scikit-learn 决策树入门实践 iris花分类
背景
为了了解sklearn的API,以及决策树的工作原理,本文以经典的花分类问题为例,编写代码并讲解。最后深入源代码查看其实现
关键词:决策树、基尼系数、决策树可视化、特征重要性。
代码案例
训练决策树
首先要准备数据集,并调用sklearn的API训练决策树。
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn import tree
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
iris = load_iris()
print("feature names", iris.feature_names)
print("target names", iris.target_names)
X = iris.data[:, 2:]
y = iris.target
print("data shape", iris.data.shape)
print("X shape", X.shape)
输出如下,每个样本有4个特征,且标签有3种取值。
feature names ['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
target names ['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
取出特征集和标签集。本案例每个样本只选取后两个特征"petal length"和"petal width"(通过切片方式iris.data[:, 2:])。
X = iris.data[:, 2:]
y = iris.target
print("data shape", iris.data.shape)
print("X shape", X.shape)
尝试输出特征集如下:
data shape (150, 4)的含义是,原本数据集有150个样本,每个样本原本有4个特征。X shape (150, 2)的含义是,由于每个样本只取后两个特征,其列数只为2。
data shape (150, 4)
X shape (150, 2)
之后,创建决策树并拟合,这里设置了最大深度为2,限制决策树的高度最多为2。
tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2)
tree_clf.fit(X, y)
绘制决策树
绘制决策树图片。sklearn提供了plot_tree的接口。
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(25,20))
_ = tree.plot_tree(
tree_clf,
feature_names=iris.feature_names[2:],
class_names=iris.target_names,
filled=True
)
# Save picture
fig.savefig("decistion_tree.png")
调用tree_clf.feature_importances_可以输出决策树的特征重要性:
print("feature_importances_", tree_clf.feature_importances_)
其输出如下,两个特征的重要性分别是0.0和1.0,为什么这样呢?
feature_importances_ [0. 1.]
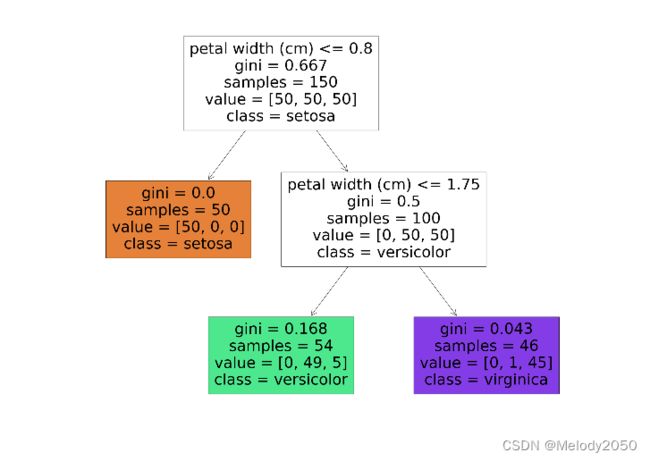
回看决策树的图,可以发现两个树中节点的判断条件分别是"petal width <= 0.8"和"petal width <= 1.75",也就是说,只用到了"petal width"这个属性,而没用到"petal length"属性。
另外,可以检验图中节点的基尼系数。取绿色的树节点为例,样本数为54,判断成3种类别的样本数分别是0、49、5。
根据基尼系数公式,计算得到 1 − ( 49 / 54 ) 2 − ( 5 / 54 ) 2 = 0.168 1-(49/54)^2-(5/54)^2=0.168 1−(49/54)2−(5/54)2=0.168。
决策树的基尼系数公式此处不再赘述,不是本文重点
代码案例2 观察特征重要性
上一例生成的决策树节点只用到了pedal width属性,从而难以校验特征重要性的计算公式。本例把决策树的最大深度从2改为3,鼓励其使用到两种属性。
tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3)
其生成的决策树可视化如下:
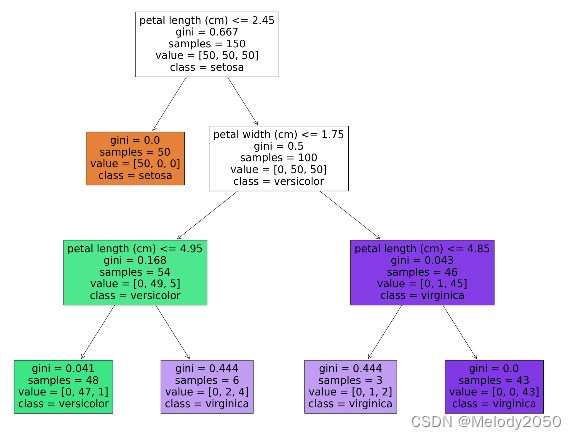
输出的两个特征的特征重要性分别是0.58和0.41
feature_importances_ [0.58561555 0.41438445]
验证特征重要性
本节将对这两个数据做验证。两种属性各个取值的基尼系数增益如下
- "petal length<=4.85"的基尼系数增益为 0.043 − 0.444 ∗ 3 46 − 0.0 ∗ 43 46 = 0.014 0.043-0.444 * \frac{3}{46} - 0.0 * \frac{43}{46}=0.014 0.043−0.444∗463−0.0∗4643=0.014
- "petal length<=4.95"的基尼系数增益为 0.168 − 0.041 ∗ 48 54 − 0.444 ∗ 6 54 = 0.082 0.168-0.041 * \frac{48}{54} - 0.444 * \frac{6}{54}=0.082 0.168−0.041∗5448−0.444∗546=0.082
- "petal length<=2.45"的基尼系数增益为 0.667 − 0.0 ∗ 50 150 − 0.5 ∗ 100 150 = 0.33 0.667-0.0 * \frac{50}{150} - 0.5* \frac{100}{150}=0.33 0.667−0.0∗15050−0.5∗150100=0.33
- "petal width<=1.75"的基尼系数增益为 0.5 − 0.168 ∗ 54 100 − 0.043 ∗ 46 100 = 0.38 0.5- 0.168 * \frac{54}{100} - 0.043 * \frac{46}{100}=0.38 0.5−0.168∗10054−0.043∗10046=0.38
所以,属性的基尼系数增益之和,为其各个划分点的基尼系数加权和。
- petal length的基尼系数增益之和为 0.014 ∗ 46 / 150 + 0.082 ∗ 54 / 150 + 0.33 ∗ 150 / 150 = 0.36 0.014*46/150+0.082*54/150+0.33*150/150=0.36 0.014∗46/150+0.082∗54/150+0.33∗150/150=0.36
- petal width的基尼系数增益之和 0.38 ∗ 100 / 150 = 0.25 0.38*100/150=0.25 0.38∗100/150=0.25
两者作归一化后,得到0.36 / (0.36+0.25)=0.59,似乎与输出有一点偏差,这是由于舍去小数位末尾导致的。
二次验证
合并公式计算并观察可知,加权系数之间的分子分母可以消除。
也就是说 ( 0.043 − 0.444 ∗ 3 46 − 0.0 ∗ 43 46 ) ∗ 46 / 150 = 0.043 ∗ 46 / 150 − 0.444 ∗ 3 / 150 − 0.0 ∗ 43 / 150 = 0.0043 (0.043-0.444 * \frac{3}{46} - 0.0 * \frac{43}{46})*46/150=0.043*46/150-0.444*3/150-0.0*43/150=0.0043 (0.043−0.444∗463−0.0∗4643)∗46/150=0.043∗46/150−0.444∗3/150−0.0∗43/150=0.0043
以此法引用于每个划分点,可以计算得到另外几项:
- 0.168 ∗ 54 / 150 − 0.041 ∗ 48 / 150 − 0.444 ∗ 6 / 150 = 0.0296 0.168*54/150-0.041 *48/150 - 0.444 *6/150=0.0296 0.168∗54/150−0.041∗48/150−0.444∗6/150=0.0296
- 0.667 − 0.0 ∗ 50 / 150 − 0.5 ∗ 100 / 150 = 0.33 0.667-0.0 * 50/150 - 0.5* 100/150=0.33 0.667−0.0∗50/150−0.5∗100/150=0.33
- 0.5 ∗ 100 / 150 − 0.168 ∗ 54 / 150 − 0.043 ∗ 46 / 150 = 0.259 0.5*100/150- 0.168 * 54/150 - 0.043 * 46/150=0.259 0.5∗100/150−0.168∗54/150−0.043∗46/150=0.259
所以,两个属性的基尼系数增益之和为0.367、和0.259,归一化得到0.586和0.414,非常接近于程序输出。
由此,我们可以得出结论,计算某属性的特征重要性,首先要求各个特征值的基尼系数增益,再各自乘以全局加权系数,并求和,
特征重要性的源码实现
建议先阅读参考文章:
- feature_importances_ - 从决策树到gbdt
- sklearn源码解析:ensemble模型 零碎记录;如何看sklearn代码,以tree的feature_importance为例
在sklearn,特征重要性的计算核心函数是cpython文件_tree.pyx的的compute_feature_importances。
cpdef compute_feature_importances(self, normalize=True):
"""Computes the importance of each feature (aka variable)."""
cdef Node* left
cdef Node* right
cdef Node* nodes = self.nodes
cdef Node* node = nodes
cdef Node* end_node = node + self.node_count
cdef double normalizer = 0.
cdef np.ndarray[np.float64_t, ndim=1] importances
importances = np.zeros((self.n_features,))
cdef DOUBLE_t* importance_data = <DOUBLE_t*>importances.data
with nogil:
while node != end_node:
if node.left_child != _TREE_LEAF:
# ... and node.right_child != _TREE_LEAF:
left = &nodes[node.left_child]
right = &nodes[node.right_child]
importance_data[node.feature] += (
node.weighted_n_node_samples * node.impurity -
left.weighted_n_node_samples * left.impurity -
right.weighted_n_node_samples * right.impurity)
node += 1
importances /= nodes[0].weighted_n_node_samples
if normalize:
normalizer = np.sum(importances)
if normalizer > 0.0:
# Avoid dividing by zero (e.g., when root is pure)
importances /= normalizer
return importances
其中,以下代码所做行为就是在计算某特征值的加权基尼系数增益。
importance_data[node.feature] += (
node.weighted_n_node_samples * node.impurity -
left.weighted_n_node_samples * left.impurity -
right.weighted_n_node_samples * right.impurity)
importance_data[node.feature]的+=符号代表这个节点的增益值归属于它的所属特征,由于一个特征可能会有多个划分值(比如"petal length<=4.85"和"petal length<=4.95"都属于petal length),所以它们的增益要累加。
.impurity里的其实就是基尼系数。
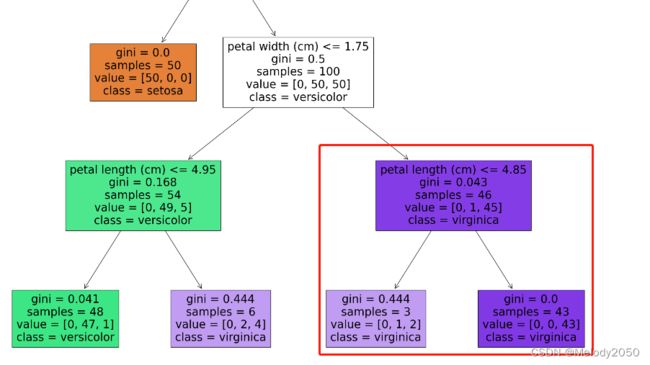
weighted_n_node_samples 的含义应该是该节点的全局加权系数,即该节点的样本数除以全局样本数 n n o d e / n t o t a l n_{node}/n_{total} nnode/ntotal。比如对于上一例里右下角三个节点的全局加权系数分别是46/150、3/150、43/150。
importances /= nodes[0].weighted_n_node_samples的含义是,最后除以根节点的全局加权系数。但笔者认为通常这个值就是1。
如果设置要进行归一化,就最后除以总和,保证各特征值相加为1。
if normalize:
normalizer = np.sum(importances)
if normalizer > 0.0:
# Avoid dividing by zero (e.g., when root is pure)
importances /= normalizer
总结
- 以sklearn基于iris数据集构建决策树为例,实践了构建决策树、可视化决策树的API。
- 证实了"特征重要性等于基尼系数增益"的说法,以及全局加权系数的含义指 n n o d e / n t o t a l n_{node}/n_{total} nnode/ntotal,手推了计算过程,并结合源码分析进一步作证。