《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第7章 语音信号的减噪
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第7章 语音信号的减噪
- 前言
- 1. 数据与函数路径设置
- 2. MATLAB仿真一:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪一
- 3. MATLAB仿真二:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪二
- 4. MATLAB仿真三:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪三
- 5. MATLAB仿真四:谱减法滤波减噪
- 6. MATLAB仿真五:改进谱减法滤波减噪
- 7. MATLAB仿真六:维纳滤波法滤波减噪一
- 8. MATLAB仿真七:维纳滤波法滤波减噪二
- 9. MATLAB仿真八:维纳滤波法滤波减噪三
- 小结
前言
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》是中科院声学所的大佬宋知用老师数十年经验积累下的呕心之作,对于语音信号处理相关感兴趣的同学,日后希望在语音信号分析、处理与合成相关领域进行一定研究的话,可以以此进行入门。
语音信号处理是数字信号处理的一个重要分支。本书含有许多数字信号处理的方法和 MATLAB函数。 全书共10章。第1-4章介绍语音信号处理的一些基本分析方法和手段,以及相应的MATLAB函数;第5-9章介绍语音信号预处理和特征的提取,包括消除趋势项和基本的减噪方法,以及端点检测、基音的提取和共 振峰的提取,并利用语音信号处理的基本方法,给出了多种提取方法和相应的 MATLAB程序;第10章结合 各种参数的检测介绍了语音信号的合成、语音信号的变速和变调处理,还介绍了时域基音同步叠加( TD PSOLA)的语音合成,并给出了相应的MATLAB程序。附录A中给出了调试复杂程序的方法和思路。 本书可作为从事语音信号处理的本科高年级学生、研究生或科研工程技术人员的辅助读物,也可作为从 事信号处理研究与应用的科研工程技术人员的参考用书。
我的研究生导师的主攻方向就是语音信号处理相关,虽然自己研究生期间的大论文方向是数字图像处理,但所谓语音图像不分家,自己在老师的研究生主讲课小波变换上虽然划水,但在后期导师的语音信号处理的课程设计和工程应用上自己在语音上还算入了一点小门道,在结课测试中拿到了小组第一,导师还特地发了三百大洋的伙食经费以资鼓励。
这次重新捡起语音识别,正好入手了宋老师的这本书,算是自己重新复习一遍吧,主要以介绍各章节中源码为主,这是本书的第七章的8个仿真应用实例,话不多说,开始!
1. 数据与函数路径设置
书中经常会调用的一些函数(自编函数或取自其他应用工具箱中的函数)已集中在basic_tbx工具箱中,在运行本书的程序前请把该工具箱设置(用set path设置)在工作路径下;
当要运行EMD处理时,要把emd工具箱设置在工作路径下;
当要运行主体延伸基音检测时,要把Pitch_ztlib工具箱设置在工作路径下;
当要进行时域基音同步叠加语音合成时,要把psola_lib工具箱设置在工作路径下;
当要应用本书提供的语音数据时,最好把speech_signal设置在工作路径下。
本书的所有函数和程序都在MATLAB R2009a版本下调试通过。(我用的是MATLAB2015b,有些函数已经更新,所以我会进行修改,以便调试通过)
路径设置的方法如下:
打开MATLAB,点击“主页”,找到设置路径
![]()
将上述文件夹路径全部添加到MATLAB搜索路径中
![]()
添加完毕,保存,开始仿真。
2. MATLAB仿真一:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪一
%
% pr7_1_1
close all;clear all; clc;
filedir=[]; % 设置路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 设置文件名
fle=[filedir filename]; % 构成完整的路径和文件名
% [s, fs, bits] = wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[s, fs] = audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
s=s-mean(s); % 消除直流分量
s=s/max(abs(s)); % 幅值归一
N=length(s); % 语音长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间刻度
SNR=5; % 设置信噪比
r2=randn(size(s)); % 产生随机噪声
b=fir1(31,0.5); % 设计FIR滤波器,代替H
r21=filter(b,1,r2); % FIR滤波
[r1,r22]=add_noisedata(s,r21,fs,fs,SNR);% 产生带噪语音,信噪比为SNR
M=32; % 设置M和mu
mu=0.001;
snr1=SNR_singlech(s,r1); % 计算初始信噪比
h = adaptfilt.lms(M,mu); % LMS滤波
[y,e] = filter(h,r2,r1);
output=e; % LMS滤波输出
snr2=SNR_singlech(s,output); % 计算滤波后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
SN1=snr1; SN2=snr2; SN3=snr;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(r1,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
audioplayer(r1,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
% 作图
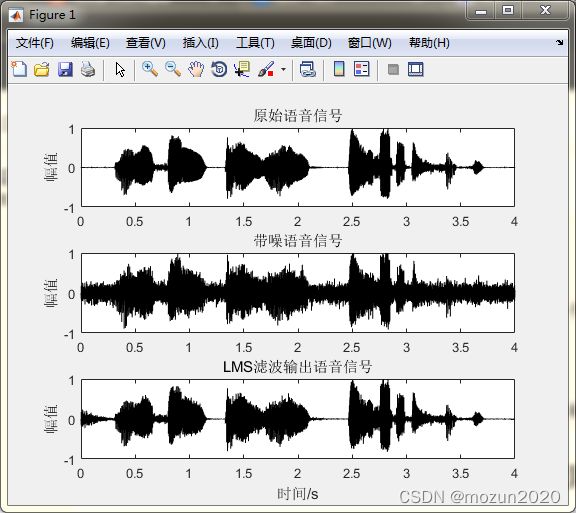
subplot 311; plot(time,s,'k'); ylabel('幅值')
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('原始语音信号');
subplot 312; plot(time,r1,'k'); ylabel('幅值')
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('带噪语音信号');
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('LMS滤波输出语音信号');
xlabel('时间/s'); ylabel('幅值')
function [signal,noise]=add_noisedata(s,data,fs,fs1,snr)
s=s(:); % 把信号转换成列数据
s=s-mean(s); % 消除直流分量
sL=length(s); % 求出信号的长度
if fs~=fs1 % 若纯语音信号的采样频率与噪声的采样频率不相等
x=resample(data,fs,fs1); % 对噪声重采样,使噪声采样频率与纯语音信号的采样频率相同
else
x=data;
end
x=x(:); % 把噪声数据转换成列数据
x=x-mean(x); % 消除直流分量
xL=length(x); % 求噪声数据长度
if xL>=sL % 如果噪声数据长度与信号数据长度不等,把噪声数据截断或补足
x=x(1:sL);
else
disp('Warning: 噪声数据短于信号数据,以补0来补足!')
x=[x; zeros(sL-xL,1)];
end
Sr=snr;
Es=sum(x.*x); % 求出信号的能量
Ev=sum(s.*s); % 求出噪声的能量
a=sqrt(Ev/Es/(10^(Sr/10))); % 计算出噪声的比例因子
noise=a*x; % 调整噪声的幅值
signal=s+noise; % 构成带噪语音
function snr=SNR_singlech(I,In)
% 计算带噪语音信号的信噪比
% I 是纯语音信号
% In 是带噪的语音信号
% 信噪比计算公式是
% snr=10*log10(Esignal/Enoise)
I=I(:)'; % 把数据转为一列
In=In(:)';
Ps=sum((I-mean(I)).^2); % 信号的能量
Pn=sum((I-In).^2); % 噪声的能量
snr=10*log10(Ps/Pn); % 信号的能量与噪声的能量之比,再求分贝值
3. MATLAB仿真二:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪二
%
% pr7_1_2
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [s,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[s,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
s=s/max(abs(s)); % 幅值归一化
N=length(s); % 求出信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间
ns=0.5*cos(2*pi*50*time); % 计算出50Hz工频信号
x=s+ns'; % 语音信号和50Hz工频信号叠加
snr1=SNR_singlech(s,x); % 计算叠加50Hz工频信号后的信噪比
x1=cos(2*pi*50*time); % 设置x1和x2
x2=sin(2*pi*50*time);
w1=0.1; % 初始化w1和w2
w2=0.1;
e=zeros(1, N); % 初始化e和y
y=zeros(1, N);
mu=0.05; % 设置mu
for i=1: N % LMS自适应陷波器滤波
y(i)=w1 * x1(i)+ w2 * x2(i); % 按式(7-1-29)计算y
e(i) =x(i)-y(i); % 按式(7-1-30)计算e
w1=w1+mu * e(i) * x1(i); % 按式(7-1-31)调整w
w2=w2+mu * e(i) * x2(i);
end
output=e'; % 陷波器输出
snr2=SNR_singlech(s,output); % 计算滤波后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(x,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
audioplayer(x,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
% 作图
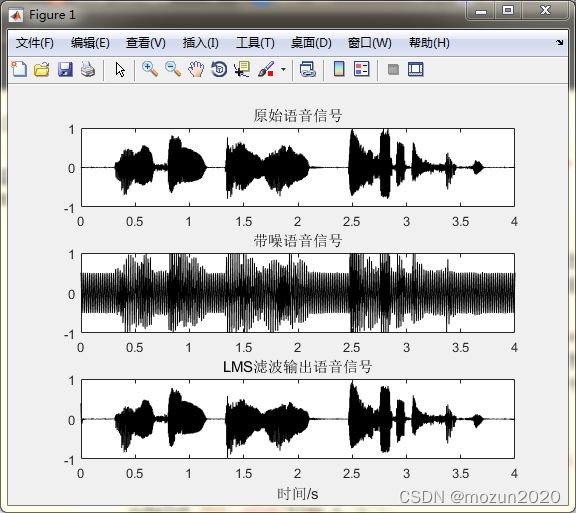
subplot 311; plot(time,s,'k');
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('原始语音信号');
subplot 312; plot(time,x,'k');
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('带噪语音信号');
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');
ylim([-1 1 ]); title('LMS滤波输出语音信号');
xlabel('时间/s')
4. MATLAB仿真三:自适应滤波器LMS滤波减噪三
%
% pr7_1_3
clear all; clc; close all;
load ecg_m.mat % 读入数据
s=x;
N=length(x); % 信号长度
fs=1000; % 采样频率
n=1:N;
n2=1:N/2;
tt=(n-1)/fs; % 时间刻度
ff=(n2-1)*fs/N; % 频率刻度
X=fft(x); % 谱分析
for k=1 : 5 % 自适应陷波器
j=(k-1)*2+1; % 设置50Hz和它的奇次谐波频率
f0=50*j;
x1=cos(2*pi*tt*f0); % 设置x1和x2
x2=sin(2*pi*tt*f0);
w1=0; % %初始化w1和w2
w2=1;
e=zeros(1,N); % %初始化e和y
y=zeros(1,N);
mu=0.1; % 设置迭代步长
for i=1:N % 自适应陷波器
y(i)=w1*x1(i)+w2*x2(i); % 计算y
e(i)=x(i)-y(i); % 计算e
w1=w1+mu*e(i)*x1(i); % 调整w
w2=w2+mu*e(i)*x2(i);
end
x=e;
end
output=e; % 陷波器输出
% 作图
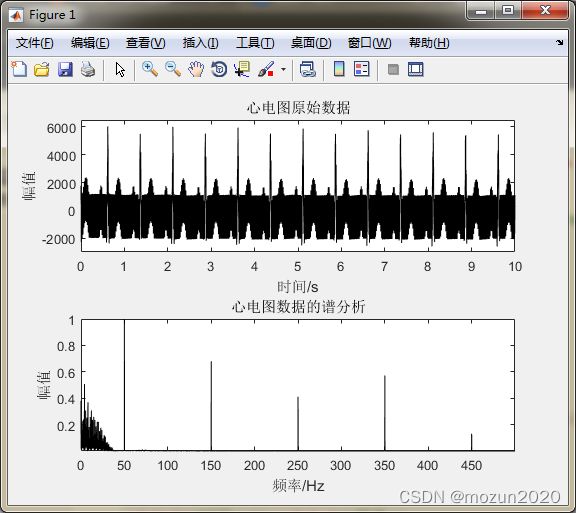
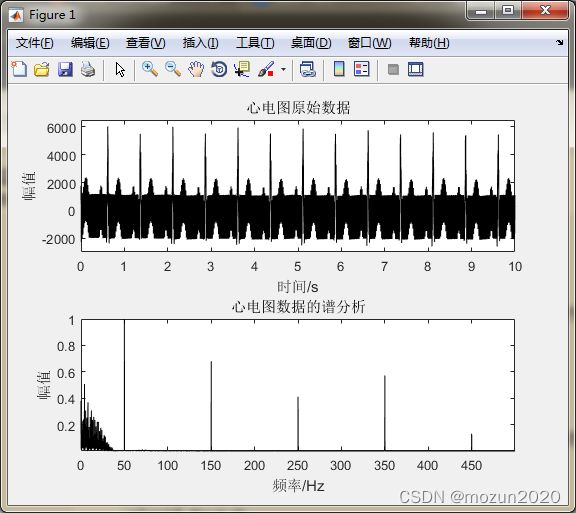
figure(1)
subplot 211; plot(tt,s,'k');
title('心电图原始数据'); xlabel('时间/s'); ylabel('幅值');
axis([0 10 -3000 6500]);
X=X/max(abs(X));
subplot 212; plot(ff,abs(X(n2)),'k');
axis tight; title('心电图数据的谱分析');
xlabel('频率/Hz'); ylabel('幅值');
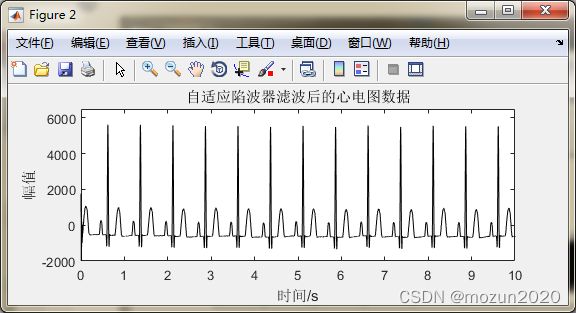
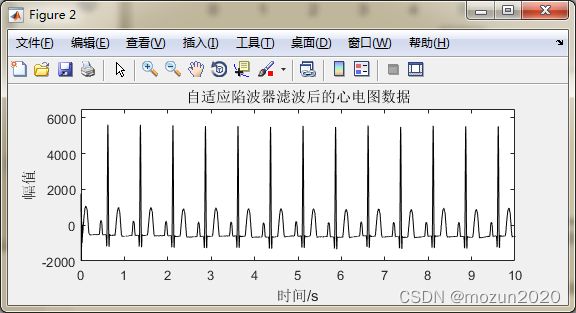
figure(2)
pos = get(gcf,'Position');
set(gcf,'Position',[pos(1), pos(2)-100,pos(3),(pos(4)-200)])
plot(tt,output,'k')
axis([0 10 -2000 6500]);
title('自适应陷波器滤波后的心电图数据');
xlabel('时间/s'); ylabel('幅值');
5. MATLAB仿真四:谱减法滤波减噪
%
% pr7_2_1
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [xx,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[xx,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
xx=xx-mean(xx); % 消除直流分量
x=xx/max(abs(xx)); % 幅值归一化
IS=0.25; % 设置前导无话段长度
wlen=200; % 设置帧长为25ms
inc=80; % 设置帧移为10ms
SNR=5; % 设置信噪比SNR
N=length(x); % 信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间
signal=Gnoisegen(x,SNR); % 叠加噪声
snr1=SNR_singlech(x,signal); % 计算初始信噪比
overlap=wlen-inc; % 求重叠区长度
NIS=fix((IS*fs-wlen)/inc +1); % 求前导无话段帧数
a=4; b=0.001; % 设置参数a和b
output=simplesubspec(signal,wlen,inc,NIS,a,b);% 谱减
snr2=SNR_singlech(x,output); % 计算谱减后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(signal,fs);
audioplayer(signal,fs);
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
% 作图
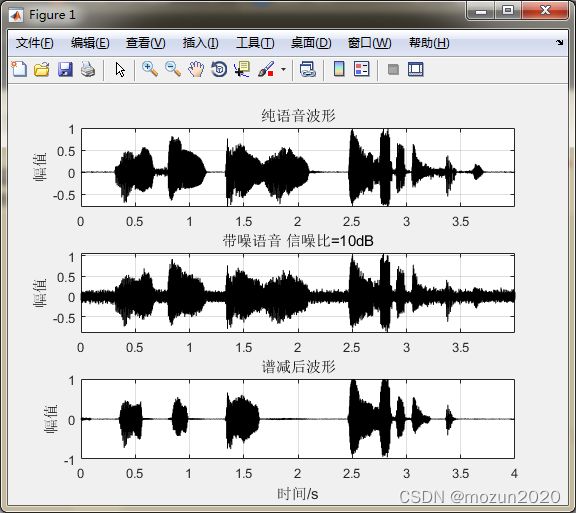
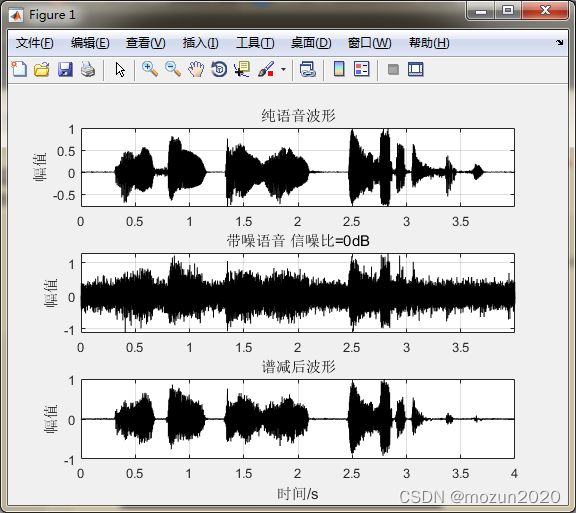
subplot 311; plot(time,x,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title('纯语音波形'); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 312; plot(time,signal,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title(['带噪语音 信噪比=' num2str(SNR) 'dB']); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');grid;%hold on;
title('谱减后波形'); ylabel('幅值'); xlabel('时间/s');
function output=simplesubspec(signal,wlen,inc,NIS,a,b)
wnd=hamming(wlen); % 设置窗函数
N=length(signal); % 计算信号长度
y=enframe(signal,wnd,inc)'; % 分帧
fn=size(y,2); % 求帧数
y_fft = fft(y); % FFT
y_a = abs(y_fft); % 求取幅值
y_phase=angle(y_fft); % 求取相位角
y_a2=y_a.^2; % 求能量
Nt=mean(y_a2(:,1:NIS),2); % 计算噪声段平均能量
nl2=wlen/2+1; % 求出正频率的区间
for i = 1:fn; % 按式(7-2-4)进行谱减
for k= 1:nl2
if y_a2(k,i)>a*Nt(k)
temp(k) = y_a2(k,i) - a*Nt(k);
else
temp(k)=b*y_a2(k,i);
end
U(k)=sqrt(temp(k)); % 把能量开方得幅值
end
X(:,i)=U;
end;
output=OverlapAdd2(X,y_phase(1:nl2,:),wlen,inc); % 合成谱减后的语音
Nout=length(output); % 把谱减后的数据长度补足与输入等长
if Nout>N
output=output(1:N);
elseif Nout<N
output=[output; zeros(N-Nout,1)];
end
output=output/max(abs(output)); % 幅值归一
6. MATLAB仿真五:改进谱减法滤波减噪
%
% pr7_2_2
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [xx,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[xx,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
xx=xx-mean(xx); % 消除直流分量
x=xx/max(abs(xx)); % 幅值归一化
SNR=10; % 设置信噪比
signal=Gnoisegen(x,SNR); % 叠加噪声
snr1=SNR_singlech(x,signal); % 计算叠加噪声后的信噪比
N=length(x); % 信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间刻度
IS=.15; % 设置IS
output=SSBoll79(signal,fs,IS); % 调用SSBoll79函数做谱减
ol=length(output); % 把output补到与x等长
if ol<N
output=[output; zeros(N-ol,1)];
end
snr2=SNR_singlech(x,output); % 计算谱减后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(signal,fs);
audioplayer(signal,fs);
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
% 作图
subplot 311; plot(time,x,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title('纯语音波形'); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 312; plot(time,signal,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title(['带噪语音 信噪比=' num2str(SNR) 'dB']); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');grid; ylim([-1 1]);
title('谱减后波形'); ylabel('幅值'); xlabel('时间/s');
function output=SSBoll79(signal,fs,IS)
% OUTPUT=SSBOLL79(S,FS,IS)
% Spectral Subtraction based on Boll 79. Amplitude spectral subtraction
% Includes Magnitude Averaging and Residual noise Reduction
% S is the noisy signal, FS is the sampling frequency and IS is the initial
% silence (noise only) length in seconds (default value is .25 sec)
%
% April-05
% Esfandiar Zavarehei
if (nargin<3 | isstruct(IS))
IS=.25; %seconds
end
W=fix(.025*fs); %Window length is 25 ms
nfft=W;
SP=.4; %Shift percentage is 40% (10ms) %Overlap-Add method works good with this value(.4)
wnd=hamming(W);
% IGNORE THIS SECTION FOR CAMPATIBALITY WITH ANOTHER PROGRAM FROM HERE.....
if (nargin>=3 & isstruct(IS))%This option is for compatibility with another programme
W=IS.windowsize
SP=IS.shiftsize/W;
nfft=IS.nfft;
wnd=IS.window;
if isfield(IS,'IS')
IS=IS.IS;
else
IS=.25;
end
end
% .......IGNORE THIS SECTION FOR CAMPATIBALITY WITH ANOTHER PROGRAM T0 HERE
NIS=fix((IS*fs-W)/(SP*W) +1);%number of initial silence segments
Gamma=1;%Magnitude Power (1 for magnitude spectral subtraction 2 for power spectrum subtraction)
y=segment(signal,W,SP,wnd);
Y=fft(y,nfft);
YPhase=angle(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)); %Noisy Speech Phase
Y=abs(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)).^Gamma;%Specrogram
numberOfFrames=size(Y,2);
FreqResol=size(Y,1);
N=mean(Y(:,1:NIS)')'; %initial Noise Power Spectrum mean
NRM=zeros(size(N));% Noise Residual Maximum (Initialization)
NoiseCounter=0;
NoiseLength=9;%This is a smoothing factor for the noise updating
Beta=.03;
YS=Y; %Y Magnitude Averaged
for i=2:(numberOfFrames-1)
YS(:,i)=(Y(:,i-1)+Y(:,i)+Y(:,i+1))/3;
end
for i=1:numberOfFrames
[NoiseFlag, SpeechFlag, NoiseCounter, Dist]=vad(Y(:,i).^(1/Gamma),N.^(1/Gamma),NoiseCounter); %Magnitude Spectrum Distance VAD
if SpeechFlag==0
N=(NoiseLength*N+Y(:,i))/(NoiseLength+1); %Update and smooth noise
NRM=max(NRM,YS(:,i)-N);%Update Maximum Noise Residue
X(:,i)=Beta*Y(:,i);
else
D=YS(:,i)-N; % Specral Subtraction
if i>1 && i<numberOfFrames %Residual Noise Reduction
for j=1:length(D)
if D(j)<NRM(j)
D(j)=min([D(j) YS(j,i-1)-N(j) YS(j,i+1)-N(j)]);
end
end
end
X(:,i)=max(D,0);
end
end
output=OverlapAdd2(X.^(1/Gamma),YPhase,W,SP*W);
function ReconstructedSignal=OverlapAdd2(XNEW,yphase,windowLen,ShiftLen);
%Y=OverlapAdd(X,A,W,S);
%Y is the signal reconstructed signal from its spectrogram. X is a matrix
%with each column being the fft of a segment of signal. A is the phase
%angle of the spectrum which should have the same dimension as X. if it is
%not given the phase angle of X is used which in the case of real values is
%zero (assuming that its the magnitude). W is the window length of time
%domain segments if not given the length is assumed to be twice as long as
%fft window length. S is the shift length of the segmentation process ( for
%example in the case of non overlapping signals it is equal to W and in the
%case of %50 overlap is equal to W/2. if not givven W/2 is used. Y is the
%reconstructed time domain signal.
%Sep-04
%Esfandiar Zavarehei
if nargin<2
yphase=angle(XNEW);
end
if nargin<3
windowLen=size(XNEW,1)*2;
end
if nargin<4
ShiftLen=windowLen/2;
end
if fix(ShiftLen)~=ShiftLen
ShiftLen=fix(ShiftLen);
disp('The shift length have to be an integer as it is the number of samples.')
disp(['shift length is fixed to ' num2str(ShiftLen)])
end
[FreqRes FrameNum]=size(XNEW);
Spec=XNEW.*exp(j*yphase);
if mod(windowLen,2) %if FreqResol is odd
Spec=[Spec;flipud(conj(Spec(2:end,:)))];
else
Spec=[Spec;flipud(conj(Spec(2:end-1,:)))];
end
sig=zeros((FrameNum-1)*ShiftLen+windowLen,1);
weight=sig;
for i=1:FrameNum
start=(i-1)*ShiftLen+1;
spec=Spec(:,i);
sig(start:start+windowLen-1)=sig(start:start+windowLen-1)+real(ifft(spec,windowLen));
end
ReconstructedSignal=sig;
function [NoiseFlag, SpeechFlag, NoiseCounter, Dist]=vad(signal,noise,NoiseCounter,NoiseMargin,Hangover)
%[NOISEFLAG, SPEECHFLAG, NOISECOUNTER, DIST]=vad(SIGNAL,NOISE,NOISECOUNTER,NOISEMARGIN,HANGOVER)
%Spectral Distance Voice Activity Detector
%SIGNAL is the the current frames magnitude spectrum which is to labeld as
%noise or speech, NOISE is noise magnitude spectrum template (estimation),
%NOISECOUNTER is the number of imediate previous noise frames, NOISEMARGIN
%(default 3)is the spectral distance threshold. HANGOVER ( default 8 )is
%the number of noise segments after which the SPEECHFLAG is reset (goes to
%zero). NOISEFLAG is set to one if the the segment is labeld as noise
%NOISECOUNTER returns the number of previous noise segments, this value is
%reset (to zero) whenever a speech segment is detected. DIST is the
%spectral distance.
%Saeed Vaseghi
%edited by Esfandiar Zavarehei
%Sep-04
if nargin<4
NoiseMargin=3;
end
if nargin<5
Hangover=8;
end
if nargin<3
NoiseCounter=0;
end
FreqResol=length(signal);
SpectralDist= 20*(log10(signal)-log10(noise));
SpectralDist(find(SpectralDist<0))=0;
Dist=mean(SpectralDist);
if (Dist < NoiseMargin)
NoiseFlag=1;
NoiseCounter=NoiseCounter+1;
else
NoiseFlag=0;
NoiseCounter=0;
end
% Detect noise only periods and attenuate the signal
if (NoiseCounter > Hangover)
SpeechFlag=0;
else
SpeechFlag=1;
end
function Seg=segment(signal,W,SP,Window)
% SEGMENT chops a signal to overlapping windowed segments
% A= SEGMENT(X,W,SP,WIN) returns a matrix which its columns are segmented
% and windowed frames of the input one dimentional signal, X. W is the
% number of samples per window, default value W=256. SP is the shift
% percentage, default value SP=0.4. WIN is the window that is multiplied by
% each segment and its length should be W. the default window is hamming
% window.
% 06-Sep-04
% Esfandiar Zavarehei
if nargin<3
SP=.4;
end
if nargin<2
W=256;
end
if nargin<4
Window=hamming(W);
end
Window=Window(:); %make it a column vector
L=length(signal);
SP=fix(W.*SP);
N=fix((L-W)/SP +1); %number of segments
Index=(repmat(1:W,N,1)+repmat((0:(N-1))'*SP,1,W))';
hw=repmat(Window,1,N);
Seg=signal(Index).*hw;
7. MATLAB仿真六:维纳滤波法滤波减噪一
%
% pr7_2_3
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [xx,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[xx,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
xx=xx-mean(xx); % 消除直流分量
x=xx/max(abs(xx)); % 幅值归一化
SNR=10; % 设置信噪比
signal=Gnoisegen(x,SNR); % 叠加噪声
snr1=SNR_singlech(x,signal); % 计算叠加噪后的信噪比
N=length(x); % 信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间
IS=.15; % 设置IS
% 调用SSBoll79m_2函数做谱减
[output,voiceseg,vosl,SF,Ef]=SSBoll79m_2(signal,fs,IS,0.12);
ol=length(output); % 把output补到与x等长
if ol<N
output=[output; zeros(N-ol,1)];
end
snr2=SNR_singlech(x,output); % 计算谱减后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(signal,fs);
audioplayer(signal,fs);
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
% 作图
subplot 311; plot(time,x,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title('纯语音波形'); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 312; plot(time,signal,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title(['带噪语音 信噪比=' num2str(SNR) 'dB']); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');grid; ylim([-1 1]);
title('谱减后波形'); ylabel('幅值'); xlabel('时间/s');
function [output,voiceseg,vosl,SF,Ef]=SSBoll79m_2(signal,fs,IS,T1)
% OUTPUT=SSBOLL79(S,FS,IS)
% Spectral Subtraction based on Boll 79. Amplitude spectral subtraction
% Includes Magnitude Averaging and Residual noise Reduction
% S is the noisy signal, FS is the sampling frequency and IS is the initial
% silence (noise only) length in seconds (default value is .25 sec)
%
% April-05
% Esfandiar Zavarehei
if (nargin<3 | isstruct(IS)) % 如果输入参数小于3个或IS是结构数据
IS=.25; %seconds
end
W=fix(.025*fs); % 帧长为25ms
nfft=W; % 设置FFT长度
SP=.4; % 帧移比例取40%(10ms)
wnd=hamming(W); % 设置窗函数
% 如果输入参数大于或等于3个并IS是结构数据(为了兼容其他程序)
if (nargin>=3 & isstruct(IS))
W=IS.windowsize
SP=IS.shiftsize/W;
nfft=IS.nfft;
wnd=IS.window;
if isfield(IS,'IS')
IS=IS.IS;
else
IS=.25;
end
end
% .......IGNORE THIS SECTION FOR CAMPATIBALITY WITH ANOTHER PROGRAM T0 HERE
NIS=fix((IS*fs-W)/(SP*W) +1); % 计算无话段帧数
% Gamma=1时为幅值谱减法,Gamma=2为功率谱减法
Gamma=1; % 设置Gamma
y=segment(signal,W,SP,wnd);
Y=fft(y,nfft);
YPhase=angle(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)); % 带噪语音的相位角
Y=abs(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)).^Gamma; % 取正频率谱值
numberOfFrames=size(Y,2); % 计算总帧数
FreqResol=size(Y,1); % 计算频谱中的谱线数
N=mean(Y(:,1:NIS)')'; % 计算无话段噪声平均谱值
NRM=zeros(size(N)); % 初始化
NoiseCounter=0;
NoiseLength=9; % 设置噪声平滑区间长度
Beta=.03; % 设置谱平滑因子
fn=numberOfFrames;
miniL=5;
[voiceseg,vosl,SF,Ef]=pitch_vad1(y,fn,T1,miniL); %端点检测
YS=Y; % 谱在相邻帧之间平均
for i=2:(numberOfFrames-1)
YS(:,i)=(Y(:,i-1)+Y(:,i)+Y(:,i+1))/3;
end
for i=1:numberOfFrames
% 取来一帧数据判断是否为有话帧
% [NoiseFlag, SpeechFlag, NoiseCounter, Dist]=vad(Y(:,i).^(1/Gamma),...
% N.^(1/Gamma),NoiseCounter);
SpeechFlag=SF(i);
if SpeechFlag==0 % 在无话段中平滑更新噪声谱值
N=(NoiseLength*N+Y(:,i))/(NoiseLength+1);
NRM=max(NRM,YS(:,i)-N); % 求取噪声最大残留值
X(:,i)=Beta*Y(:,i);
else
D=YS(:,i)-N; % 谱减法消噪
if i>1 && i<numberOfFrames % 消去噪声的残留值
for j=1:length(D)
if D(j)<NRM(j)
D(j)=min([D(j) YS(j,i-1)-N(j) YS(j,i+1)-N(j)]);
end
end
end
X(:,i)=max(D,0); % 每条谱线幅值都大于0
end
end
output=OverlapAdd2(X.^(1/Gamma),YPhase,W,SP*W);% 消噪后的频谱幅值和相位角合成语音
output=output/max(abs(output));
8. MATLAB仿真七:维纳滤波法滤波减噪二
%
% pr7_2_4
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [xx,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[xx,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
xx=xx-mean(xx); % 消除直流分量
x=xx/max(abs(xx)); % 幅值归一化
SNR=0; % 设置初始信噪比
[signal,n0]=Gnoisegen(x,SNR); % 叠加噪声
snr1=SNR_singlech(x,signal); % 计算叠加噪后的信噪比
IS=0.15; % 前导无话段长度(s)
alpha=2.8; % 过减因子
beta=0.001; % 增益补偿因子
%c=0时,用功率谱计算增益矩阵不进行开方运算,c=1时,进行开方运算
c=1;
N=length(signal); % 信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间
wlen=200; % 设置帧长
inc=80; % 设置帧移
NIS=fix((IS*fs-wlen)/inc +1); % 前导无话段帧数
output=Mtmpsd_ssb(signal,wlen,inc,NIS,alpha,beta,c);% 多窗谱改进谱减法减噪处理
snr2=SNR_singlech(x,output); % 计算谱减后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(signal,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
audioplayer(signal,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
%作图
subplot 311; plot(time,x,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title('纯语音波形'); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 312; plot(time,signal,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title(['带噪语音 信噪比=' num2str(SNR) 'dB']); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');grid;%hold on;
title('谱减后波形'); ylabel('幅值'); xlabel('时间/s');
function output=Mtmpsd_ssb(signal,wlen,inc,NIS,alpha,beta,c)
w2=wlen/2+1;
wind=hamming(wlen); % 定义汉明窗
y=enframe(signal,wind,inc)'; % 分帧
fn=size(y,2); % 求帧数
N=length(signal); % 信号长度
fft_frame=fft(y); % 对每帧信号计算FFT
abs_frame=abs(fft_frame(1:w2,:)); % 取正频率部分的幅值
ang_frame=angle(fft_frame(1:w2,:)); % 取正频率部分的相位角
% 相邻3帧平滑
abs_frame_f=abs_frame;
for i=2:fn-1;
abs_frame_f(:,i)=.25*abs_frame(:,i-1)+.5*abs_frame(:,i)+.25*abs_frame(:,i+1);
end;
abs_frame=abs_frame_f;
% 用多窗谱法对每一帧数据进行功率谱估计
for i=1:fn;
per_PSD(:,i)=pmtm(y(:,i),3,wlen);
end;
% 对功率谱的相邻3帧进行平滑
per_PSD_f=per_PSD;
for i=2:fn-1;
per_PSD_f(:,i)=.25*per_PSD(:,i-1)+.5*per_PSD(:,i)+.25*per_PSD(:,i+1);
end;
per_PSD=per_PSD_f;
% 在前导无话段中求取噪声平均功率谱
noise_PSD=mean(per_PSD(:,1:NIS),2);
% 谱减求取增益因子
for k=1:fn;
g(:,k)=(per_PSD(:,k)-alpha*noise_PSD)./per_PSD(:,k);
g_n(:,k)=beta*noise_PSD./per_PSD(:,k);
gix=find(g(:,k)<0);
g(gix,k)=g_n(gix,k);
end;
gf=g;
if c==0, g=gf; else g=gf.^0.5; end; % 按参数c开方与否
sub_frame=g.*abs_frame; % 用增益因子计算谱减后的幅值
output=OverlapAdd2(sub_frame,ang_frame,wlen,inc); % 语音合成
output=output/max(abs(output)); % 幅值归一化
ol=length(output); % 把output补到与x等长
if ol<N
output=[output; zeros(N-ol,1)];
end
9. MATLAB仿真八:维纳滤波法滤波减噪三
%
% pr7_3_1
clear all; clc; close all;
filedir=[]; % 指定文件路径
filename='bluesky1.wav'; % 指定文件名
fle=[filedir filename] % 构成路径和文件名的字符串
% [xx,fs]=wavread(fle); % 读入数据文件
[xx,fs]=audioread(fle); % 读入数据文件
xx=xx-mean(xx); % 消除直流分量
x=xx/max(abs(xx)); % 幅值归一化
SNR=5; % 设置SNR
signal=Gnoisegen(x,SNR); % 叠加噪声
snr1=SNR_singlech(x,signal); % 计算叠加噪声后的信噪比
N=length(x); % 信号长度
time=(0:N-1)/fs; % 设置时间
IS=.15; % 设置IS
% 调用WienerScalart96m_2函数做维纳滤波
output=WienerScalart96m_2(signal,fs,IS,0.12);
ol=length(output); % 把output补到与x等长
if ol<N
output=[output; zeros(N-ol,1)];
end
snr2=SNR_singlech(x,output); % 计算维纳滤波后的信噪比
snr=snr2-snr1;
fprintf('snr1=%5.4f snr2=%5.4f snr=%5.4f\n',snr1,snr2,snr);
% wavplay(signal,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
audioplayer(signal,fs); % 从声卡发声比较
pause(1)
% wavplay(output,fs);
audioplayer(output,fs);
% 作图
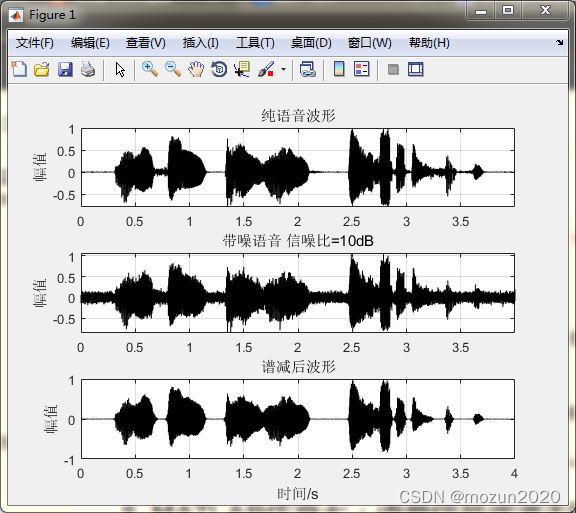
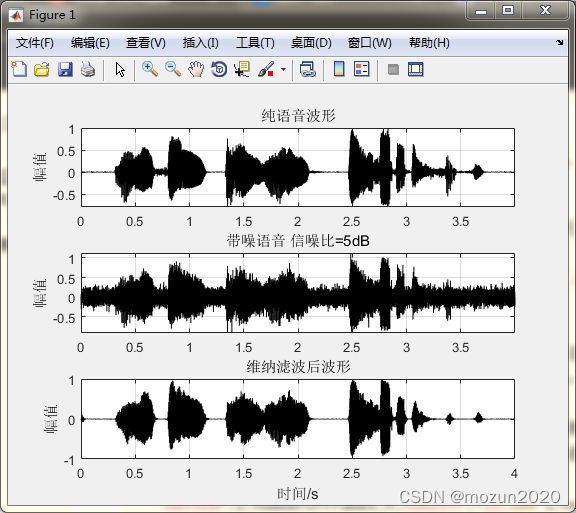
subplot 311; plot(time,x,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title('纯语音波形'); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 312; plot(time,signal,'k'); grid; axis tight;
title(['带噪语音 信噪比=' num2str(SNR) 'dB']); ylabel('幅值')
subplot 313; plot(time,output,'k');grid; ylim([-1 1]);
title('维纳滤波后波形'); ylabel('幅值'); xlabel('时间/s');
function output=WienerScalart96m_2(signal,fs,IS,T1)
% output=WIENERSCALART96(signal,fs,IS)
% Wiener filter based on tracking a priori SNR usingDecision-Directed
% method, proposed by Scalart et al 96. In this method it is assumed that
% SNRpost=SNRprior +1. based on this the Wiener Filter can be adapted to a
% model like Ephraims model in which we have a gain function which is a
% function of a priori SNR and a priori SNR is being tracked using Decision
% Directed method.
% Author: Esfandiar Zavarehei
% Created: MAR-05
if (nargin<3 | isstruct(IS)) % 如果输入参数小于3个或IS是结构数据
IS=.25;
end
W=fix(.025*fs); % 帧长为25ms
SP=.4; % 帧移比例取40%(10ms)
wnd=hamming(W); % 设置窗函数
% 如果输入参数大于或等于3个并IS是结构数据(为了兼容其他程序)
if (nargin>=3 & isstruct(IS))
SP=IS.shiftsize/W;
nfft=IS.nfft;
wnd=IS.window;
if isfield(IS,'IS')
IS=IS.IS;
else
IS=.25;
end
end
pre_emph=0;
signal=filter([1 -pre_emph],1,signal); % 预加重
NIS=fix((IS*fs-W)/(SP*W) +1); % 计算无话段帧数
y=segment(signal,W,SP,wnd); % 分帧
Y=fft(y); % FFT
YPhase=angle(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)); % 带噪语音的相位角
Y=abs(Y(1:fix(end/2)+1,:)); % 取正频率谱值
numberOfFrames=size(Y,2); % 计算总帧数
FreqResol=size(Y,1); % 计算频谱中的谱线数
N=mean(Y(:,1:NIS)')'; % 计算无话段噪声平均谱值
LambdaD=mean((Y(:,1:NIS)').^2)'; % 初始噪声功率谱方差
alpha=.99; % 设置平滑系数
fn=numberOfFrames;
miniL=5; % 设置miniL
[voiceseg,vosl,SF,Ef]=pitch_vad1(y,fn,T1,miniL); %端点检测
NoiseCounter=0; % 初始化NoiseCounter
NoiseLength=9; % 设置噪声平滑区间长度
G=ones(size(N)); % 初始化谱估计器
Gamma=G;
X=zeros(size(Y)); % 初始化X
h=waitbar(0,'Wait...'); % 设置运行进度条图
for i=1:numberOfFrames
SpeechFlag=SF(i);
if i<=NIS % 若i<=NIS在前导无声(噪声)段
SpeechFlag=0;
NoiseCounter=100;
%else % i>NIS判断是否为有话帧
%[NoiseFlag, SpeechFlag, NoiseCounter, Dist]=vad(Y(:,i),N,NoiseCounter);
end
if SpeechFlag==0 % 在无话段中平滑更新噪声谱值
N=(NoiseLength*N+Y(:,i))/(NoiseLength+1);
LambdaD=(NoiseLength*LambdaD+(Y(:,i).^2))./(1+NoiseLength);%更新和平滑噪声方差
end
gammaNew=(Y(:,i).^2)./LambdaD; % 计算后验信噪比
xi=alpha*(G.^2).*Gamma+(1-alpha).*max(gammaNew-1,0); % 计算先验信噪比
Gamma=gammaNew;
G=(xi./(xi+1)); % 计算维纳滤波器的谱估计器
X(:,i)=G.*Y(:,i); % 维纳滤波后的幅值
%显示运行进度条图
waitbar(i/numberOfFrames,h,num2str(fix(100*i/numberOfFrames)));
end
close(h); % 关闭运行进度条图
output=OverlapAdd2(X,YPhase,W,SP*W); % 语音合成
output=filter(1,[1 -pre_emph],output); % 消除预加重影响
output=output/max(abs(output));
小结
语音信号的滤波减噪是语音识别在现实应用中的关键环节,因为在现实生活的应用场景下,噪声无处不在,各种各样,针对不同类型的噪声,不同的滤波处理方式效果不同。本章就是介绍针对常见的噪声类型时,应用的一些的滤波处理方法,实现语音滤波减噪。
对本章内容感兴趣或者想充分学习了解的,建议去研习书中第七章节的内容。后期会对其中一些知识点在自己理解的基础上进行讨论补充,欢迎大家一起学习交流。
关于宋老师:宋知用——默默传授MATLAB与信号处理知识的老人家
本系列文章列表如下:
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第2章 语音信号的时域、频域特性和短时分析技术
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第3章 语音信号在其他变换域中的分析技术和特性
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第4章 语音信号的线性预测分析
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第5章 带噪语音和预处理
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第6章 语音端点的检测(1)
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第6章 语音端点的检测(2)
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第7章 语音信号的减噪
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第8章 基音周期的估算方法
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第9章 共振峰的估算方法
《MATLAB语音信号分析与合成(第二版)》:第10章 语音信号的合成算法