv21(x)
x = self.conv22(x)
x = self.batchnorm2(x)
x = self.prelu2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.batchnorm3(x)
# Main Branch
if self.in_channels != self.out_channels:
out_shape = self.out_channels - self.in_channels
extras = torch.zeros((bs, out_shape, x.shape[2], x.shape[3]))
if torch.cuda.is_available():
extras = extras.cuda()
x_copy = torch.cat((x_copy, extras), dim = 1)
# Sum of main and side branches
x = x + x_copy
x = self.prelu3(x)
return xBlock5: 上采样模块
class UBNeck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, relu=False, projection_ratio=4):
super().__init__()
# Define class variables
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.reduced_depth = int(in_channels / projection_ratio)
if relu:
activation = nn.ReLU()
else:
activation = nn.PReLU()
self.main_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.out_channels, kernel_size=1)
# self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.unpool = nn.MaxUnpool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 上采样模块,与下采样模块匹配,其中上下采样位置保持一致
self.convt1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.batchnorm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu1 = activation
self.convt2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.reduced_depth, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, output_padding=1, bias=False)
self.batchnorm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.reduced_depth)
self.prelu2 = activation
self.convt3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=self.reduced_depth, out_channels=self.out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.batchnorm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=0.1)
self.prelu3 = activation
def forward(self, x, indices):
x_copy = x
# Side Branch
x = self.convt1(x)
x = self.batchnorm1(x)
x = self.prelu1(x)
x = self.convt2(x)
x = self.batchnorm2(x)
x = self.prelu2(x)
x = self.convt3(x)
x = self.batchnorm3(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
# Main Branch
x_copy = self.main_conv(x_copy)
# x_copy = self.up(x_copy)
x_copy = self.unpool(x_copy, indices, output_size=x.size())
# Concat
x = x + x_copy
x = self.prelu3(x)
return x整个模型结构
class ENet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes):
super().__init__()
self.cla = classes
# The initial block
self.init = InitialBlock()
# 编码器
# The first bottleneck
self.b10 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=16, out_channels=64, down_flag=True, p=0.01)
self.b11 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, p=0.01)
self.b12 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, p=0.01)
self.b13 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, p=0.01)
self.b14 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, p=0.01)
# The second bottleneck
self.b20 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=128, down_flag=True)
self.b21 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b22 = RDDNeck(dilation=2, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b23 = ASNeck(in_channels=128, out_channels=128)
self.b24 = RDDNeck(dilation=4, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b25 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b26 = RDDNeck(dilation=8, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b27 = ASNeck(in_channels=128, out_channels=128)
self.b28 = RDDNeck(dilation=16, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
# The third bottleneck
self.b31 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b32 = RDDNeck(dilation=2, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b33 = ASNeck(in_channels=128, out_channels=128)
self.b34 = RDDNeck(dilation=4, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b35 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b36 = RDDNeck(dilation=8, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
self.b37 = ASNeck(in_channels=128, out_channels=128)
self.b38 = RDDNeck(dilation=16, in_channels=128, out_channels=128, down_flag=False)
# 解码器
# The fourth bottleneck
self.b40 = UBNeck(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, relu=True)
self.b41 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, relu=True)
self.b42 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=64, out_channels=64, down_flag=False, relu=True)
# The fifth bottleneck
self.b50 = UBNeck(in_channels=64, out_channels=16, relu=True)
self.b51 = RDDNeck(dilation=1, in_channels=16, out_channels=16, down_flag=False, relu=True)
# Final ConvTranspose Layer
self.fullconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=16, out_channels=self.cla, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, output_padding=1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
# The initial block
x = self.init(x) # 1/2
# The first bottleneck
x, i1 = self.b10(x) # 1/4
x = self.b11(x)
x = self.b12(x)
x = self.b13(x)
x = self.b14(x)
# The second bottleneck
x, i2 = self.b20(x) # 1/8
x = self.b21(x)
x = self.b22(x)
x = self.b23(x)
x = self.b24(x)
x = self.b25(x)
x = self.b26(x)
x = self.b27(x)
x = self.b28(x)
# The third bottleneck
x = self.b31(x) # 1/8
x = self.b32(x)
x = self.b33(x)
x = self.b34(x)
x = self.b35(x)
x = self.b36(x)
x = self.b37(x)
x = self.b38(x)
# The fourth bottleneck
x = self.b40(x, i2) # 1/4
x = self.b41(x)
x = self.b42(x)
# The fifth bottleneck
x = self.b50(x, i1) # 1/2
x = self.b51(x)
# The final head
out = self.fullconv(x) # 1
return out二、ERFnet网络结构及代码实现
1. 网络特点
1、 提前降低维度
这个类似于enet模型,在模型初期便连续两次降采样,尽快降低特征维度;
2、非对称的网络结构
这个类似于enet模型,在模型中encoder的尺寸大于decoder的尺寸;
3、有限的下采样次数
这个类似于enet模型,只是下采样了3次;
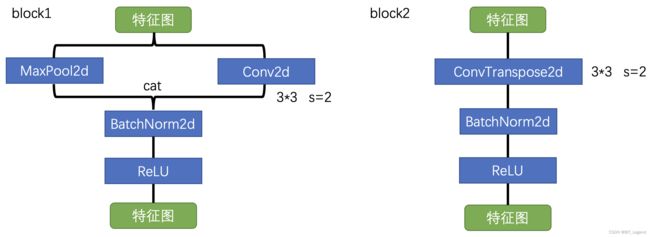
4、下采样结构采用并行结构
这个类似于enet模型,是池化和stride=2同步进行下采样;
5、上采样
这个与enet不同,采用单支的转置卷积进行上采样;
6、采用空洞卷积
2. 网络结构和代码
整个网络模型由下面3种block,分别组成encoder和decoder,进而组成整个模型,encoder包含3个子层,decoder包含3个子层,模型输入输出尺寸相同
Block1: 下采样模块 + Block2: 上采样模块
# block1: 下采样模块
class DownsamplerBlock (nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ninput, noutput):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(ninput, noutput-ninput, (3, 3), stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(noutput, eps=1e-3)
def forward(self, input):
output = torch.cat([self.conv(input), self.pool(input)], 1)
output = self.bn(output)
return F.relu(output)
# block2: 上采样模块
class UpsamplerBlock (nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ninput, noutput):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(ninput, noutput, 3, stride=2, padding=1, output_padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(noutput, eps=1e-3)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.conv(input)
output = self.bn(output)
return F.relu(output)Block3: 通用特征提取模块
# block3: 通用特征提取模块
class non_bottleneck_1d (nn.Module):
def __init__(self, chann, dropprob, dilated):
super().__init__()
self.conv3x1_1 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (3, 1), stride=1, padding=(1,0), bias=True)
self.conv1x3_1 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=(0,1), bias=True)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(chann, eps=1e-03)
self.conv3x1_2 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (3, 1), stride=1, padding=(1*dilated,0), bias=True, dilation = (dilated,1))
self.conv1x3_2 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (1, 3), stride=1, padding=(0,1*dilated), bias=True, dilation = (1,dilated))
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(chann, eps=1e-03)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(dropprob)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.conv3x1_1(input)
output = F.relu(output)
output = self.conv1x3_1(output)
output = self.bn1(output)
output = F.relu(output)
output = self.conv3x1_2(output)
output = F.relu(output)
output = self.conv1x3_2(output)
output = self.bn2(output)
if (self.dropout.p != 0):
output = self.dropout(output)
return F.relu(output+input)编码器、解码器
# 特征编码器
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super().__init__()
self.initial_block = DownsamplerBlock(3, 16) # 1/2
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
self.layers.append(DownsamplerBlock(16,64)) # 1/4
for x in range(0, 5): # 5 times
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(64, 0.03, 1))
self.layers.append(DownsamplerBlock(64, 128)) # 1/8
for x in range(0, 2): # 2 times
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(128, 0.3, 2))
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(128, 0.3, 4))
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(128, 0.3, 8))
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(128, 0.3, 16))
# Only in encoder mode:
self.output_conv = nn.Conv2d(128, num_classes, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
def forward(self, input, predict=False):
output = self.initial_block(input)
for layer in self.layers:
output = layer(output)
if predict:
output = self.output_conv(output)
return output
# 特征解码器
class Decoder (nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
self.layers.append(UpsamplerBlock(128, 64)) # 1/4
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(64, 0, 1))
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(64, 0, 1))
self.layers.append(UpsamplerBlock(64, 16)) # 1/2
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(16, 0, 1))
self.layers.append(non_bottleneck_1d(16, 0, 1))
self.layers.append(UpsamplerBlock(16, num_classes)) # 1
def forward(self, input):
output = input
for layer in self.layers:
output = layer(output)
return output
# 搭建ErfNet网络
class ERFNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(ERFNet, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(128)
self.decoder = Decoder(num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.encoder(x)
out = self.decoder(out)
return out参考:
0. 轻量级语义分割网络:ENet
1. 轻量级实时语义分割:ENet & ERFNet