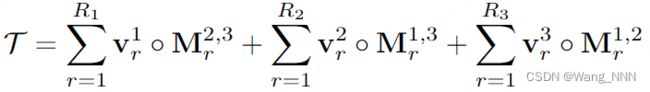[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields
Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Contributions
- Method
-
- Overview
- Neural radiance fields
- Wavelet transform on decomposed tensors
-
- Multi-level wavelet transform
- Learning to mask
- Compression pipeline
- Experiments
-
- Results
- Ablation Studies
- Paper Notes
- References
Abstract
神经辐射场(NeRF)已经证明了基于坐标的神经表示(神经场或隐式神经表示)在神经绘制中的潜力。然而,使用多层感知器(MLP)来表示3D场景或对象需要巨大的计算资源和时间。最近有一些关于通过使用额外的数据结构(如网格或树)来减少这些计算低效的研究。尽管性能大有希望,但显式数据结构需要大量的内存。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种在不影响拥有额外数据结构的优点的情况下减小大小的方法。具体来说,我们提出了将小波变换应用于基于网格的神经场。基于网格的神经场是为了快速收敛,而小波变换的有效性已经在高性能的标准编解码器中得到了证明,它是为了提高网格的参数效率。此外,为了在保持重建质量的同时获得更高的网格系数稀疏性,我们提出了一种新的可训练掩码方法。实验结果表明,非空间网格系数,如小波系数,能够达到比空间网格系数更高的稀疏性,从而获得更紧凑的表示。使用我们建议的掩码和压缩流水线,我们在2MB的内存预算中获得了最先进的性能。
Introduction
本文的目的是在保持渲染质量的前提下,进一步提高空间复杂度和计算复杂度。利用几十年来对标准压缩算法的研究,我们建议使用基于频率的变换来压缩基于网格的神经场。在频域中,可以在不显著降低重建质量的情况下丢弃大部分系数,并且大多数标准压缩算法都利用了频域表示。因此,我们建议在基于网格的神经场中使用这一性质来最大化参数效率。在各种备选方案中,我们使用离散小波变换(DWT),因为它的紧凑性和有效地捕获全局和局部信息的能力。
一旦我们通过频域表示获得稀疏表示,我们就可以利用现有的压缩技术。然而,与传统的媒体数据(例如图像和音频)不同,没有现成的压缩工具可供我们在不进行复杂的工程工作的情况下加以利用。此外,由于NeRF神经渲染网络是一种相对较新的数据格式,其系数的特征或模式还没有得到彻底的研究。因此,我们提出一种用于基于网格的NeRF的压缩管道。为了自动滤除不必要的系数,我们提出了一种可训练的二值掩模。对于每个3D场景,我们联合优化网格参数及其对应的掩码。这种逐场景优化策略可以比标准图像压缩编解码器中使用的全局量化表更优。
为了压缩稀疏网格表示,我们应用了标准压缩算法。我们利用游程编码来编码关于哪些系数不为零的二进制信息。为了进一步压缩,我们对这些编码输出应用了其中一种熵编码算法,即哈夫曼编码。
Contributions
- We propose using wavelet coefficients to improve parameter sparsity and reconstruction quality. Through experiments, we show that the wavelet coefficients can be more compact than the spatial domain coefficients in neural radiance fields.
- We propose a trainable mask that can be applied to any grid-based neural representation. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed masking method can zero out more than 95% of the total grid parameters while maintaining high reconstruction quality.
- We achieve state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis under a memory budget of 2 MB.
Method
Overview
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b0357bdadf964632b8f5343872649869.jpg)
Images with purple borders illustrate wavelet coefficients, while those with orange borders visualize spatial coefficients. White and orange blocks in 1D grids indicate masked features and unmasked features respectively. The wavelet coefficients in each 2D grid are multiplied with a binarized mask to form a masked wavelet coefficient grid. Masked wavelet coefficients are then inverse-transformed to spatial features. 1D spatial grids are also multiplied by their corresponding binarized masks. We sample feature vectors for input coordinates using bilinear (linear) interpolation on 2D (1D) grids. We multiply and add feature vectors from 1D and 2D grids in order to estimate opacity. For color estimation, sampled feature vectors are concatenated (denoted with ⊕) and then fed to the following MLP, which processes feature vectors to estimate corresponding colors.
Neural radiance fields
利用网格表示的神经辐射场。
采用输入坐标x∈R3和观察方向d∈R2,生成由密度和三通道rgb颜色组成的四维矢量。
θ是MLP的参数,γ={γσ,γc}是一组grid参数,M={Mσ,Mc}是一组grid参数的掩码。
![]()
![]()
体积渲染方程:(Detailed: NeRF [R1])
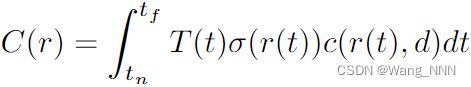
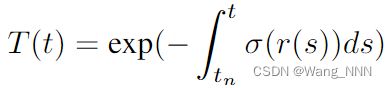
Wavelet transform on decomposed tensors
Baseline: TensoRF [R2]
(From TensoRF)
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/30dcf1edab4a4fe686cd3f7c7caffe99.jpg)
CP分解(左)
VM分解(右)
TensoRF使用一组矢量(V)和矩阵(M)将场景建模为张量辐射场,这些矢量(V)和矩阵(M)描述了场景外观和沿其对应轴的几何形状。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6b3cbadc9c294f948b0a13328c5d3fd6.jpg)
基于频率的算法,如离散余弦变换(DCT)或离散小波变换(DWT),在过去的几十年里得到了发展和改进。为了获得高压缩性能,标准编解码器使用它们来进行稀疏表示。然而,在3D格网表示的情况下,其计算复杂性随着格网分辨率的增加而成倍增加,使得高分辨率的3D场景和对象表示变得不切实际。为了使用基于频率的算法进行紧凑表示,我们需要更低维的数据,例如2D平面或1D线。
最近的研究已经探索了各种分解方法来降低基于3D网格的表示的空间复杂性。其中,基于平面的表示在减少参数数目的同时保持绘制性能方面取得了显著的成功 [R2,R3]。他们建议将3D张量分解成一组2D平面或1D矢量。
为了结合两者的优点,本文建议在2D平面神经场上使用小波变换[R2]。使用小波变换,是因为它的紧凑性,特别是对于非重复、非光滑的信号。
使用一组2D矩阵和1D向量来表示网格,Nr是矩阵向量分解的秩数
γσ=![]()
σ表示密度,为简明起见,将省略下标σ
![]() ,
,![]()
3D网格表示G:
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ce4b4c0419c1456ea6ad920f262fbfb5.jpg)
IDWT(·)是二维离散小波逆变换(IDWT):
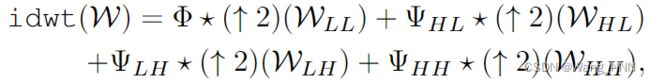
Multi-level wavelet transform
为了进一步提高参数稀疏性和重建质量,使用多层小波变换。实验发现,更高级别的小波变换会导致网格中更高的稀疏性。
然而,对网格参数直接使用多层小波变换会降低表示质量。因此,本文建议将小波系数乘以与频率倒数成比例的尺度。s是比例因子。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/41e343c584d04901842d929b7943df74.jpg)
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7fee064b86a24edbaa6baf4d78e1f245.jpg)
Learning to mask
尽管小波系数可以是稀疏的,但我们需要额外的方法来获得更高的稀疏性。因此,使用逐元素掩码来增加网格中零元素的比例。通过联合优化二值掩码和网格参数,本文的目标是在不显著降低渲染质量的情况下将大部分系数置零。
M=![]() ,是一组可训练的masks。
,是一组可训练的masks。
在训练过程中,网格参数和相应的二值化掩码被逐个元素相乘。由于直接从二值化模板计算梯度是不可行的,使用straight-through-estimator technique来训练和使用模板。形式上,Wr的掩码矩阵参数可以表示如下:
![]()
sg(·)是停止梯度算子。σ(·)和H(·)分别表示单元Sigmoid函数和Heaviside阶跃函数。掩码向量参数的计算类似。
Masked 3D grid representation:
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ae8e7b0734614a93a6499d81e6657906.jpg)
为了使二进制化的掩码值稀疏,使用所有掩码值的和作为附加损失项Lm。总损失函数是渲染损失Lr和掩模正则化项Lm之和。使用λm控制grid表示参数的稀疏性。
![]()
Compression pipeline
利用提出的掩蔽方法和多层离散小波变换,网格的零元素比例可以达到95%以上。但是,稀疏表示本身并不会减少总大小。
本文不是按原样存储网格,而是分别存储非零系数和位图(或掩码),这些位图(或掩码)指示哪些系数是非零的。
就算使用1位位图,但由于参数数量较多,总体位图大小较大。
为了减小位图大小,本文提出了一种具有以下三个阶段的压缩流水线:N位转换、游程编码(RLE)和哈夫曼编码。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/11b20493685841708e02b9792d462402.jpg)
Experiments
Results
- Performance on the NeRF synthetic dataset
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c421012f269444809dc9530946db7277.jpg)
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f7e92c105a3d4aa885ad8dc9cb2f63b9.jpg)
可训练mask去除了97%以上的网格参数;然而,渲染结果仍然准确,定性差异几乎不可察觉。这表明本文提出的方法通过利用可训练掩码有效地消除了不必要的小波系数。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c9b4a67edc8c4d46aa845b4d5d4013f9.jpg)
首先,稀疏性随小波变换级别的不同而变化。如下图(b)所示,频率较低的系数具有较低的稀疏性,而频率较高的系数具有较高的稀疏性。有趣的是,原始掩码值似乎反映了相应的小波系数的特征。可以在垂直、水平和对角系数的原始掩码值中分别找到垂直、水平和对角图案。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9012e4a57b1a4f6cace8e64df3addd9e.jpg)
- Performance on the NSVF synthetic dataset
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e34b2b9282bd4cf7bf3e306e49172efd.jpg)
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c046fdf7c39a4fbcaef4953b0bb0b702.jpg)
- Performance on the Tanks&Temples synthetic dataset
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第16张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ae6198b009144903897e72efdb07d037.jpg)
Ablation Studies
与DCT相比,DWT显示出更好的压缩和表示性能。这可能是由于网格中的非重复、非平滑信息造成的,而离散小波变换更适合这种情况。
缩放小波系数可提高重建性能。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第17张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/452296cdb39942fd9bc46ba0a8705624.jpg)
小波函数的类型对重建质量影响不大。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第18张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/926e058bcf994d34970f1225af6c5fbb.jpg)
基于小波的网格表示在空间域上优于网格,特别是在稀疏度较高的情况下。此外,较高level的小波变换改善了视觉质量和稀疏性。
![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第19张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8ec4332d0e1844e7ad3ed5a4f59788f9.jpg)
Paper Notes
- What problem is addressed in the paper?
ANS: Compact representation for grid-based NeRF. - Is it a new problem? If so, why does it matter? If not, why does it still matter?
ANS: No. Using wavelet coefficients to improve parameter sparsity and reconstruction quality. - What is the key to the solution? What is the main contribution?
ANS:
(1) Wavelet coefficients. Wavelet coefficients can be more compact than the spatial domain coefficients in neural radiance fields.
(2) Trainable mask. Zero out more than 95% of the total grid parameters while maintaining high reconstruction quality. - How the experiments sufficiently support the claims?
ANS: Achieve sota performance under a memory budget of 2 MB and efficiently eliminate unnecessary wavelet coefficients by leveraging trainable masks. - What can we learn from ablation studies?
ANS:
(1) Due to the non-repeating, non-smooth information in grids, for which DWT is more appropriate than DCT.
(2) Type of wavelet function has little effect on reconstruction quality.
(3) Wavelet-based grid representation outperforms the grid in the spatial domain, especially when the sparsity is high.
(4) Scaling wavelet coefficients improves reconstruction performance. - Potential fundamental flaws; how this work can be improved?
ANS:
(1) Developed for bounded scenes or objects.
(2) Only use the PSNR as evaluation metric.
References
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09069
Project Page: https://daniel03c1.github.io/masked_wavelet_nerf/
Code: https://github.com/daniel03c1/masked_wavelet_nerf
Related works
[R1] NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
[R2] TensoRF: Tensorial Radiance Fields
[R3] PERF: Performant, Explicit Radiance Fields
[R4] 3D Scene Compression through Entropy Penalized Neural Representation Functions
[R5] KiloNeRF: Speeding up Neural Radiance Fields with Thousands of Tiny MLPs
[R6] Variable bitrate neural fields

![[论文精读][NeRF] Masked Wavelet Representation for Compact Neural Radiance Fields_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c738207193c144cabb29229ded31bcc5.jpg)