lr schedule
文章目录
-
-
- constant_schedule
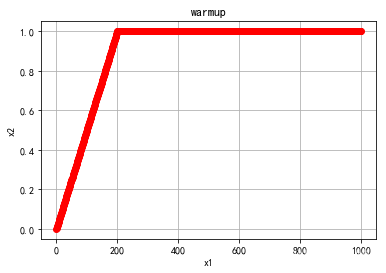
- warmup
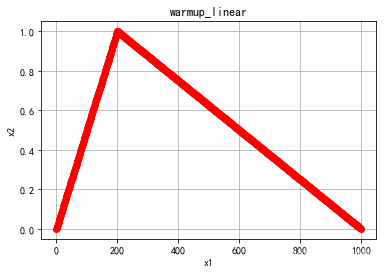
- warmup_linear
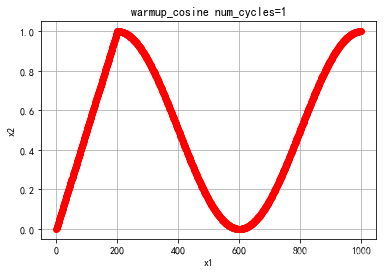
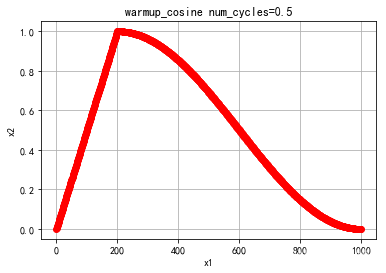
- warmup_consine
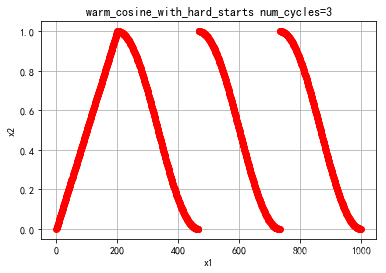
- warm_cosine_with_hard_starts
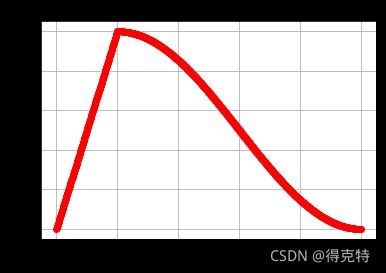
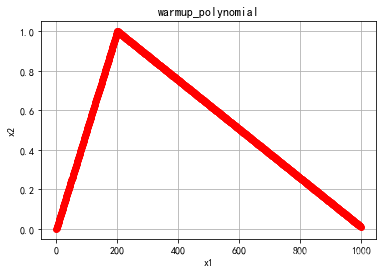
- warmup_polynomial
- 画图code
-
constant_schedule
学习率不变
def get_constant_schedule(optimizer: Optimizer, last_epoch: int = -1):
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lambda _: 1, last_epoch=last_epoch)
warmup
def get_constant_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer: Optimizer, num_warmup_steps: int, last_epoch: int = -1):
def lr_lambda(current_step: int):
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1.0, num_warmup_steps))
return 1.0
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch=last_epoch)
warmup_linear
def get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, num_warmup_steps, num_training_steps, last_epoch=-1):
def lr_lambda(current_step: int):
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
return max(
0.0, float(num_training_steps - current_step) / float(max(1, num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps))
)
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch)
warmup_consine
def get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer: Optimizer, num_warmup_steps: int, num_training_steps: int, num_cycles: float = 0.5, last_epoch: int = -1
):
"""num_cycles控制形状,默认值刚好从1~0
"""
def lr_lambda(current_step):
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
progress = float(current_step - num_warmup_steps) / float(max(1, num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps))
return max(0.0, 0.5 * (1.0 + math.cos(math.pi * float(num_cycles) * 2.0 * progress)))
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch)
参数num_cycles调节余弦线的形状,下图分别是num_cycles=0.5, 1的学习率变化
warm_cosine_with_hard_starts
类似于上述warm_cosine的默认值的形状,这里锁定了初始值。
def get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer: Optimizer, num_warmup_steps: int, num_training_steps: int, num_cycles: int = 1, last_epoch: int = -1
):
def lr_lambda(current_step):
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
progress = float(current_step - num_warmup_steps) / float(max(1, num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps))
if progress >= 1.0:
return 0.0
return max(0.0, 0.5 * (1.0 + math.cos(math.pi * ((float(num_cycles) * progress) % 1.0))))
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch)
warmup_polynomial
def get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer, num_warmup_steps, num_training_steps, lr_end=1e-7, power=1.0, last_epoch=-1
):
lr_init = optimizer.defaults["lr"]
assert lr_init > lr_end, f"lr_end ({lr_end}) must be be smaller than initial lr ({lr_init})"
def lr_lambda(current_step: int):
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
elif current_step > num_training_steps:
return lr_end / lr_init # as LambdaLR multiplies by lr_init
else:
lr_range = lr_init - lr_end
decay_steps = num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps
pct_remaining = 1 - (current_step - num_warmup_steps) / decay_steps
decay = lr_range * pct_remaining ** power + lr_end
return decay / lr_init # as LambdaLR multiplies by lr_init
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch)
画图code
l = []
for i in range(1000):
l.append(lr_lambda(i))
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x2")
plt.grid(True)#显示网格
plt.plot(list(range(1000)),l,'ro')
plt.title("warmup_polynomial")
plt.show()