bert-pytorch版源码详细解读
前言
bert作为当下最火的NLP模型(或者说该类型的模型,包括AlBert,XLNet等)。对于志在NLP的同学,有必要对其原理和代码都进行比较深入的了解。废话不多说,进入正题。
PS:1.这里的代码有些参数传入是阉割过的,而且代码版本也是比较老版的,但更容易理解,更详细的还是参考:https://huggingface.co/transformers/
2.关键的注解都在代码的注释里。
主要代码
1.主函数入口
class BertModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: BertConfig):
super(BertModel, self).__init__()
self.embeddings = BERTEmbeddings(config)
self.encoder = BERTEncoder(config)
self.pooler = BERTPooler(config)
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None):
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(input_ids)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
# attention_mask的维度应保持和多头的hidden_states一致
#!!!个人感觉这里extended_attention_mask 还应该扩展一下,感觉这个维度不太对!
extended_attention_mask = attention_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
extended_attention_mask = extended_attention_mask.float()
# mask部分token的权重直接给-10000,使其在self-att的时候基本不起作用。
extended_attention_mask = (1.0 - extended_attention_mask) * -10000.0
#根据input_ids, token_type_ids以及position_ids来确定初始embeddings
embedding_output = self.embeddings(input_ids, token_type_ids)
#核心层,由以多层self_attention为主的神经网络构成
all_encoder_layers = self.encoder(embedding_output, extended_attention_mask)
#最后一层隐藏层
sequence_output = all_encoder_layers[-1]
#取出最后一层隐藏层的[cls]的表征,经过网络层(self.pooler)后得到pooled_output
pooled_output = self.pooler(sequence_output)
return all_encoder_layers, pooled_output
大致讲一下吧:
一般必传的三个参数input_idx,token_type_ids,attention_mask。
维度均为(batch_size, max_sent_length)
- input_idx就是每个token对应的idx,对应关系在预训练模型文件集的vocab.txt里
- token_type_ids有两种取值(0对应sentenceA,1对应sentenceB)该tensor会在self.embeddings的时候和input_iput生成的embedding相加生成初始的embeddings。
- attention_mask有两种取值(1代表非mask词,0代表mask掉的词)一般来说在finetune阶段,我们会把padding部分都设成mask掉的词。
其他基本也都注释了。
2.BertEmbedding层
class BERTEmbeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTEmbeddings, self).__init__()
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.max_position_embeddings, config.hidden_size)
self.token_type_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.type_vocab_size, config.hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = BERTLayerNorm(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None):
#根据每个token的位置生成position_ids,很直观
seq_length = input_ids.size(1)
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, dtype=torch.long, device=input_ids.device)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(input_ids)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
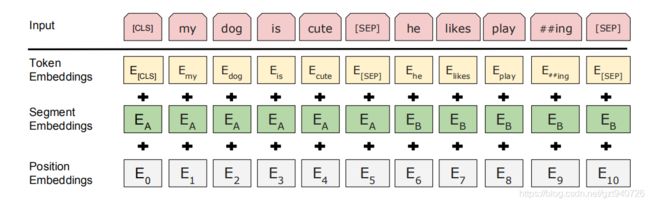
#这三个embeddings相信大家可以参见下图就一目了然了
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
token_type_embeddings = self.token_type_embeddings(token_type_ids)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings + token_type_embeddings
#最后过一个layerNorm和dropout层
embeddings = self.LayerNorm(embeddings)
embeddings = self.dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
3.BertEnocder层
class BERTEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTEncoder, self).__init__()
layer = BERTLayer(config)
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(layer) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
all_encoder_layers = []
for layer_module in self.layer:
hidden_states = layer_module(hidden_states, attention_mask)
all_encoder_layers.append(hidden_states)
return all_encoder_layers
class BERTLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTLayer, self).__init__()
self.attention = BERTAttention(config)
self.intermediate = BERTIntermediate(config)
self.output = BERTOutput(config)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
attention_output = self.attention(hidden_states, attention_mask)
intermediate_output = self.intermediate(attention_output)
layer_output = self.output(intermediate_output, attention_output)
return layer_output
BertEncoder层实质上就是由多个(num_hidden_layers)BertLayer层堆叠而成。
而BertLayer又由attention,intermediate和output三部分组成,下面分别来看。
3.1BertTAttention
重头戏开始!详见注释,看完你会发现很简单。
class BERTAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTAttention, self).__init__()
self.self = BERTSelfAttention(config)
self.output = BERTSelfOutput(config)
def forward(self, input_tensor, attention_mask):
self_output = self.self(input_tensor, attention_mask)
attention_output = self.output(self_output, input_tensor)
return attention_output
class BERTSelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTSelfAttention, self).__init__()
if config.hidden_size % config.num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention"
"heads (%d)" % (config.hidden_size, config.num_attention_heads))
self.num_attention_heads = config.num_attention_heads#多头self_attention
self.attention_head_size = int(config.hidden_size /config.num_attention_heads)#每个头的维度,一般是768/12=64
self.all_head_size = self.num_attention_heads * self.attention_head_size
self.query = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.key = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.value = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.all_head_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.attention_probs_dropout_prob)
def transpose_for_scores(self, x):
new_x_shape = x.size()[:-1] + (self.num_attention_heads, self.attention_head_size)
x = x.view(*new_x_shape)
return x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask):
#经典生成QKV
#(batch_size, max_sen_length, hidden_size)->(batch_size, max_sen_length, hidden_size)
#(8, 512, 768)->(8, 512, 768)
mixed_query_layer = self.query(hidden_states)
mixed_key_layer = self.key(hidden_states)
mixed_value_layer = self.value(hidden_states)
#改变维度,形成多头,记住是在生成QKV之后才干的事
#(batch_size, max_sen_length, hidden_size)->(batch_size, num_attention_heads, max_sen_length, attention_head_size)
#(8, 512, 768)->(8, 12, 512, 64)
query_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_query_layer)
key_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_key_layer)
value_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_value_layer)
#QK tensor相乘,只对最后两维做矩阵乘法
#(batch_size, num_attention_heads, max_sen_length, attention_head_size)*(batch_size, num_attention_heads, attention_head_size, max_sen_length)->(batch_size, num_attention_heads, max_sen_length, max_sen_length)
#(8, 12, 512, 64)*(8, 12, 64, 512)->(8, 12, 512, 512)
attention_scores = torch.matmul(query_layer, key_layer.transpose(-1, -2))
#除以维度的开方,这是为了使QV的结果方差变为1,使得sortmax后不会发生梯度消失。
attention_scores = attention_scores / math.sqrt(self.attention_head_size)
#之前传的attention_mask在此刻发挥它的作用了!把mask掉的词的“权重”变成-10000,softmax后就基本等于0。
attention_scores = attention_scores + attention_mask
# softmax加一个dropout, 这也没啥好说的
attention_probs = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(attention_scores)
attention_probs = self.dropout(attention_probs)
# 最后再和V相乘,至此就完成了经典的softmax(QK/sqrt(dk))*V的操作!
#(8, 12, 512, 512)*(8, 12, 512, 64)->(8, 12, 512, 64)
context_layer = torch.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
#之后就是把维度进行还原
#(8, 12, 512, 64)->(8, 512,12 ,64)->(8, 512, 768)
context_layer = context_layer.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous()
new_context_layer_shape = context_layer.size()[:-2] + (self.all_head_size,)
context_layer = context_layer.view(*new_context_layer_shape)
return context_layer
class BERTSelfOutput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTSelfOutput, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = BERTLayerNorm(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, input_tensor):
#很平淡的全连接层加上dropout和LayerNorm
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.LayerNorm(hidden_states + input_tensor)
return hidden_states
3.2 BertIntermediate&& BertOutput
class BERTIntermediate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTIntermediate, self).__init__()
#之前一直不清楚这个intermediate_size是干嘛的,原来是self_attention后还跟了BERTIntermediate和BERTOutput2个全连接层。
self.dense = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.intermediate_size)
self.intermediate_act_fn = gelu
def forward(self, hidden_states):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.intermediate_act_fn(hidden_states)
return hidden_states
class BERTOutput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTOutput, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(config.intermediate_size, config.hidden_size)
self.LayerNorm = BERTLayerNorm(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
def forward(self, hidden_states, input_tensor):
hidden_states = self.dense(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.LayerNorm(hidden_states + input_tensor)
return hidden_states
!!!这个和我之前看的transformers的残差连接层差别还挺大的,所以并不完全和transformers的encoder部分结构一致。
这之后就是主函数里的几步骤收尾工作了,这里也不再赘述。
4.补充
下面补充一下中途涉及到的相关类(LayerNorm)的代码
4.1 BertLayerNorm
class BERTLayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, variance_epsilon=1e-12):
"""Construct a layernorm module in the TF style (epsilon inside the square root).
"""
super(BERTLayerNorm, self).__init__()
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(config.hidden_size))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(config.hidden_size))
self.variance_epsilon = variance_epsilon
def forward(self, x):
u = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True)
s = (x - u).pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
x = (x - u) / torch.sqrt(s + self.variance_epsilon)
return self.gamma * x + self.beta
1.batchNorm是对多个样本进行标准化,而layerNorm是对单样本标准化。
2.BertLayerNorm除了标准化以外还加上了gamma和beta的变化。
4.2 BertPooler
class BERTPooler(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BERTPooler, self).__init__()
self.dense = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size)
self.activation = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, hidden_states):
#取出[cls]后过一个全连接层和激活函数。
first_token_tensor = hidden_states[:, 0]
pooled_output = self.dense(first_token_tensor)
pooled_output = self.activation(pooled_output)
return pooled_output
上文也提到了,BertPooler就是专门为[cls]设计的
4.3 gelu
def gelu(x):
"""Implementation of the gelu activation function.
"""
return x * 0.5 * (1.0 + torch.erf(x / math.sqrt(2.0)))
4.4 transpose_for_scores
def transpose_for_scores(self, x):
new_x_shape = x.size()[:-1] + (self.num_attention_heads, self.attention_head_size)
x = x.view(*new_x_shape)
return x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
总结
到此基本就结束了,整体流程看下来其实很快,关键是理清里面每一步的维度的变换和几个核心的类就行。希望能对大家有所帮助。
代码参考来自于:https://github.com/DA-southampton/Read_Bert_Code