VGG16_Tensorflow版本实现图片分类
![]()
start
首先将本文涉及到的代码、预训练模型和数据集上传,大家可以自行下载:
VGG16代码链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Xy5H3t9SVnQM2OMorH4pmQ
提取码:zju1
预训练模型VGG16.npy链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-HQL4Ixkm8G2j01y8sstFA
提取码:o9g2
数据集链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1z9Y5L1B10huqGF-nBu0mug
提取码:fqnb
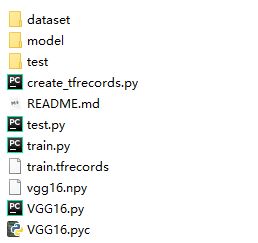
01文件目录介绍
“
本文介绍使用tensorflow实现VGG16网络模型并进行图像分类,主文件夹VGG16_Tensorflow下目录如下:
”
其中dataset文件夹下为数据集文件,model文件夹为训练模型的储存目录,test文件夹为测试集图像的存放位置。
主文件夹下包含4个py文件,分别实现不同的功能:
create_tfrecords.py 生成tfrecords数据脚本
VGG16.py 网络结构定义文件
train.py 训练脚本
test.py 测试脚本
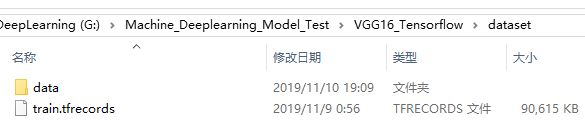
dataset文件夹包含子目录data:
data目录下式五个类别的图片
test文件夹下存放的是测试集图像,如下:
![]()
02制作tfrecord数据文件
“
首先,制作数据集并按照如下格式保存到dataset/data/文件夹下
”
然后,生成train.tfrecords文件
按照如上目录要求制作完数据集后,在主目录下直接运行python create_tfrecords.py即可在主目录下生成train.tfrecords文件。以下是create_tfrecords.py代码:
#coding=utf-8
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
import sys
def creat_tf(imgpath):
cwd = os.getcwd()
classes = os.listdir(cwd + imgpath)
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter("train.tfrecords")
for index, name in enumerate(classes):
class_path = cwd + imgpath + name + "/"
print(class_path)
if os.path.isdir(class_path):
for img_name in os.listdir(class_path):
img_path = class_path + img_name
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = img.resize((224, 224))
img_raw = img.tobytes() #将图片转化为原生bytes
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[int(name)])),
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) #序列化为字符串
print(img_name)
writer.close()
def read_example():
#简单的读取例子:
for serialized_example in tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator("train.tfrecords"):
example = tf.train.Example()
example.ParseFromString(serialized_example)
#image = example.features.feature['img_raw'].bytes_list.value
label = example.features.feature['label'].int64_list.value
# 可以做一些预处理之类的
print(label)
if __name__ == '__main__':
imgpath = './dataset/data/'# 训练集图像的储存目录
creat_tf(imgpath)
03模型训练
“
制作完数据后便可进行模型的训练工作,直接运行python train.py即可。
”
模型训练过程中会调用预训练模型文件vgg16.npy,可以自行从下面的链接中下载:
链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-HQL4Ixkm8G2j01y8sstFA
提取码:o9g2
#coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pdb
from datetime import datetime
from VGG16 import *
batch_size = 64#批大小
lr = 0.00001#学习率
n_cls = 17
max_steps = 10000#训练次数
def read_and_decode(filename):
#根据文件名生成一个队列
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue) #返回文件名和文件
features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'img_raw' : tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
})
img = tf.decode_raw(features['img_raw'], tf.uint8)
img = tf.reshape(img, [224, 224, 3])
# 转换为float32类型,并做归一化处理
img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32)# * (1. / 255)
label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int64)
#print 'images的样子是:', img
#print 'label的样子是:', label
#pdb.set_trace()
return img, label
def train():
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 224, 224, 3], name='input')
y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, n_cls], name='label')
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
output = VGG16(x, keep_prob, n_cls)
#probs = tf.nn.softmax(output)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=output, labels=y))
#train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(loss)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=lr).minimize(loss)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(output,1), tf.argmax(y, 1)), tf.float32))
images, labels = read_and_decode('./train.tfrecords')
img_batch, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([images, labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=392,
min_after_dequeue=200)
label_batch = tf.one_hot(label_batch, n_cls, 1, 0)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(max_steps):
batch_x, batch_y = sess.run([img_batch, label_batch])
# print batch_x, batch_x.shape
# print batch_y
# pdb.set_trace()
_, loss_val = sess.run([train_step, loss], feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:0.8})
if i%10 == 0:
train_arr = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.0})
print("%s: Step [%d] Loss : %f, training accuracy : %g" % (datetime.now(), i, loss_val, train_arr))
if (i + 1) == max_steps:
#checkpoint_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.train_dir, './model/model.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, './model/model.ckpt', global_step=i)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
#saver.save(sess, 'model/model.ckpt')
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
模型训练结束后会在model文件夹下生成模型文件,以我的数据集为例,训练10000步后生成如下文件:
04模型测试
♡♡♡
模型训练完毕后运行python test.py即可完成模型测试工作,test.py文件代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pdb
from datetime import datetime
from VGG16 import *
import cv2
import os
def test(path):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 224, 224, 3], name='input')
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
output = VGG16(x, keep_prob, 17)
score = tf.nn.softmax(output)
f_cls = tf.argmax(score, 1)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, './model/model.ckpt-9999')#调用模型的名称和路径
for i in os.listdir(path):
imgpath = os.path.join(path, i)
im = cv2.imread(imgpath)
im = cv2.resize(im, (224 , 224))# * (1. / 255)
im = np.expand_dims(im, axis=0)
#pred = sess.run(f_cls, feed_dict={x:im, keep_prob:1.0})
pred, _score = sess.run([f_cls, score], feed_dict={x:im, keep_prob:1.0})
prob = round(np.max(_score), 4)
#print "{} flowers class is: {}".format(i, pred)
print("{} flowers class is: {}, score: {}".format(i, int(pred), prob))
sess.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = './test'#测试集图像路径
test(path)
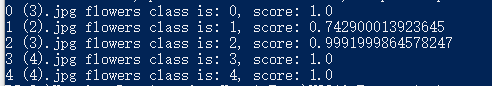
以我当前的数据集为例进行测试,测试结果如下:
大家在训练过程中如有疑问,欢迎后台留言讨论!
参考:
https://github.com/LiMingda92/VGG16_TF
![]()