OCR文字识别之CTC原理和实现
CTC
最近在学习文字识别相关内容,这里记录一下CTC的实现过程,欢迎批评指正
CNN+RNN阶段提取特征就先不说了,本文只简要总结一下CTC原理和keras实现代码。
首先放上原文和解释CTC最好的几个文章:
CTC Algorithm Explained Part 1:Training the Network(CTC算法详解之训练篇 https://xiaodu.io/ctc-explained/
CTC Algorithm Explained Part 2:Decoding the Network(CTC算法详解之解码篇 https://xiaodu.io/ctc-explained-part2/
一文读懂CRNN+CTC文字识别 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/43534801
CTC原理简要总结
一般来说我们需要输入和输出都是一一对应且标注好的,如果这样对于文本识别来说你不仅需要标注字符还需要标注位置,这是非常困难的,CTC的出现解决了这种对齐问题。CTC引入了空格字符‘-’,定义了一个多对一的β变换,举个例子:abbcd ,经过β变换可能输出abbcd的情况有-a-bb-b-cd, a-b-b-c-d-等等很多(但是是有限的,因为你的input_length是定值)。
定义x是输入,z是正确输出,我们希望p(z|x)尽可能的大,如果要计算p(z|x)我们可以选择计算所有能映射到abbcd的‘路径’。

这里补充解释一下图中CTC loss第一行,S是样本集合。实际训练时就是一个batch里的数据,我们希望这个batch所有数据预测对的概率最大,所以求最大似然(把每条数据预测对的概率累乘),这里求loss希望loss小所以取负对数似然。
直接暴力计算p(z|x)在识别较长序列时显然不现实,作者借鉴HMM的Forward-Backward算法思路采用动态规划的方法求解。

这里详情参考引用1
CTC训练bug解决
这里在提一下之前训练时遇到的一个bug:
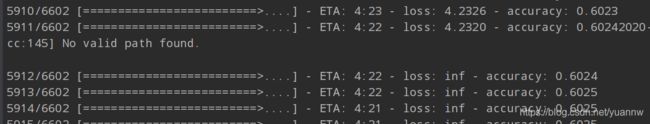
原因是:网上说是label_legth>input_length,查询之后发现没有label_legth>input_length。实际是这样的,比如你的label是abb, input_length是3,那么必然报错,因为你至少输出ab-b四个字符才能得到abb。
解决方法:
- 修改CTC Loss里参数preprocess_collapse_repeated = True
- 过滤掉可能出现这种情况的数据
keras CTC实现代码
def ctc_batch_cost(y_true, y_pred, input_length, label_length):
"""Runs CTC loss algorithm on each batch element.
# Arguments
y_true: tensor `(samples, max_string_length)`
containing the truth labels.
y_pred: tensor `(samples, time_steps, num_categories)`
containing the prediction, or output of the softmax.
input_length: tensor `(samples, 1)` containing the sequence length for
each batch item in `y_pred`.
label_length: tensor `(samples, 1)` containing the sequence length for
each batch item in `y_true`.
# Returns
Tensor with shape (samples,1) containing the
CTC loss of each element.
"""
label_length = tf.cast(tf.squeeze(label_length, axis=-1), tf.int32)
input_length = tf.cast(tf.squeeze(input_length, axis=-1), tf.int32)
sparse_labels = tf.cast(
ctc_label_dense_to_sparse(y_true, label_length), tf.int32)
y_pred = tf_math_ops.log(tf.transpose(y_pred, perm=[1, 0, 2]) + epsilon())
return tf.expand_dims(ctc.ctc_loss(inputs=y_pred,
labels=sparse_labels,
sequence_length=input_length), 1)
首先看**ctc_batch_cost(y_true, y_pred, input_length, label_length)**这个函数,需要四个参数:
- y_true:在generate data阶段,由于每条数据label长度不一样,我们需要设置一个max_length把每条label补成统一的长度,所以y_true的维度应该是(batchsize, max_length)。
- y_pred:y_true是由CRNN,然后每个时间步长的特征向量经过一个ncalss (可识别字符数+1个占位符) 个神经元的全连接层然后经softmax激活输出的,y_pred维度为(batchsize, time_steps, nclass)。
- input_length:每条数据经过RNN的时间步长T,即有T个时间输入(这个和CNN提取特征有关,原始图(h,w,c)=>最终特征(1,w’,c’),w’就是T),input_length的维度为(batchsize, 1),1那个维度用来记录T。
- label_length: 每条数据label的长度为s(不补全成max_length的长度),label_length的维度为(batchsize, 1),1那个维度用来记录s。
def ctc_label_dense_to_sparse(labels, label_lengths):
"""Converts CTC labels from dense to sparse.
# Arguments
labels: dense CTC labels.
label_lengths: length of the labels.
# Returns
A sparse tensor representation of the labels.
"""
label_shape = tf.shape(labels)
num_batches_tns = tf.stack([label_shape[0]])
max_num_labels_tns = tf.stack([label_shape[1]])
def range_less_than(_, current_input):
return tf.expand_dims(tf.range(label_shape[1]), 0) < tf.fill(
max_num_labels_tns, current_input)
init = tf.cast(tf.fill([1, label_shape[1]], 0), tf.bool)
dense_mask = functional_ops.scan(range_less_than, label_lengths,
initializer=init, parallel_iterations=1)
dense_mask = dense_mask[:, 0, :]
label_array = tf.reshape(tf.tile(tf.range(label_shape[1]), num_batches_tns),
label_shape)
label_ind = tf.boolean_mask(label_array, dense_mask)
tmp = tf.tile(tf.range(label_shape[0]), max_num_labels_tns)
batch_array = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(tmp, reverse(label_shape, 0)))
batch_ind = tf.boolean_mask(batch_array, dense_mask)
indices = concatenate([batch_ind, label_ind], axis=0)
indices = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(indices, [2, -1]))
vals_sparse = tf.gather_nd(labels, indices)
indices = tf.cast(indices, tf.int64)
label_shape = tf.cast(label_shape, tf.int64)
return tf.SparseTensor(indices, vals_sparse, label_shape)
注意**ctc_label_dense_to_sparse(y_true, label_length)**这个函数,这个函数将CTC label 从密集转为稀疏,这里要先介绍一下这个函数的输出SparseTensor。
如图,SparseTensor有三个属性indices,value,dense_shape。
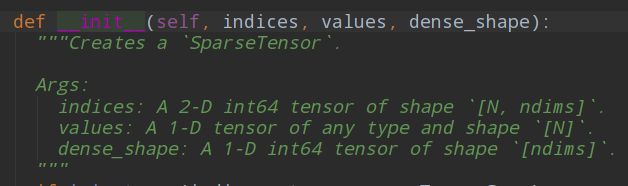
我们直接实验一下看看他的输出是什么:
输入两个label,其中第一个label的长度为3,也就是说那个‘x’是补全符或者其他和这个label不相关的字符。
labels = tf.constant([['s','s','q','x'],['a','b','c','d']])
label_lengths = tf.constant([3,4])
a = ctc_label_dense_to_sparse(labels,label_lengths)
print(a)
看一下输出,这里感觉dense_shape[2 4]的意思就是说这个输出的稀疏tensor矩阵维度为2*4,indices和values是对应的,比如说[0 0]位置对应value ‘s’,[1 2]位置对应value ‘c’。
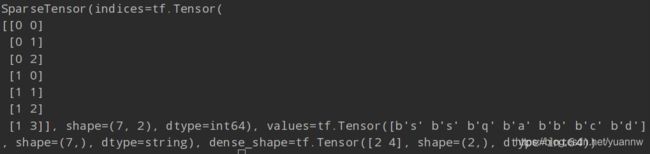
注意这里实验输入的label是string格式,到这之前应该要进行一次编码把string转成int,这个实验只为看下这个稀疏矩阵是什么
继续看ctc_batch_cost(y_true, y_pred, input_length, label_length),y_pred经过了一个维度交换变成(time_steps, samples, num_categories)并且每个元素加一个epsilon,然后取log得到新得y_pred。
最后我们简单看一下ctc_loss这个函数:
- preprocess_collapse_repeated=True,默认是false,改成true的话会把label里相邻重复的元素合并,所以它可以解决上面的bug(但是感觉对训练影响不小)
- ctc_merge_repeated=True,将重复的空格字符合并
- ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs=False,如果设置成true输出的长度比输入的长就不会报错了
def ctc_loss(labels,
inputs=None,
sequence_length=None,
preprocess_collapse_repeated=False,
ctc_merge_repeated=True,
ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs=False,
time_major=True,
logits=None):
"""Computes the CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) Loss.
This op implements the CTC loss as presented in the article:
[A. Graves, S. Fernandez, F. Gomez, J. Schmidhuber.
Connectionist Temporal Classification: Labeling Unsegmented Sequence Data
with Recurrent Neural Networks. ICML 2006, Pittsburgh, USA,
pp. 369-376.](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~graves/icml_2006.pdf)
Input requirements:
sequence_length(b) <= time for all b
max(labels.indices(labels.indices[:, 1] == b, 2))
<= sequence_length(b) for all b.
Notes:
This class performs the softmax operation for you, so inputs should
be e.g. linear projections of outputs by an LSTM.
The `inputs` Tensor's innermost dimension size, `num_classes`, represents
`num_labels + 1` classes, where num_labels is the number of true labels, and
the largest value `(num_classes - 1)` is reserved for the blank label.
For example, for a vocabulary containing 3 labels `[a, b, c]`,
`num_classes = 4` and the labels indexing is `{a: 0, b: 1, c: 2, blank: 3}`.
Regarding the arguments `preprocess_collapse_repeated` and
`ctc_merge_repeated`:
If `preprocess_collapse_repeated` is True, then a preprocessing step runs
before loss calculation, wherein repeated labels passed to the loss
are merged into single labels. This is useful if the training labels come
from, e.g., forced alignments and therefore have unnecessary repetitions.
If `ctc_merge_repeated` is set False, then deep within the CTC calculation,
repeated non-blank labels will not be merged and are interpreted
as individual labels. This is a simplified (non-standard) version of CTC.
Here is a table of the (roughly) expected first order behavior:
* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=False`, `ctc_merge_repeated=True`
Classical CTC behavior: Outputs true repeated classes with blanks in
between, and can also output repeated classes with no blanks in
between that need to be collapsed by the decoder.
* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=True`, `ctc_merge_repeated=False`
Never learns to output repeated classes, as they are collapsed
in the input labels before training.
* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=False`, `ctc_merge_repeated=False`
Outputs repeated classes with blanks in between, but generally does not
require the decoder to collapse/merge repeated classes.
* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=True`, `ctc_merge_repeated=True`
Untested. Very likely will not learn to output repeated classes.
The `ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs` option allows to specify the behavior
of the CTCLoss when dealing with sequences that have longer outputs than
inputs. If true, the CTCLoss will simply return zero gradient for those
items, otherwise an InvalidArgument error is returned, stopping training.
Args:
labels: An `int32` `SparseTensor`.
`labels.indices[i, :] == [b, t]` means `labels.values[i]` stores the id
for (batch b, time t). `labels.values[i]` must take on values in `[0,
num_labels)`. See `core/ops/ctc_ops.cc` for more details.
inputs: 3-D `float` `Tensor`.
If time_major == False, this will be a `Tensor` shaped: `[batch_size,
max_time, num_classes]`.
If time_major == True (default), this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
`[max_time, batch_size, num_classes]`. The logits.
sequence_length: 1-D `int32` vector, size `[batch_size]`. The sequence
lengths.
preprocess_collapse_repeated: Boolean. Default: False. If True, repeated
labels are collapsed prior to the CTC calculation.
ctc_merge_repeated: Boolean. Default: True.
ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs: Boolean. Default: False. If True,
sequences with longer outputs than inputs will be ignored.
time_major: The shape format of the `inputs` Tensors. If True, these
`Tensors` must be shaped `[max_time, batch_size, num_classes]`. If False,
these `Tensors` must be shaped `[batch_size, max_time, num_classes]`.
Using `time_major = True` (default) is a bit more efficient because it
avoids transposes at the beginning of the ctc_loss calculation. However,
most TensorFlow data is batch-major, so by this function also accepts
inputs in batch-major form.
logits: Alias for inputs.
Returns:
A 1-D `float` `Tensor`, size `[batch]`, containing the negative log
probabilities.
Raises:
TypeError: if labels is not a `SparseTensor`.
"""
# The second, third, etc output tensors contain the gradients. We use it in
# _CTCLossGrad() below.
if not isinstance(labels, sparse_tensor.SparseTensor):
raise TypeError("Expected labels (first argument) to be a SparseTensor")
# For internal calculations, we transpose to [time, batch, num_classes]
inputs = deprecation.deprecated_argument_lookup("logits", logits, "inputs",
inputs)
if not time_major:
inputs = array_ops.transpose(inputs, [1, 0, 2]) # (B,T,N) => (T,B,N)
loss, _ = gen_ctc_ops.ctc_loss(
inputs,
labels.indices,
labels.values,
sequence_length,
preprocess_collapse_repeated=preprocess_collapse_repeated,
ctc_merge_repeated=ctc_merge_repeated,
ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs=ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs)
return loss