深度学习笔记(13.numpy实现LSTM)
摘要
Ng深度学习课程第五部分序列化模型,第一周作业numpy实现,并利用LSTM生成恐龙名称实验。涉及到正向传播、反向传播公式,程序的整合,部分理论学习。代码注释添加了部分说明。和RNN程序流程基本一样,部分代码流程做了优化。实验程序用于检验程序是否正确,loss逐步下降,名称越来越像。
程序地址:https://github.com/ConstellationBJUT/Coursera-DL-Study-Notes
代码结构
dinos.txt:数据文件,每行是一个恐龙名称
lstm.py:numpy实现的lstm模型
lstm_dinasaurus_name.py:lstm生成恐龙名字程序

程序查看顺序:
(1)lstm_dinosaurus_name.py的model():实验入口程序,完成数据变换,将名称转换为rnn认识的数据格式。
(2)lstm.py的optimize:lstm正向传播、损失计算、反向传播、参数更新。
(3)lstm_dinosaurus_name.py的sample():根据模型计算得到的参数,按概率生成字符,字符拼接成名字
LSTM网络结构

比RNN多了ci,其它如输入X和输出Y与上一篇RNN保持一致,具体参考如下https://blog.csdn.net/bjjoy2009/article/details/103506065
cell结构
正向传播,实现下图的公式。中间圈符号表示矩阵按照位置乘,[a,x]表示将矩阵a和x拼接,例如a.shape=(n_a, 1),x.shape=(n_x, 1),[a, x].shape=(n_a + n_x, 1)

LSTM算法和程序
1.正向传播
(1) lstm_forward(),用于接收输入数据、初始化参数,调用lstm_cell_forward()来时先每个cell的计算。
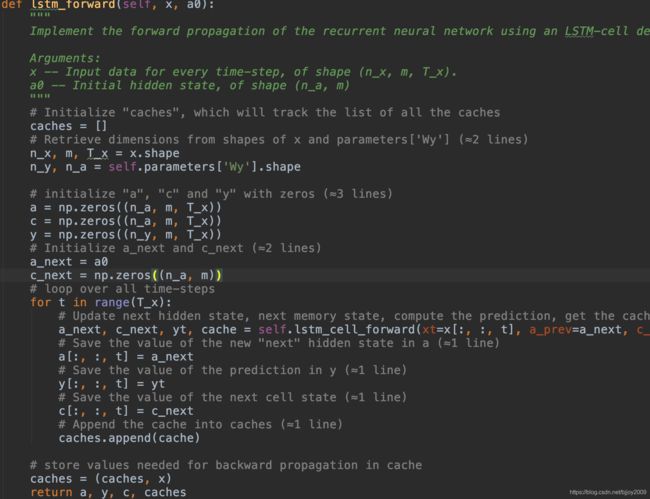
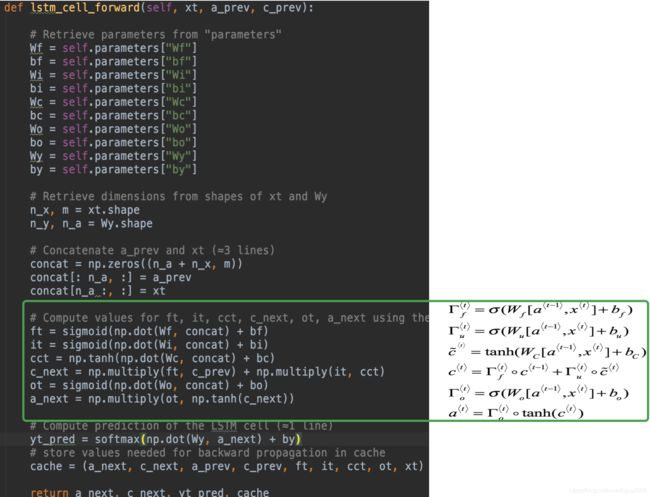
(2)lstm_cell_forward(),绿色框对应的6个公式,concat对应[a, x]。it对应公式第二个( Γ u < t > \Gamma_u^{
2. loss计算
就是softmax交叉熵损失函数,每个cell的损失求和,有m个样本就除以m。
def compute_loss(self, y_hat, y):
"""
计算损失函数
:param y_hat: (n_y, m, T_x),经过rnn正向传播得到的值
:param y: (n_y, m, T_x),标记的真实值
:return: loss
"""
n_y, m, T_x = y.shape
for t in range(T_x):
self.loss -= 1/m * np.sum(np.multiply(y[:, :, t], np.log(y_hat[:, :, t])))
return self.loss
3. 反向传播
(1)lstm_backward,初始化每次反向传播参数,然后调用lstm_cell_backward
注意:
i) dz=y_hat - y,是softmax(z)对z求导公式。
ii) for循环调用lstm_cell_backward,计算序列每个时刻cell反向传播,并对序列中每个cell中对应参数变化量gradients求和,gradients[‘da_next’]和gradients[‘dc_next’]是前一时刻cell的反向传播的输入。
def lstm_backward(self, y, y_hat, caches):
"""
Implement the backward pass for the RNN with LSTM-cell (over a whole sequence).
Arguments:
:param y: one_hot label, shape (n_y, m, T_x)
:param y_hat: lstm_forward 计算结果, shape (n_y, m, T_x)
caches -- cache storing information from the forward pass (lstm_forward)
Returns:
gradients -- python dictionary containing:
dx -- Gradient of inputs, of shape (n_x, m, T_x)
da0 -- Gradient w.r.t. the previous hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, m)
dWf -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWi -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWc -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the memory gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dWo -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of the save gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
dbf -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the forget gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbi -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the update gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbc -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the memory gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dbo -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of the save gate, of shape (n_a, 1)
dWy -- Gradient w.r.t. the weight matrix of output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a)
dby -- Gradient w.r.t. biases of output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
# Retrieve values from the first cache (t=1) of caches.
(caches, x) = caches
# Retrieve dimensions from da's and x1's shapes (≈2 lines)
n_x, m, T_x = x.shape
n_a = self.n_a
# initialize the gradients with the right sizes (≈12 lines)
dx = np.zeros((n_x, m, T_x))
da0 = np.zeros((n_a, m))
da_next = np.zeros((n_a, m))
dc_next = np.zeros((n_a, m))
dWf = np.zeros((n_a, n_a + n_x))
dWi = np.zeros((n_a, n_a + n_x))
dWc = np.zeros((n_a, n_a + n_x))
dWo = np.zeros((n_a, n_a + n_x))
dWy = np.zeros((self.n_y, n_a))
dbf = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
dbi = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
dbc = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
dbo = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
dby = np.zeros((self.n_y, 1))
dz = y_hat - y # y_hat=softmax(z), dz=dl/dy_hat * dy_hat/dz
# loop back over the whole sequence
for t in reversed(range(T_x)):
# Compute all gradients using lstm_cell_backward
gradients = self.lstm_cell_backward(dz=dz[:, :, t], da_next=da_next, dc_next=dc_next, cache=caches[t])
# Store or add the gradient to the parameters' previous step's gradient
dx[:, :, t] = gradients["dxt"]
dWf = dWf+gradients["dWf"]
dWi = dWi+gradients["dWi"]
dWc = dWc+gradients["dWc"]
dWo = dWo+gradients["dWo"]
dWy = dWy+gradients["dWy"]
dbf = dbf+gradients["dbf"]
dbi = dbi+gradients["dbi"]
dbc = dbc+gradients["dbc"]
dbo = dbo+gradients["dbo"]
dby = dby+gradients["dby"]
da_next = gradients['da_next']
dc_next = gradients['dc_next']
# Set the first activation's gradient to the backpropagated gradient da_prev.
da0 = gradients['da_next']
gradients = {"dx": dx, "da0": da0, "dWf": dWf, "dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi, "dbi": dbi,
"dWc": dWc, "dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo, "dbo": dbo, "dWy": dWy, "dby": dby}
return gradients
(2)lstm_cell_backward,计算t时刻cell反向传播,公式太长,先贴出公式图片。
红色框程序实现时候出现了点问题,*符号乘法应该替换为np.dot。
说明:np.dot表示矩阵乘法,np.multiply表示矩阵按位置乘。*做乘法有2种情况,如果是np.mat数据格式表示矩阵乘法(相当于np.dot),如果是np.array数据格式表示按位置乘(相当于np.multiply)

程序流程,先计算dWy和dby,da(2部分组成,输出da和da_naxt),然后按照上图公式列出来。
def lstm_cell_backward(self, dz, da_next, dc_next, cache):
"""
Implement the backward pass for the LSTM-cell (single time-step).
Arguments:
dz -- cell输出y_hat=softmax(z)对z求导
da_next -- Gradients of next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m)
dc_next -- Gradients of next cell state, of shape (n_a, m)
cache -- cache storing information from the forward pass
"""
# Retrieve information from "cache"
(a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt) = cache
# Retrieve dimensions from xt's and a_next's shape (≈2 lines)
n_a, m = a_next.shape
dWy = np.dot(dz, a_next.T)
dby = np.sum(dz, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# cell的da由两部分组成
da_next = np.dot(self.parameters['Wy'].T, dz) + da_next
# Compute gates related derivatives, you can find their values can be found by looking carefully at equations (7) to (10) (≈4 lines)
dot = da_next * np.tanh(c_next) * ot * (1 - ot)
dcct = (dc_next * it + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * it * da_next) * (1 - np.square(cct))
dit = (dc_next * cct + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * cct * da_next) * it * (1 - it)
dft = (dc_next * c_prev + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * c_prev * da_next) * ft * (1 - ft)
# Compute parameters related derivatives. Use equations (11)-(14) (≈8 lines)
concat = np.vstack((a_prev, xt)).T
dWf = np.dot(dft, concat)
dWi = np.dot(dit, concat)
dWc = np.dot(dcct, concat)
dWo = np.dot(dot, concat)
dbf = np.sum(dft, axis=1, keepdims=True)
dbi = np.sum(dit, axis=1, keepdims=True)
dbc = np.sum(dcct, axis=1, keepdims=True)
dbo = np.sum(dot, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# Compute derivatives w.r.t previous hidden state, previous memory state and input. Use equations (15)-(17). (≈3 lines)
da_prev = np.dot(self.parameters['Wf'][:, :n_a].T, dft) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wi'][:, :n_a].T, dit) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wc'][:, :n_a].T, dcct) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wo'][:, :n_a].T, dot)
dc_prev = dc_next * ft + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * ft * da_next
dxt = np.dot(self.parameters['Wf'][:, n_a:].T, dft) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wi'][:, n_a:].T, dit) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wc'][:, n_a:].T, dcct) + np.dot(self.parameters['Wo'][:, n_a:].T, dot)
# Save gradients in dictionary
gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_next": da_prev, "dc_next": dc_prev, "dWf": dWf, "dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi, "dbi": dbi,
"dWc": dWc, "dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo, "dbo": dbo, "dWy": dWy, "dby": dby}
return gradients
4.梯度算法更新参数
self.alpha = learning_rate
def update_parameters(self, gradients):
"""
梯度下降
:param gradients:
:return:
"""
self.parameters['Wf'] += -self.alpha * gradients["dWf"]
self.parameters['Wi'] += -self.alpha * gradients["dWi"]
self.parameters['Wc'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dWc']
self.parameters['Wo'] += -self.alpha * gradients["dWo"]
self.parameters['Wy'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dWy']
self.parameters['bf'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dbf']
self.parameters['bi'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dbi']
self.parameters['bc'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dbc']
self.parameters['bo'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dbo']
self.parameters['by'] += -self.alpha * gradients['dby']
实验结果
实验生成字符程序在sample()函数中,就是生成一个字符(输出y)的one_hot向量,作为下一个cell的输入x,直到生成字符\n或者生成了50个字符结束。
Iteration: 6000, Loss: 26.024013
Khvsrolonos
Hiecalosaurus
Hwtosaurus
Kecalosaurus
Xtppeonos
Caalosaurus
Usnanerontisaurus
Iteration: 8000, Loss: 24.694760
Jhytrognesaurus
Hicabdosaurus
Hytrognesaurus
Jacakton
Ytroeomor
Caagtona
Usodonnonus
总结
(1)单纯的实现了LSTM的基本流程,感觉和RNN流程没有啥差别,有了RNN实现的基础,感觉LSTM实现也容易多了。
(2)没有推导反向传播公式,感觉的确推导挺难的,需要根据cell那个图确定每个参数变化由哪些参数变化确定,再进行加和。
(3)第三点还有啥呢?凑一下吧,还是得用keras或者tensorflow做做,感觉用框架也不是啥容易事。