灰度图像处理——基于GPU的并行编程模型CUDA程序设计
灰度图像处理——基于GPU的并行编程模型CUDA程序设计
目录
- 灰度图像处理——基于GPU的并行编程模型CUDA程序设计
-
- 1 题目描述
- 2 设计思路
-
- 实验环境
- 3 源码
-
- 3.1 串行程序
- 3.2 并行程序
- 3.3 性能对比与分析
- 4 OpenCV与RGB2Gray及其算法的具体解释优化
1 题目描述
用CUDA设计一个将RGB图像转换生成灰度图像的程序,要求通过实例测试串行程序和GPU并行程序的执行效率(要求处理至少100张图片)。
效果如图:

2 设计思路
RGB彩色图像中,一种彩色由R(红色),G(绿色),B(蓝色)三原色按比例混合而成。图像的基本单元是一个像素,就像一个巨幅电子广告屏上远处看是衣服图像,走近你会看到一个一个的方格,这个方格的颜色是一种,从远处看,觉察不到这个方格的存在。
一个像素需要3块表示,分别代表R,G,B,如果8为表示一个颜色,就由0-255区分不同亮度的某种原色。一张9像素的8位RGB图像,在计算机内存中的分布大概示意如下:
实际中数都是二进制形式的,并且未必按照R,G,B顺序,比如OpenCV是按照B,G,R顺序将三个色值保存在3个连续的字节里
灰度图像是用不同饱和度的黑色来表示每个图像点,比如用8位 0-255数字表示“灰色”程度,每个像素点只需要一个灰度值,8位即可,这样一个3X3的灰度图,只需要9个byte就能保存RGB值和灰度的转换,实际上是人眼对于彩色的感觉到亮度感觉的转换,这是一个心理学问题,有一个公式:
Grey = 0.299*R + 0.587*G + 0.114*B
根据这个公式,依次读取每个像素点的R,G,B值,进行计算灰度值(转换为整型数),将灰度值赋值给新图像的相应位置,所有像素点遍历一遍后完成转换。
实验环境
操作系统:Windows10
开发环境:Visual Studio 2019 + CUDA Toolkit 11.0 + OpenCV
3 源码
文件位置说明:
彩色图片素材应存放在项目文件夹下的Picture文件夹下
转为灰度的图片存放在项目文件夹下的GrayPicture文件夹下
存放gputime和cputime的文件为time.txt,位于项目文件夹下
100张彩色图片资源链接:
https://wwe.lanzoui.com/iDYY4swrahe
https://wwe.lanzoui.com/i7QQUswrchg
https://wwe.lanzoui.com/itU8Cswre5g
3.1 串行程序
灰度图像处理的CPU程序
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include 3.2 并行程序
灰度图像处理的GPU程序并记录下GPU程序和CPU程序消耗的时间
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include 3.3 性能对比与分析
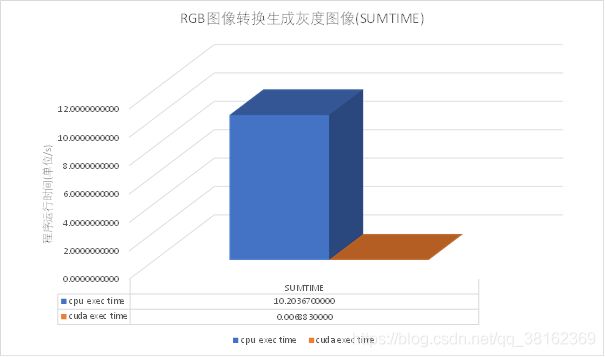
我们从图1和图2中可以看出通过CUDA编程的GPU程序处理RGB图像转换生成灰度图像问题时消耗的时间远小于通过CPU处理的时间,处理120张图片CPU程序的耗时大约是GPU程序耗时的1482倍。
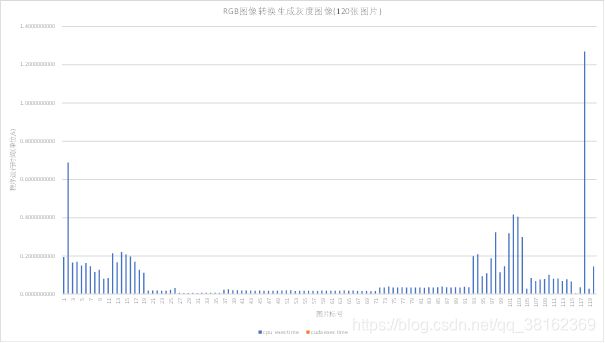
图2 RGB图像转换生成灰度图像(SUMTIME)
4 OpenCV与RGB2Gray及其算法的具体解释优化
RGB彩色图像中,一种彩色由R(红色),G(绿色),B(蓝色)三原色按比例混合而成。图像的基本单元是一个像素,就像一个巨幅电子广告屏上远处看是衣服图像,走近你会看到一个一个的方格,这个方格的颜色是一种,从远处看,觉察不到这个方格的存在。
一个像素需要3块表示,分别代表R,G,B,如果8为表示一个颜色,就由0-255区分不同亮度的某种原色。
实际中数都是二进制形式的,并且未必按照R,G,B顺序,比如OpenCV是按照B,G,R顺序将三个色值保存在3个连续的字节里。
灰度图像是用不同饱和度的黑色来表示每个图像点,比如用8位 0-255数字表示“灰色”程度,每个像素点只需要一个灰度值,8位即可,这样一个3X3的灰度图,只需要9个byte就能保存RGB值和灰度的转换,实际上是人眼对于彩色的感觉到亮度感觉的转换,这是一个心理学问题,有一个公式:
Grey = 0.299*R + 0.587*G + 0.114*B
根据这个公式,依次读取每个像素点的R,G,B值,进行计算灰度值(转换为整型数),将灰度值赋值给新图像的相应位置,所有像素点遍历一遍后完成转换。
一张500X500的图像转换为同样大小的灰度图需要进行25万次上述公式的计算。进行优化是很有必要的,这个简单的算法是O(n)复杂度的,应该是不能优化了(或者用并行进行优化,本文不涉及),但是Grey = 0.299*R + 0.587*G + 0.114*B有更加高效的等价形式。
在ALU中,位操作快于整数加法,整数加法快于整数乘法(快多少取决于有没有乘法电路,乘法电路的结构),整数运算又比浮点数运算快得多。所以可以通过将浮点数运算转化为整数运算,整数运算转换为位操作进行优化
Grey = 0.299*R + 0.587*G + 0.114*B
可以转化为
Grey = (299*R + 587*G + 114*B + 500) /1000;
整数运算会截断小数部分,加上500是为了四舍五入(找两个例子便可理解),减少精度损失。这里的除法( 即使是整数除法计算也是很耗时),转换为移位操作可以优化,那么怎么转换为位操作?左右移位对应于乘除2的幂,为了把除法转为右移操作,做如下处理:
Grey = 0.299*R+0.587*G+0.114*B
Grey = (299*R+587*G+114*B)÷ 1000
Grey = (1024*299*R+1024*587*G+1024*114*B)÷(1024*1000)
Grey = (306176*R+601088*G+116736*B)÷(1024*1000)
Grey = (306.176*R+601.088*G+116.736*B)÷(1024)
Grey = (306*R+601*G+116*B)÷(1024)//截断误差
Grey = (306*R+601*G+116*B) >> 10;
误差最大是多少?(0.176*255+0.088*255+0.736*255)÷1024 = 255÷1024 = 0.249,可能会导致1个灰度值的波动。有一种计算方法可以降低误差
R的系数 = 1024*0.229 = 306.176 ≈ 306
G的系数 = 1024*0.587+0.176 = 601.264 ≈ 601
B的系数 = 1024*0.114+0.264 = 117
保留了小数部分的作用,可以得到一个误差较小的公式:
Grey = (306*R+601*G+117*B) >> 10;
这样得来的是10位精度的。
同样的方法可以获得其他精度的,比如
Grey = (R*1 + G*2 + B*1) >> 2 (Grey = (R + G<<1 + B) >> 2
Grey = (R*38 + G*75 + B*15) >> 7
Grey = (R*76 + G*150 + B*30) >> 8
Grey = (R*19595 + G*38469 + B*7472) >> 16