场景描述
①需要实现一个定时发布系统通告的功能,如何实现? ②支付超时,订单自动取消,如何实现?
实现方式
一、挂起线程
推荐指数:★★☆ 优点: JDK原生(JUC包下)支持,无需引入新的依赖; 缺点: (1)基于内存,应用重启(或宕机)会导致任务丢失 (2)基于内存挂起线程实现延时,不支持集群 (3)代码耦合性大,不易维护 (4)一个任务就要新建一个线程绑定任务的执行,容易造成资源浪费
①配置延迟任务专用线程池
/**
* 线程池配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThreadPoolProperties.class)
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
//ThreadPoolProperties的配置依据需求和服务器配置自行配置
@Resource
private ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties;
//延迟任务队列容量
private final static int DELAY_TASK_QUEUE_CAPACITY = 100;
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor delayTaskExecutor() {
log.info("start delayTaskExecutor");
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//配置核心线程数
threadPool.setCorePoolSize(threadPoolProperties.getCorePoolSize());
//配置最大线程数
threadPool.setMaxPoolSize(threadPoolProperties.getMaxPoolSize());
//配置队列大小
threadPool.setQueueCapacity(DELAY_TASK_QUEUE_CAPACITY);
//线程最大存活时间
threadPool.setKeepAliveSeconds (threadPoolProperties.getKeepAliveSeconds());
//配置线程池中的线程的名称前缀
threadPool.setThreadNamePrefix(threadPoolProperties.getThreadNamePrefix());
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候执行的策略
threadPool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//执行初始化
threadPool.initialize();
return threadPool;
}
}
②创建延时任务
在需要执行的代码块创建延时任务
delayTaskExecutor.execute(() -> {
try {
//线程挂起指定时间
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(time);
//执行业务逻辑
doSomething();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("线程被打断,执行业务逻辑失败");
}
});
二、ScheduledExecutorService 延迟任务线程池
推荐指数:★★★ 优点: 代码简洁,JDK原生支持 缺点: (1)基于内存,应用重启(或宕机)会导致任务丢失 (2)基于内存存放任务,不支持集群 (3)一个任务就要新建一个线程绑定任务的执行,容易造成资源浪费
class Task implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId()+":"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("scheduledExecutorService====>>>延时器");
}
}
public class ScheduleServiceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService=new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(10);
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Task(),1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Task(),2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Task(),1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
三、DelayQueue(延时队列)
推荐指数:★★★☆ 优点: (1)JDK原生(JUC包下)支持,无需引入新的依赖; (2)可以用一个线程对整个延时队列按序执行; 缺点: (1)基于内存,应用重启(或宕机)会导致任务丢失 (2)基于内存存放队列,不支持集群 (3)依据compareTo方法排列队列,调用take阻塞式的取出第一个任务(不调用则不取出),比较不灵活,会影响时间的准确性
①新建一个延时任务
public class DelayTask implements Delayed {
private Integer taskId;
private long executeTime;
DelayTask(Integer taskId, long executeTime) {
this.taskId = taskId;
this.executeTime = executeTime;
}
/**
* 该任务的延时时长
* @param unit
* @return
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return executeTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
DelayTask t = (DelayTask) o;
if (this.executeTime - t.executeTime <= 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "延时任务{" +
"任务编号=" + taskId +
", 执行时间=" + new Date(executeTime) +
'}';
}
/**
* 执行具体业务代码
*/
public void doTask(){
System.out.println(this+":");
System.out.println("线程ID-"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+":线程名称-"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+":do something!");
}
}
②执行延时任务
public class TestDelay {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 新建3个任务,并依次设置超时时间为 30s 10s 60s
DelayTask d1 = new DelayTask(1, System.currentTimeMillis() + 3000L);
DelayTask d2 = new DelayTask(2, System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000L);
DelayTask d3 = new DelayTask(3, System.currentTimeMillis() + 6000L);
DelayQueue queue = new DelayQueue<>();
queue.add(d1);
queue.add(d2);
queue.add(d3);
System.out.println("开启延时队列时间:" + new Date()+"\n");
// 从延时队列中获取元素
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
queue.take().doTask();
}
System.out.println("\n任务结束");
}
}
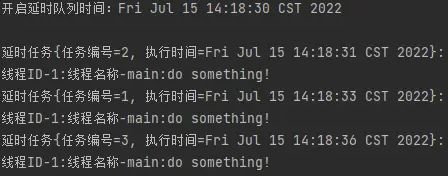
执行结果:
四、Redis-为key指定超时时长,并监听失效key
推荐指数:★★★☆ 优点: 对于有依赖redis的业务且有延时任务的需求,能够快速对接 缺点: (1)客户端断开后重连会导致所有事件丢失 (2)高并发场景下,存在大量的失效key场景会导出失效时间存在延迟 (3)若有多个监听器监听该key,是会重复消费这个过期事件的,需要特定逻辑判断
① 修改Redis配置文件并重启Redis
notify-keyspace-events Ex
注意: redis配置文件不能有空格,否则会启动报错
②Java中关于Redis的配置类
redisTemplate实例bean需要自定义生成; RedisMessageListenerContainer 是redis-key过期监听需要的监听器容器;
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class RedisConfiguration {
/**
* Redis配置
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(redisSerializer);
//key hashmap序列化
template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
return template;
}
/**
* 消息监听器容器bean
* @param connectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisMessageListenerContainer container(LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return container;
}
}
③监听器代码
@Slf4j
@Component
public class RedisKeyExpirationListener extends KeyExpirationEventMessageListener {
private static final String TEST_REDIS_KEY = "testExpired";
public RedisKeyExpirationListener(RedisMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer,
RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
super(listenerContainer);
/**
* 设置一个Redis延迟过期key(key名:testExpired,过期时间:30秒)
*/
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(TEST_REDIS_KEY, "1", 20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("设置redis-key");
}
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
try {
String expiredKey = message.toString();
if (TEST_REDIS_KEY.equals(expiredKey)) {
//业务处理
log.info(expiredKey + "过期,触发回调");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("key 过期通知处理异常,{}", e);
}
}
}
测试结果:
五、时间轮
推荐指数:★★★★ 优点: (1)对于大量定时任务,时间轮可以仅用一个工作线程对编排的任务进行顺序运行; (2)自动运行,可以自定义时间轮每轮的tick数,tick间隔,灵活且时间精度可控 缺点: (1)基于内存,应用重启(或宕机)会导致任务丢失 (2)基于内存存放任务,不支持集群
public class WheelTimerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置每个格子是 100ms, 总共 256 个格子
HashedWheelTimer hashedWheelTimer = new HashedWheelTimer(100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 256);
//加入三个任务,依次设置超时时间是 10s 5s 20s
System.out.println("加入一个任务,ID = 1, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
hashedWheelTimer.newTimeout(timeout -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("执行一个任务,ID = 1, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
}, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("加入一个任务,ID = 2, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
hashedWheelTimer.newTimeout(timeout -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("执行一个任务,ID = 2, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
}, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("加入一个任务,ID = 3, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
hashedWheelTimer.newTimeout(timeout -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("执行一个任务,ID = 3, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
}, 20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("加入一个任务,ID = 4, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
hashedWheelTimer.newTimeout(timeout -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("执行一个任务,ID = 4, time= " + LocalDateTime.now());
}, 20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("等待任务执行===========");
}
}
六、消息队列-延迟队列
针对任务丢失的代价过大,高并发的场景 推荐指数:★★★★ 优点: 支持集群,分布式,高并发场景; 缺点: 引入额外的消息队列,增加项目的部署和维护的复杂度。
场景:为一个委托指定期限,委托到期后,委托关系终止,相关业务权限移交回原拥有者 这里采用的是RabbitMq的死信队列加TTL消息转化为延迟队列的方式(RabbitMq没有延时队列)
①声明一个队列设定其的死信队列
@Configuration
public class MqConfig {
public static final String GLOBAL_RABBIT_TEMPLATE = "rabbitTemplateGlobal";
public static final String DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME = "dlxExchange";
public static final String AUTH_EXCHANGE_NAME = "authExchange";
public static final String DLX_QUEUE_NAME = "dlxQueue";
public static final String AUTH_QUEUE_NAME = "authQueue";
public static final String DLX_AUTH_QUEUE_NAME = "dlxAuthQueue";
@Bean
@Qualifier(GLOBAL_RABBIT_TEMPLATE)
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
return rabbitTemplate;
}
@Bean
@Qualifier(AUTH_EXCHANGE_NAME)
public Exchange authExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange (AUTH_EXCHANGE_NAME).durable (true).build ();
}
/**
* 死信交换机
* @return
*/
@Bean
@Qualifier(DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME)
public Exchange dlxExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange (DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME).durable (true).build ();
}
/**
* 记录日志的死信队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
@Qualifier(DLX_QUEUE_NAME)
public Queue dlxQueue() {
// Queue(String name, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete, Map arguments)
return QueueBuilder.durable (DLX_QUEUE_NAME).build ();
}
/**
* 委托授权专用队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
@Qualifier(AUTH_QUEUE_NAME)
public Queue authQueue() {
return QueueBuilder
.durable (AUTH_QUEUE_NAME)
.withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME)
.withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "dlx_auth")
.build ();
}
/**
* 委托授权专用死信队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
@Qualifier(DLX_AUTH_QUEUE_NAME)
public Queue dlxAuthQueue() {
// Queue(String name, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete, Map arguments)
return QueueBuilder
.durable (DLX_AUTH_QUEUE_NAME)
.withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME)
.withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "dlx_key")
.build ();
}
@Bean
public Binding bindDlxQueueExchange(@Qualifier(DLX_QUEUE_NAME) Queue dlxQueue, @Qualifier(DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME) Exchange dlxExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind (dlxQueue).to (dlxExchange).with ("dlx_key").noargs ();
}
/**
* 委托授权专用死信队列绑定关系
* @param dlxAuthQueue
* @param dlxExchange
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindDlxAuthQueueExchange(@Qualifier(DLX_AUTH_QUEUE_NAME) Queue dlxAuthQueue, @Qualifier(DLX_EXCHANGE_NAME) Exchange dlxExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind (dlxAuthQueue).to (dlxExchange).with ("dlx_auth").noargs ();
}
/**
* 委托授权专用队列绑定关系
* @param authQueue
* @param authExchange
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindAuthQueueExchange(@Qualifier(AUTH_QUEUE_NAME) Queue authQueue, @Qualifier(AUTH_EXCHANGE_NAME) Exchange authExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind (authQueue).to (authExchange).with ("auth").noargs ();
}
}
②发送含过期时间的消息
向授权交换机,发送路由为"auth"的消息(指定了业务所需的超时时间) =》发向MqConfig.AUTH_QUEUE_NAME 队列
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(MqConfig.AUTH_EXCHANGE_NAME, "auth", "类型:END,信息:{id:1,fromUserId:111,toUserId:222,beginData:20201204,endData:20211104}", message -> {
/**
* MessagePostProcessor:消息后置处理
* 为消息设置属性,然后返回消息,相当于包装消息的类
*/
//业务逻辑:过期时间=xxxx
String ttl = "5000";
//设置消息的过期时间
message.getMessageProperties ().setExpiration (ttl);
return message;
});
③超时后队列MqConfig.AUTH_QUEUE_NAME会将消息转发至其配置的死信路由"dlx_auth",监听该死信队列即可消费定时的消息
/**
* 授权定时处理
* @param channel
* @param message
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = MqConfig.DLX_AUTH_QUEUE_NAME)
public void dlxAuthQ(Channel channel, Message message) throws IOException {
System.out.println ("\n死信原因:" + message.getMessageProperties ().getHeaders ().get ("x-first-death-reason"));
//1.判断消息类型:1.BEGIN 2.END
try {
//2.1 类型为授权到期(END)
//2.1.1 修改报件办理人
//2.1.2 修改授权状态为0(失效)
//2.2 类型为授权开启(BEGIN)
//2.2.1 修改授权状态为1(开启)
System.out.println (new String(message.getBody (), Charset.forName ("utf8")));
channel.basicAck (message.getMessageProperties ().getDeliveryTag (), false);
System.out.println ("已处理,授权相关信息修改成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
//拒签消息
channel.basicNack (message.getMessageProperties ().getDeliveryTag (), false, false);
System.out.println ("授权相关信息处理失败, 进入死信队列记录日志");
}
}
以上就是盘点Java中延时任务的多种实现方式的详细内容,更多关于Java延时任务的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!