Neuralizing Regular Expressions for Slot Filling 神经网络转回自动机
Neuralizing Regular Expressions for Slot Filling 神经网络转回自动机
本文为作者个人观点,仅供参考、交流、学习
论文地址:Neuraling Regular Expressions for Slot Filling
GitHub地址:RE2NN-SEQ
在论文中,讲述了如何将正则表达式转换为神经网络(具体流程见Neuralizing Regular Expressions for Slot Filling 流程解析)并且在zero-shot或者few-shot的情况下均优于其它方法
与其它方法对比图
根据屠可伟教授的分享,正则表达式转换成的神经网络可以转换成自动机,为研究神经网络的可解释性提供了新的思路。但在文中并没有提出具体的转换方法。于是我按照屠可伟教授的思路,将i-FST分解成的三个权值矩阵经过训练后重新合并,然后对其round,尝试获得新的自动机。
合并三个权值矩阵
with torch.no_grad():
V = tl.tensor(model.V_embed)
S1 = tl.tensor(model.S1)
S2 = tl.tensor(model.S2)
t_mat = tl.kruskal_to_tensor((np.ones(args.rank), [V, S1, S2]))
t_mat = np.round(t_mat)
构建新的自动机
new_automata = AutomataMultipleStart()
automata_dicts = load_pkl(args.automata_path)
new_automata.states = automata_dicts['automata']['states']
new_automata.startstate = automata_dicts['automata']['startstate']
new_automata.finalstates = automata_dicts['automata']['finalstates']
# 可选项,加上则是在原自动机的基础上新增转移情况,不加则是单纯构建新的自动机,本文选择不加
# new_automata.transitions = automata_dicts['automata']['transitions']
for i in trange(t_mat.shape[0]):
for j in range(t_mat.shape[1]):
for k in range(t_mat.shape[2]):
if t_mat[i][j][k] == 1:
for s in range(C_output_mat.shape[0]):
if C_output_mat[s][k] == 1:
break
if s == C_output_mat.shape[0]-1:
new_automata.addtransition(j, k, '{}<:>{}'.format(i2t[i], 'oo'))
else:
new_automata.addtransition(j, k, '{}<:>{}'.format(i2t[i], i2s[s]))
- 由于状态数众多,仅展示部分状态转移条件
- 新自动机转移情况复杂不在此展示
原始状态转移图
原状态 s0
{0: {'$<:>oo'}, 1: {'download<:>o', 'show<:>o', 'find<:>o', 'get<:>o'}, 2: {'looking<:>o'}}
新状态 s0
{1: {'download<:>o', 'show<:>o', 'find<:>o', 'get<:>o'}, 9: {'show<:>o'}, 2: {'looking<:>o'}}
可见新状态 s0没有保留自循环部分,并且新增了至状态9的转移
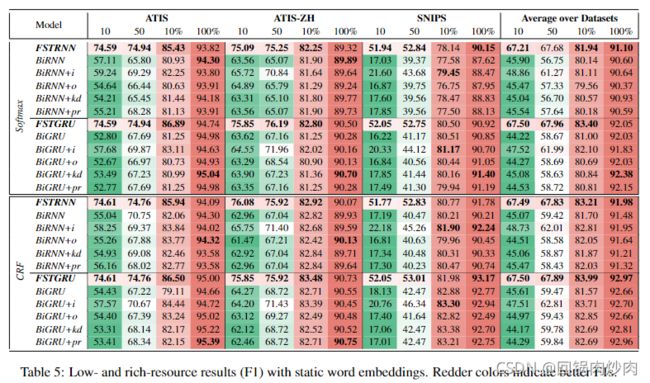
原状态 s3
{4: {'the<:>o', 'a<:>o'}}
新状态 s3
{4: {'the<:>o', 'a<:>o'}, 35: {'the<:>i-playlist', 'a<:>i-playlist'}, 91: {'a<:>b-service', 'the<:>b-service'}, 33: {'playlist<:>o'}, 38: {'playlist<:>o'}, 143: {'2011<:>b-year', 'thirties<:>b-year', 'fourties<:>b-year', 'nineties<:>b-year', 'fifties<:>b-year', 'sixties<:>b-year', 'seventies<:>b-year', 'twenties<:>b-year', '2003<:>b-year', 'eighties<:>b-year', '2016<:>b-year', '1958<:>b-year'}, 84: {'see<:>o', 'watch<:>o'}}
除了状态4还增加了许多新的状态转移
原状态 s9
{10: {'$<:>b-object_name'}}
新状态 s9
{73: {'the<:>i-spatial_relation'}, 9: {'called<:>o'}, 136: {'house<:>i-object_location_type', 'theatre<:>i-object_location_type'}}
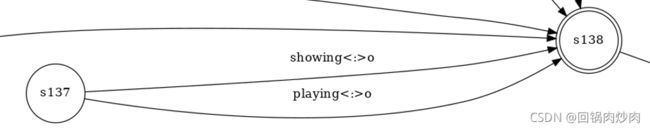
原状态s137
新状态s137
总结
RE2NN通过神经网络将并行的多个独立规则变得相互联系,形成一个状态转移网络,同时去掉了一些“不必要”的转移情况,可能是数据集中未出现的转移情况,使其更加合理。感谢屠可伟教授提供的思路,确实让人耳目一新。