【学习笔记】机器学习算法(三)基于LightGBM的分类预测
这里写自定义目录标题
- 一、LightGBM简介
-
- 优缺点
- 二、学习目标
- 三、实例:基于英雄联盟数据集的LightGBM分类实践
-
- 3.1 代码流程
- 3.2 数据集
- 3.3 模型训练
- 3.4 利用 LightGBM 进行特征选择
- 3.5 调参
一、LightGBM简介
LightGBM的设计思路主要集中在减小数据对内存与计算性能的使用,以及减少多机器并行计算时的通讯代价。
LightGBM可以看作是XGBoost的升级豪华版,在获得与XGBoost近似精度的同时,又提供了更快的训练速度与更少的内存消耗。
优缺点
LightGBM的主要优点:
- 简单易用。提供了主流的Python\C++\R语言接口,用户可以轻松使用LightGBM建模并获得相当不错的效果。
- 高效可扩展。在处理大规模数据集时高效迅速、高准确度,对内存等硬件资源要求不高。
- 鲁棒性强。相较于深度学习模型不需要精细调参便能取得近似的效果。
- LightGBM直接支持缺失值与类别特征,无需对数据额外进行特殊处理
LightGBM的主要缺点:
- 相对于深度学习模型无法对时空位置建模,不能很好地捕获图像、语音、文本等高维数据。
- 在拥有海量训练数据,并能找到合适的深度学习模型时,深度学习的精度可以遥遥领先LightGBM。
二、学习目标
- 了解 LightGBM 的参数与相关知识
- 掌握 LightGBM 的Python调用并将其运用到英雄联盟游戏胜负预测数据集上
三、实例:基于英雄联盟数据集的LightGBM分类实践
直接输入1次#,并按下space后,将生成1级标题。
输入2次#,并按下space后,将生成2级标题。
以此类推,我们支持6级标题。有助于使用TOC语法后生成一个完美的目录。
3.1 代码流程
Step1: 库函数导入
Step2: 数据读取/载入
Step3: 数据信息简单查看
Step4: 可视化描述
Step5: 利用 LightGBM 进行训练与预测
Step6: 利用 LightGBM 进行特征选择
Step7: 通过调整参数获得更好的效果
3.2 数据集
这里的数据集直接从天池下载

数据集简介:
现在共有9881场英雄联盟韩服钻石段位以上的排位比赛数据,数据提供了在十分钟时的游戏状态,包括击杀数、死亡数、金币数量、经验值、等级……等信息。列blueWins是数据的标签,代表了本场比赛是否为蓝队获胜。

利用.head和.tail对数据进行查看

利用.describe()查看统计描述

对这些信息进行分析,不难发现
- 我们发现不同对局中插眼数和拆眼数的取值范围存在明显差距,甚至有前十分钟插了250个眼的异常值。
- 我们发现EliteMonsters的取值相当于Deagons + Heralds。
- 我们发现TotalGold 等变量在大部分对局中差距不大。
- 我们发现两支队伍的经济差和经验差是相反数。
- 我们发现红队和蓝队拿到首次击杀的概率大概都是50%
根据上面的描述,我们可以去除一些重复变量,比如只要知道蓝队是否拿到一血,我们就知道红队有没有拿到,可以去除红队的相关冗余数据。
## 根据上面的描述,我们可以去除一些重复变量,比如只要知道蓝队是否拿到一血,我们就知道红队有没有拿到,可以去除红队的相关冗余数据。
drop_cols = ['redFirstBlood','redKills','redDeaths'
,'redGoldDiff','redExperienceDiff', 'blueCSPerMin',
'blueGoldPerMin','redCSPerMin','redGoldPerMin']
x.drop(drop_cols, axis=1, inplace=True)
数据可视化
data = x
data_std = (data - data.mean()) / data.std()
data = pd.concat([y, data_std.iloc[:, 0:9]], axis=1)
data = pd.melt(data, id_vars='blueWins', var_name='Features', value_name='Values')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(15,5))
# 绘制小提琴图
sns.violinplot(x='Features', y='Values', hue='blueWins', data=data, split=True,
inner='quart', ax=ax[0], palette='Blues')
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=45)
data = x
data_std = (data - data.mean()) / data.std()
data = pd.concat([y, data_std.iloc[:, 9:18]], axis=1)
data = pd.melt(data, id_vars='blueWins', var_name='Features', value_name='Values')
# 绘制小提琴图
sns.violinplot(x='Features', y='Values', hue='blueWins',
data=data, split=True, inner='quart', ax=ax[1], palette='Blues')
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=45)
plt.show()
小提琴图:
小提琴图 (Violin Plot)是用来展示多组数据的分布状态以及概率密度。这种图表结合了箱形图和密度图的特征,主要用来显示数据的分布形状。
从图中我们可以看出:
- 击杀英雄数量越多更容易赢,死亡数量越多越容易输(bluekills与bluedeaths左右的区别)。
- 助攻数量与击杀英雄数量形成的图形状类似,说明他们对游戏结果的影响差不多。
- 一血的取得情况与获胜有正相关,但是相关性不如击杀英雄数量明显。
- 经济差与经验差对于游戏胜负的影响较小。
- 击杀野怪数量对游戏胜负的影响并不大。
plt.figure(figsize=(18,14))
sns.heatmap(round(x.corr(),2), cmap='Blues', annot=True)
plt.show()

相关性热力图:
颜色越深代表特征之间相关性越强,我们剔除那些相关性较强的冗余特征。
# 去除冗余特征
drop_cols = ['redAvgLevel','blueAvgLevel']
x.drop(drop_cols, axis=1, inplace=True)
sns.set(style='whitegrid', palette='muted')
# 构造两个新特征
x['wardsPlacedDiff'] = x['blueWardsPlaced'] - x['redWardsPlaced']
x['wardsDestroyedDiff'] = x['blueWardsDestroyed'] - x['redWardsDestroyed']
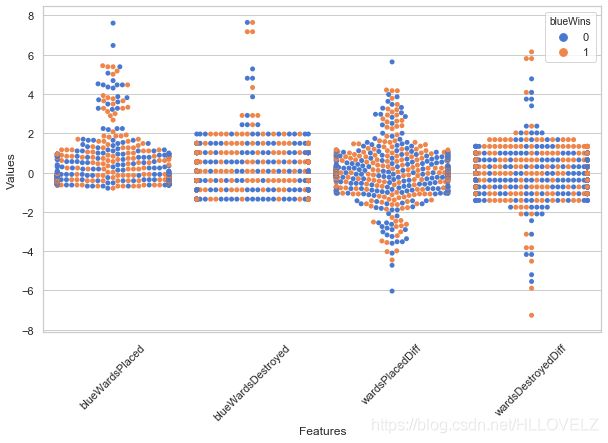
data = x[['blueWardsPlaced','blueWardsDestroyed','wardsPlacedDiff','wardsDestroyedDiff']].sample(1000)
data_std = (data - data.mean()) / data.std()
data = pd.concat([y, data_std], axis=1)
data = pd.melt(data, id_vars='blueWins', var_name='Features', value_name='Values')
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
sns.swarmplot(x='Features', y='Values', hue='blueWins', data=data)
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.show()
## 去除和眼位相关的特征
drop_cols = ['blueWardsPlaced','blueWardsDestroyed','wardsPlacedDiff',
'wardsDestroyedDiff','redWardsPlaced','redWardsDestroyed']
x.drop(drop_cols, axis=1, inplace=True)
x['killsDiff'] = x['blueKills'] - x['blueDeaths']
x['assistsDiff'] = x['blueAssists'] - x['redAssists']
x[['blueKills','blueDeaths','blueAssists','killsDiff','assistsDiff','redAssists']].hist(figsize=(12,10), bins=20)
plt.show()

我们发现击杀、死亡与助攻数的数据分布差别不大。但是击杀减去死亡、助攻减去死亡的分布与原分布差别很大,因此我们新构造这么两个特征。
3.3 模型训练
## 为了正确评估模型性能,将数据划分为训练集和测试集,并在训练集上训练模型,在测试集上验证模型性能。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
## 选择其类别为0和1的样本 (不包括类别为2的样本)
data_target_part = y
data_features_part = x
## 测试集大小为20%, 80%/20%分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data_features_part, data_target_part, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 2020)
## 导入LightGBM模型
from lightgbm.sklearn import LGBMClassifier
## 定义 LightGBM 模型
clf = LGBMClassifier()
# 在训练集上训练LightGBM模型
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
## 在训练集和测试集上分布利用训练好的模型进行预测
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
from sklearn import metrics
## 利用accuracy(准确度)【预测正确的样本数目占总预测样本数目的比例】评估模型效果
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
## 查看混淆矩阵 (预测值和真实值的各类情况统计矩阵)
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# 利用热力图对于结果进行可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()
我们可以发现共有718 + 707个样本预测正确,306 + 245个样本预测错误。
3.4 利用 LightGBM 进行特征选择
LightGBM的特征选择属于特征选择中的嵌入式方法,在LightGBM中可以用属性feature_importances_去查看特征的重要度。
sns.barplot(y=data_features_part.columns, x=clf.feature_importances_)
总经济差距等特征,助攻数量、击杀死亡数量等特征都具有很大的作用。插眼数、推塔数对模型的影响并不大。
初次之外,我们还可以使用LightGBM中的下列重要属性来评估特征的重要性。
gain:当利用特征做划分的时候的评价基尼指数
split:是以特征用到的次数来评价
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from lightgbm import plot_importance
def estimate(model,data):
#sns.barplot(data.columns,model.feature_importances_)
ax1=plot_importance(model,importance_type="gain")
ax1.set_title('gain')
ax2=plot_importance(model, importance_type="split")
ax2.set_title('split')
plt.show()
def classes(data,label,test):
model=LGBMClassifier()
model.fit(data,label)
ans=model.predict(test)
estimate(model, data)
return ans
ans=classes(x_train,y_train,x_test)
pre=accuracy_score(y_test, ans)
print('acc=',accuracy_score(y_test,ans))
3.5 调参
LightGBM中包括但不限于下列对模型影响较大的参数:
- learning_rate: 有时也叫作eta,系统默认值为0.3。每一步迭代的步长,很重要。太大了运行准确率不高,太小了运行速度慢。
- num_leaves:系统默认为32。这个参数控制每棵树中最大叶子节点数量。
- feature_fraction:系统默认值为1。我们一般设置成0.8左右。用来控制每棵随机采样的列数的占比(每一列是一个特征)。
- max_depth: 系统默认值为6,我们常用3-10之间的数字。这个值为树的最大深度。这个值是用来控制过拟合的。max_depth越大,模型学习的更加具体。
调节模型参数的方法有贪心算法、网格调参、贝叶斯调参等。这里我们采用网格调参,它的基本思想是穷举搜索:在所有候选的参数选择中,通过循环遍历,尝试每一种可能性,表现最好的参数就是最终的结果
## 从sklearn库中导入网格调参函数
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
## 定义参数取值范围
learning_rate = [0.1, 0.3, 0.6]
feature_fraction = [0.5, 0.8, 1]
num_leaves = [16, 32, 64]
max_depth = [-1,3,5,8]
parameters = { 'learning_rate': learning_rate,
'feature_fraction':feature_fraction,
'num_leaves': num_leaves,
'max_depth': max_depth}
model = LGBMClassifier(n_estimators = 50)
## 进行网格搜索
clf = GridSearchCV(model, parameters, cv=3, scoring='accuracy',verbose=3, n_jobs=-1)
clf = clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
## 网格搜索后的最好参数为
clf.best_params_
## 在训练集和测试集上分布利用最好的模型参数进行预测
## 定义带参数的 LightGBM模型
clf = LGBMClassifier(feature_fraction = 0.8,
learning_rate = 0.1,
max_depth= 3,
num_leaves = 16)
# 在训练集上训练LightGBM模型
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
## 利用accuracy(准确度)【预测正确的样本数目占总预测样本数目的比例】评估模型效果
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
## 查看混淆矩阵 (预测值和真实值的各类情况统计矩阵)
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# 利用热力图对于结果进行可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()
原本有306 + 245个错误,现在有 287 + 230个错误,带来了明显的正确率提升。