简单实现顺序表
目录
顺序表的定义
顺序表的实现
MyArrayList
EmptyException
PosWrongFulException
顺序表增删改减思路详解
新增元素默认在数组的最后新增元素
在 pos位置新增元素
查找某个元素对应的位置
获取 pos 位置的元素
给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
删除第一次出现的关键字key
顺序表的定义
顺序表的实现
本篇博客实现的顺序表只是简单的实现,方便对顺序表的理解。
首先我们要创建俩个类,类MyArrayList是我们的顺序表的实现,类Test是测试类MyArrayList所写的代码是否正确。
另外还有俩个异常,一个是顺序表为空的异常,一个是Pos位置不合法的异常以方便我们写某功能。
代码实现:
MyArrayList
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList {
private int[] elem;
private int useSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
//判断当前顺序表是否为空
public Boolean isEmpty(){
if(this.useSize == 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断当前顺序表是否放满了
public Boolean isFull(){
if (this.useSize >= this.elem.length){
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 打印顺序表
public void display(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.useSize; i++) {
System.out.println(elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) {
if(isFull()){
//如果满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[useSize] = data;
useSize++;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) throws PosWrongFulException {
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
if(pos<0 | pos>useSize){
throw new PosWrongFulException("在pos位置新增元素,pos位置不合法异常");
}
for (int i = this.useSize-1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
useSize++;
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < useSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < useSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
if(pos<0 | pos>this.useSize-1){
throw new PosWrongFulException("获取pos位置元素不合法异常");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
if(pos<0 | pos>this.useSize-1){
throw new PosWrongFulException("获取pos位置元素不合法异常");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
int ret = indexOf(toRemove);
if(ret == -1){
System.out.println("顺序表中没有该元素");
return;
}
for (int i = ret; i < this.useSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.useSize--;
}
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return useSize;
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.useSize = 0;
}
}EmptyException
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException() {
}
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}PosWrongFulException
public class PosWrongFulException extends RuntimeException{
public PosWrongFulException() {
}
public PosWrongFulException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}顺序表增删改减思路详解
新增元素默认在数组的最后新增元素
思路:1.我们要在数组的最后面新增元素,那么在这之前我们必须要知道数组是否满了(数组中的元素是否等于数组长度),2.如果满了就要进行扩容。3.找到数组最后一个元素的下一个坐标并赋值。4.数组中的元素增加1
第一步:我们定义了useSize来记录数组中一共有多少个元素,所以只需要判断useSize是否大于等于数组的长度(Array.length),如果是,则证明数组满了。这里可以写一个方法来实现。
第二步:用Arrays.copyof()这个方法来扩容。
第三步:数组最后一个元素的下一个坐标刚好是useSize,因为useSize记录的是元素个数,而数组是从0下标开始的
第四步:useSize+1
代码:
//判断数组是否满了
public Boolean isFull(){
if (this.useSize >= this.elem.length){
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) {
if(isFull()){
//如果满了进行扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[useSize] = data;
useSize++;
}
运行结果:
简单写一个方法遍历打印这个数组中的元素
public void display(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.useSize; i++) {
System.out.println(elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}在 pos位置新增元素
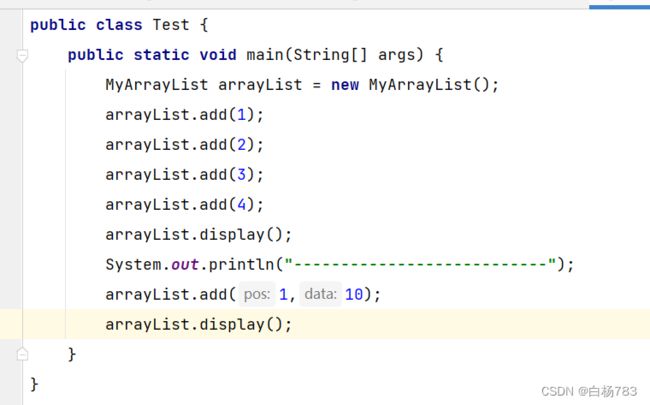
思路:1.判断数组是否满了,如果满了进行扩容。2.判断pos位置是否合法,pos位置不能小于0,也不能超过数组长度,且不能隔着一个空位或多个空位放元素。3.把pos位置及pos后面的元素后移。4.把想要增加的元素放到Pos位置。5.useSize++
public void add(int pos, int data) throws PosWrongFulException {
//判断数组是否满了
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//判断pos位置是否合法,如果不合法抛出异常
if(pos<0 | pos>useSize){
throw new PosWrongFulException("在pos位置新增元素,pos位置不合法异常");
}
//向后移动元素
for (int i = this.useSize-1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
useSize++;
}运行结果
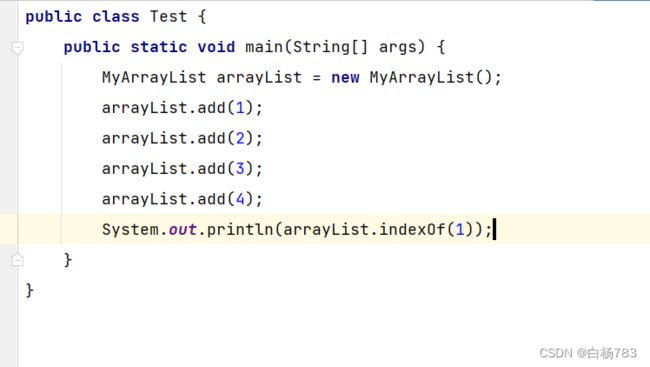
查找某个元素对应的位置
思路:遍历数组,找到元素返回坐标,如果找不到返回-1
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < useSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}运行结果:
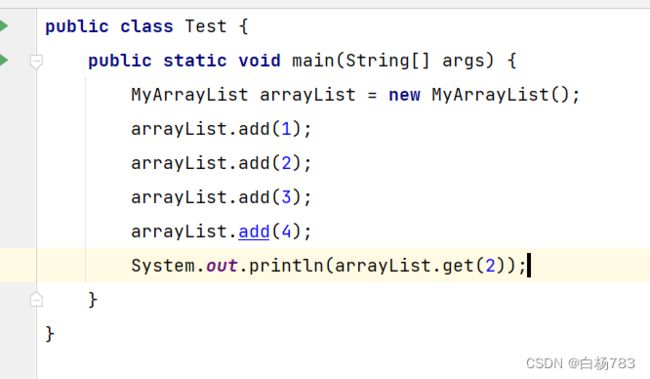
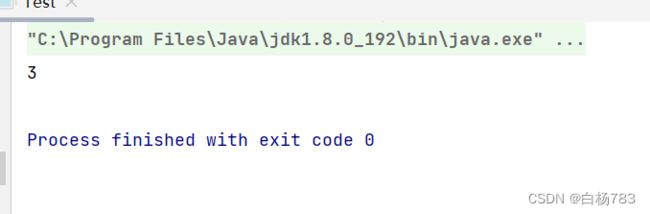
获取 pos 位置的元素
思路:1.判断数组是否为空,如果为空抛异常。2.判断给的pos位置是否合法:Pos不能小于0,也不能大于或者等于数组元素个数
代码:
public int get(int pos) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
if(pos<0 | pos>this.useSize-1){
throw new PosWrongFulException("获取pos位置元素不合法异常");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}运行结果:
给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
思路:1.判断数组是否为空。2.判断pos是否合法。3.把pos位置的元素改成value
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
if(pos<0 | pos>this.useSize-1){
throw new PosWrongFulException("获取pos位置元素不合法异常");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}运行结果:
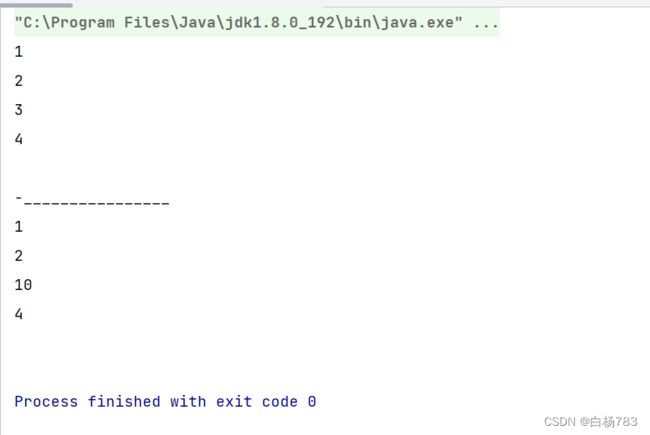
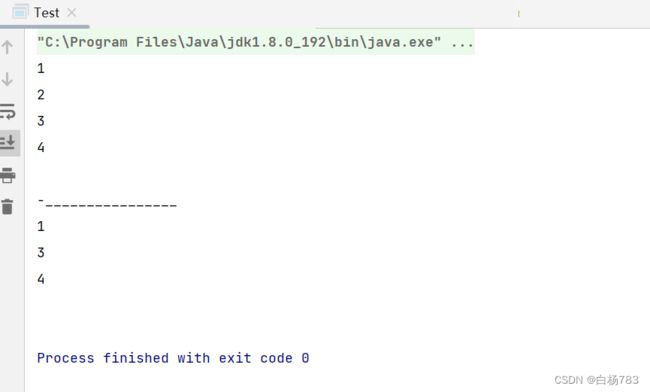
删除第一次出现的关键字key
思路:1.判断数组是否为空 2.找到key元素的下标,如果没有改元素打印没有该元素。3.删除该元素(把该元素后面的元素前移)4.useSize--
代码:
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("数组为空");
}
int ret = indexOf(toRemove);
if(ret == -1){
System.out.println("顺序表中没有该元素");
return;
}
for (int i = ret; i < this.useSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.useSize--;
}运行结果: