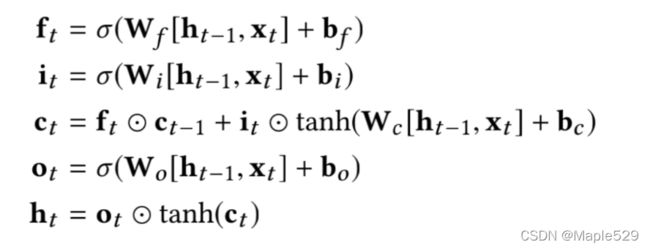PyTorch ConvLSTM复现代码解析
PyTorch ConvLSTM复现代码解析
零、前言
最近在复现一篇paper,里面有一个地方用到了ConvLSTM,由于目前本人能力有限,于是先在GitHub上找了一个ConvLSTM复现的代码,进行阅读解析
代码传送门:https://github.com/ndrplz/ConvLSTM_pytorch
一、ConvLSTM简介:
ConvLSTM是在2015年NIPS上的Convolutional lstm network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting中被提出来的
ConvLSTM基于LSTM,但和LSTM只能获取时间维度上的信息相比,因为采用了卷积核,有了聚合空间上信息的能力,因此常常应用于一些时空预测的模型中
二、LSTM和ConvLSTM的区别
-
LSTM
f t f_t ft即forget,代表“忘记”,由于sigmoid的值介于0-1之间,可以认为,当 W f [ h t − 1 , x t ] + b f W_f[h_{t-1},x_t]+b_f Wf[ht−1,xt]+bf的值趋于 + ∞ + \infin +∞的时候 f t f_t ft趋于1,反之趋于0;这个的实际含义是对上一个状态的保存程度,或者说忘记了多少
i t i_t it即input,代表“输入”,和上面的原理一样,代表对一个输入的接纳程度
c t c_t ct即状态,每个状态由对上一时刻状态的忘记程度和当前输入的接纳程度共同决定
o t o_t ot即output,代表“输出”,和上面的原理一样,代表一个状态能够输出的程度
h t h_t ht即最终的输出,由 o t o_t ot决定
-
ConvLSTM
- 分析:可以看出来,LSTM和ConvLSTM的不同之处就在于:在LSTM里面输入/状态和权重矩阵进行矩阵乘法的地方,ConvLSTM进行了卷积运算,也正因如此,ConvLSTM中得到的 f t , i t , o t f_t,i_t,o_t ft,it,ot等的维度一般是4维,包含N, C, H, W,此外两者基本保持一致
三、复现代码阅读
Part1: ConvLSTMCell
先贴一份源代码
class ConvLSTMCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, bias):
"""
Initialize ConvLSTM cell.
Parameters
----------
input_dim: int
Number of channels of input tensor.
hidden_dim: int
Number of channels of hidden state.
kernel_size: (int, int)
Size of the convolutional kernel.
bias: bool
Whether or not to add the bias.
"""
super(ConvLSTMCell, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.padding = kernel_size[0] // 2, kernel_size[1] // 2
self.bias = bias
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.input_dim + self.hidden_dim,
out_channels=4 * self.hidden_dim,
kernel_size=self.kernel_size,
padding=self.padding,
bias=self.bias)
def forward(self, input_tensor, cur_state):
h_cur, c_cur = cur_state
combined = torch.cat([input_tensor, h_cur], dim=1) # concatenate along channel axis
combined_conv = self.conv(combined)
cc_i, cc_f, cc_o, cc_g = torch.split(combined_conv, self.hidden_dim, dim=1)
i = torch.sigmoid(cc_i)
f = torch.sigmoid(cc_f)
o = torch.sigmoid(cc_o)
g = torch.tanh(cc_g)
c_next = f * c_cur + i * g
h_next = o * torch.tanh(c_next)
return h_next, c_next
def init_hidden(self, batch_size, image_size):
height, width = image_size
return (torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device),
torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device))
接着,对源代码的各个部分进行分析:
-
构造函数
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, bias): """ Initialize ConvLSTM cell. Parameters ---------- input_dim: int Number of channels of input tensor. hidden_dim: int Number of channels of hidden state. kernel_size: (int, int) Size of the convolutional kernel. bias: bool Whether or not to add the bias. """ super(ConvLSTMCell, self).__init__() self.input_dim = input_dim self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim self.kernel_size = kernel_size self.padding = kernel_size[0] // 2, kernel_size[1] // 2 self.bias = bias self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.input_dim + self.hidden_dim, out_channels=4 * self.hidden_dim, kernel_size=self.kernel_size, padding=self.padding, bias=self.bias)构造函数有四个参数:
- input_dim:代表输入的tensor的维度
- hidden_dim:代表LSTM核的状态(hidden state)的维度
- kernel_size:卷积核大小,形如(3, 3),可以通过该参数构造padding
- bias:是否需要加上bias偏置
这份构造函数中,对ConvLSTMCell的input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, padding, bias完成了初始化
同时,还新建了一个二维卷积核,该卷积核的输入的维度是input_dim和hidden_dim的和,输出的维度是4*hidden_dim
-
输入之所以是input_dim和hidden_dim的和,是因为我们在卷积层中,是把输入向量和状态拼在一起进行输入
-
输出之所以是4*hidden_dim,是因为卷积核的输出部分是由cc_i, cc_f, cc_o, cc_g四部分组成的,换言之,要保证这四部分的维度都是hidden_dim,需要保证卷积核的输出维度是4*hidden_dim
-
forward方法
def forward(self, input_tensor, cur_state): h_cur, c_cur = cur_state combined = torch.cat([input_tensor, h_cur], dim=1) # concatenate along channel axis combined_conv = self.conv(combined) cc_i, cc_f, cc_o, cc_g = torch.split(combined_conv, self.hidden_dim, dim=1) i = torch.sigmoid(cc_i) f = torch.sigmoid(cc_f) o = torch.sigmoid(cc_o) g = torch.tanh(cc_g) c_next = f * c_cur + i * g h_next = o * torch.tanh(c_next) return h_next, c_nextforward方法有两个参数:
- input_tensor:代表输入的tensor
- cur_state:代表当前的状态
该cur_state蕴含了c和h两部分,先从cur_state中提取这两部分,然后将输出张量和h拼接在一起,进行卷积
卷积运算后,利用Pytorch自带的split方法,对输出结果进行分割,分成四份,然后套用ConvLSTM的公式,该过sigmoid层的过sigmoid层,该过tanh层的过tanh层,最终得到新的c和h
注意一下,这个地方
f * c_cur用的是hadamart-product哈达姆积,和矩阵乘法不太一样还有一个值得思考的地方:在普通的LSTM中,我们可以通过设定权重矩阵的方法,使用权重矩阵乘以combined矩阵,得到最后的值,最后将求的的结果分开,得到不同的权重矩阵对应的结果;在卷积中,这个操作是怎么得以实现的呢?很简单,4倍的output_channel对应了四倍的卷积核,自然顺理成章的对应的不同的权重参数。
-
init_hidden方法
def init_hidden(self, batch_size, image_size): height, width = image_size return (torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device), torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device))作用是返回两个大小是(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width)的零张量
其中height、width构成图片大小
Part2: ConvLSTM
还是先贴一下代码
class ConvLSTM(nn.Module):
"""
Parameters:
input_dim: Number of channels in input
hidden_dim: Number of hidden channels
kernel_size: Size of kernel in convolutions
num_layers: Number of LSTM layers stacked on each other
batch_first: Whether or not dimension 0 is the batch or not
bias: Bias or no bias in Convolution
return_all_layers: Return the list of computations for all layers
Note: Will do same padding.
Input:
A tensor of size B, T, C, H, W or T, B, C, H, W
Output:
A tuple of two lists of length num_layers (or length 1 if return_all_layers is False).
0 - layer_output_list is the list of lists of length T of each output
1 - last_state_list is the list of last states
each element of the list is a tuple (h, c) for hidden state and memory
Example:
>> x = torch.rand((32, 10, 64, 128, 128))
>> convlstm = ConvLSTM(64, 16, 3, 1, True, True, False)
>> _, last_states = convlstm(x)
>> h = last_states[0][0] # 0 for layer index, 0 for h index
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, num_layers,
batch_first=False, bias=True, return_all_layers=False):
super(ConvLSTM, self).__init__()
self._check_kernel_size_consistency(kernel_size)
# Make sure that both `kernel_size` and `hidden_dim` are lists having len == num_layers
kernel_size = self._extend_for_multilayer(kernel_size, num_layers)
hidden_dim = self._extend_for_multilayer(hidden_dim, num_layers)
if not len(kernel_size) == len(hidden_dim) == num_layers:
raise ValueError('Inconsistent list length.')
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_first = batch_first
self.bias = bias
self.return_all_layers = return_all_layers
cell_list = []
for i in range(0, self.num_layers):
cur_input_dim = self.input_dim if i == 0 else self.hidden_dim[i - 1]
cell_list.append(ConvLSTMCell(input_dim=cur_input_dim,
hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim[i],
kernel_size=self.kernel_size[i],
bias=self.bias))
self.cell_list = nn.ModuleList(cell_list)
def forward(self, input_tensor, hidden_state=None):
"""
Parameters
----------
input_tensor: todo
5-D Tensor either of shape (t, b, c, h, w) or (b, t, c, h, w)
hidden_state: todo
None. todo implement stateful
Returns
-------
last_state_list, layer_output
"""
if not self.batch_first:
# (t, b, c, h, w) -> (b, t, c, h, w)
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute(1, 0, 2, 3, 4)
b, _, _, h, w = input_tensor.size()
# Implement stateful ConvLSTM
if hidden_state is not None:
raise NotImplementedError()
else:
# Since the init is done in forward. Can send image size here
hidden_state = self._init_hidden(batch_size=b,
image_size=(h, w))
layer_output_list = []
last_state_list = []
seq_len = input_tensor.size(1)
cur_layer_input = input_tensor
for layer_idx in range(self.num_layers):
h, c = hidden_state[layer_idx]
output_inner = []
for t in range(seq_len):
h, c = self.cell_list[layer_idx](input_tensor=cur_layer_input[:, t, :, :, :],
cur_state=[h, c])
output_inner.append(h)
layer_output = torch.stack(output_inner, dim=1)
cur_layer_input = layer_output
layer_output_list.append(layer_output)
last_state_list.append([h, c])
if not self.return_all_layers:
layer_output_list = layer_output_list[-1:]
last_state_list = last_state_list[-1:]
return layer_output_list, last_state_list
def _init_hidden(self, batch_size, image_size):
init_states = []
for i in range(self.num_layers):
init_states.append(self.cell_list[i].init_hidden(batch_size, image_size))
return init_states
@staticmethod
def _check_kernel_size_consistency(kernel_size):
if not (isinstance(kernel_size, tuple) or
(isinstance(kernel_size, list) and all([isinstance(elem, tuple) for elem in kernel_size]))):
raise ValueError('`kernel_size` must be tuple or list of tuples')
@staticmethod
def _extend_for_multilayer(param, num_layers):
if not isinstance(param, list):
param = [param] * num_layers
return param
还是对各个部分进行解析:
-
构造函数
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, num_layers, batch_first=False, bias=True, return_all_layers=False): super(ConvLSTM, self).__init__() self._check_kernel_size_consistency(kernel_size) # Make sure that both `kernel_size` and `hidden_dim` are lists having len == num_layers kernel_size = self._extend_for_multilayer(kernel_size, num_layers) hidden_dim = self._extend_for_multilayer(hidden_dim, num_layers) if not len(kernel_size) == len(hidden_dim) == num_layers: raise ValueError('Inconsistent list length.') self.input_dim = input_dim self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim self.kernel_size = kernel_size self.num_layers = num_layers self.batch_first = batch_first self.bias = bias self.return_all_layers = return_all_layers cell_list = [] for i in range(0, self.num_layers): cur_input_dim = self.input_dim if i == 0 else self.hidden_dim[i - 1] cell_list.append(ConvLSTMCell(input_dim=cur_input_dim, hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim[i], kernel_size=self.kernel_size[i], bias=self.bias)) self.cell_list = nn.ModuleList(cell_list)构造函数参数较多:
- input_dim:输入的维度,浅显的理解就是输入的个数,比如说一个卷积模型的通道数
- hidden_dim:代表LSTM核的状态(hidden state)的维度
- kernel_size:卷积核大小,形如(3, 3)
- num_layers:ConvLSTM的层数/深度,简洁来说就是ConvLSTMCell的个数
- batch_first:代表在输入数据的五维张量中是否应该把batch放在最开始,如果该值为True,那么代表当前的输入数据batch在最开头,则不用变换,否则需要变换。该参数的作用是确保在ConvLSTM中,batch能够位于tensor的第0维
- bias:是否有偏置
- return_all_layers:选择是返回所有的隐藏层状态和输出,还是返回最后一层的隐藏层状态和输出
在构造方法中,还定义了一个cell_list,用来存储ConvLSTMCell
cur_input_dim = self.input_dim if i == 0 else self.hidden_dim[i - 1]该语句代表,如果是第一层,那么,cur_input_dim就是ConvLSTM中的input_dim,否则就是上一层的hidden_dim
然后依次构造ConvLSTMCell,并加入cell_list中,最后将cell_list转换成一个
nn.ModuleList类型的list
注意这个地方,虽然传入的hidden_dim和kernel_size是一个数,但经过self._extend_for_multilayer()方法的转换,变成了一 个list类型的数据
- forward函数
def forward(self, input_tensor, hidden_state=None):
"""
Parameters
----------
input_tensor: todo
5-D Tensor either of shape (t, b, c, h, w) or (b, t, c, h, w)
hidden_state: todo
None. todo implement stateful
Returns
-------
last_state_list, layer_output
"""
if not self.batch_first:
# (t, b, c, h, w) -> (b, t, c, h, w)
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute(1, 0, 2, 3, 4)
b, _, _, h, w = input_tensor.size()
# Implement stateful ConvLSTM
if hidden_state is not None:
raise NotImplementedError()
else:
# Since the init is done in forward. Can send image size here
hidden_state = self._init_hidden(batch_size=b,
image_size=(h, w))
layer_output_list = []
last_state_list = []
seq_len = input_tensor.size(1)
cur_layer_input = input_tensor
for layer_idx in range(self.num_layers):
h, c = hidden_state[layer_idx]
output_inner = []
for t in range(seq_len):
h, c = self.cell_list[layer_idx](input_tensor=cur_layer_input[:, t, :, :, :],
cur_state=[h, c])
output_inner.append(h)
layer_output = torch.stack(output_inner, dim=1)
cur_layer_input = layer_output
layer_output_list.append(layer_output)
last_state_list.append([h, c])
if not self.return_all_layers:
layer_output_list = layer_output_list[-1:]
last_state_list = last_state_list[-1:]
return layer_output_list, last_state_list
forward方法有两个参数
- input_tensor:代表输入的张量,输入的张量是一个五维的张量,
- hidden_state:代表是否有隐藏层
首先,判断batch_first的值,来确保batch在tensor的第0维
if not self.batch_first:
# (t, b, c, h, w) -> (b, t, c, h, w)
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute(1, 0, 2, 3, 4)
然后,再调用_init_hidden方法,得到一个初始化的hidden_state列表,注意这是一个tuple的列表
if hidden_state is not None:
raise NotImplementedError()
else:
# Since the init is done in forward. Can send image size here
hidden_state = self._init_hidden(batch_size=b,
image_size=(h, w))
初始化第一次的输入为input_tensor
cur_layer_input = input_tensor
遍历所有的ConvLSTMCell,在每个ConvLSTMCell中,对序列长度(有几个数据)进行遍历,把每个数据喂进ConvLSTMCell中,得到对应的output,并最终采用torch.stack堆叠起来
for layer_idx in range(self.num_layers):
h, c = hidden_state[layer_idx]
output_inner = []
for t in range(seq_len):
h, c = self.cell_list[layer_idx](input_tensor=cur_layer_input[:, t, :, :, :],
cur_state=[h, c])
output_inner.append(h)
layer_output = torch.stack(output_inner, dim=1)
cur_layer_input = layer_output
layer_output_list.append(layer_output)
last_state_list.append([h, c])
最终是判断最后的返回值,根据return_all_layers来判断返回所有的状态还是最后一个状态
if not self.return_all_layers:
layer_output_list = layer_output_list[-1:]
last_state_list = last_state_list[-1:]
四、反思与总结
通过这次详细的阅读代码,可以说是对LSTM的运作过程和ConvLSTM的基本原理有了一个更深的认识,下次可以尝试一下自己复现!