OpenCV:图像锐化
目录
1.简介
2.滤波
2.1 Sobel算子
1.Sobel输出类型为CV_8U
2.Sobel输出类型为CV_16S
2.2 Laplacian算子
1.没有高斯平滑的拉普拉斯算子
2.高斯平滑后的拉普拉斯算子-LoG算子
2.3 Roberts算子
| sobel | cv::Sobel() |
| laplacian | cv::Laplacian() |
| Mat数据类型转换 | convertTo() |
1.简介
边缘定义为图像中亮度突变的区域,可以利用微分方法去检测图像中的边缘。在图像处理中最常用的应用微分方法就是计算梯度(方向导数取最大值的方向的向量)。
图像为离散的数字矩阵,因此用差分代替微分,得到梯度图像。梯度图像反映的是图像中灰度级的变化,边缘检测需要进一步判断梯度图像中的特殊点。
图像锐化的目的是加强图像中景物的边缘与轮廓,突出图像中的细节或者增强被模糊了的细节。实质是将原图像和梯度图像相加,以增强图中的变化。
2.滤波
2.1 Sobel算子
先加权平滑,再做微分运算。Sobel算子引入平均元素,对图像中随机噪声有一定的平滑作用,但不能完全排除虚假边缘,检测出的边缘容易出现多像素宽度。
详情:Sobel算子 Mat数据类型及转换
void Sobel (
InputArray src,//输入图
OutputArray dst,//输出图
int ddepth,//输出图像的深度
int dx,
int dy,
int ksize=3,
double scale=1,
double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );主要在ddepth的理解上
- 若src.depth() = CV_8U, 取ddepth =-1/CV_16S/CV_32F/CV_64F
- 若src.depth() = CV_16U/CV_16S, 取ddepth =-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- 若src.depth() = CV_32F, 取ddepth =-1/CV_32F/CV_64F
- 若src.depth() = CV_64F, 取ddepth = -1/CV_64F
ddepth =-1时,代表输出图像与输入图像相同的深度。
黑色到白色的过渡被视为正斜率(具有正值),而白色到黑色的过渡被视为负斜率(具有负值)。输出设置为CV_8U会丢失负值。如果要检测两个边缘,更好的选择是将输出数据类型保留为更高的形式,例如CV_16S,CV_64F等,取其绝对值,然后转换回CV_8U。
1.Sobel输出类型为CV_8U
Mat dst1;
Mat dst2;
Sobel(image, dst1, -1, 1, 0);#CV_8U
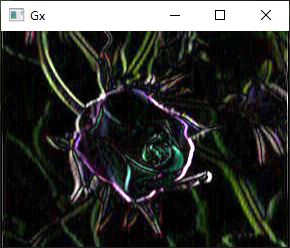
imshow("Gx", dst1);
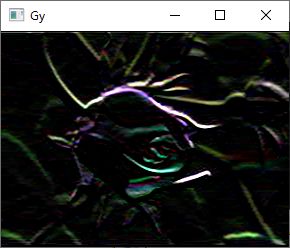
Sobel(image, dst2, -1, 0, 1);
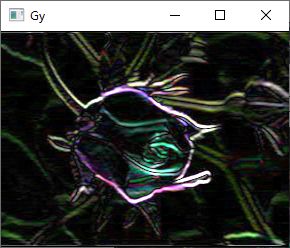
imshow("Gy", dst2);
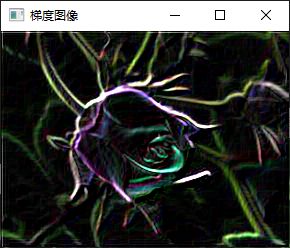
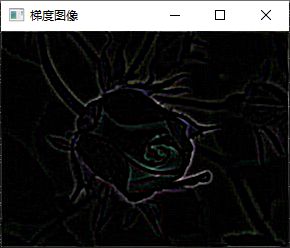
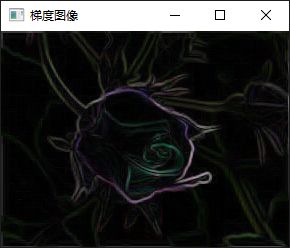
add(abs(dst1), abs(dst2), out);
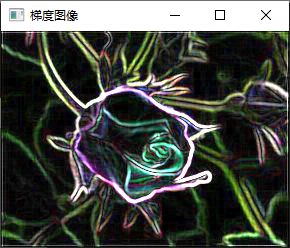
imshow("梯度图像", out);
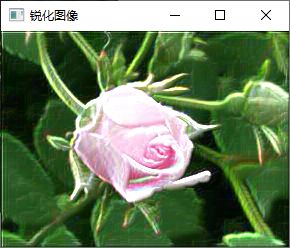
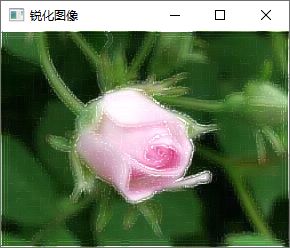
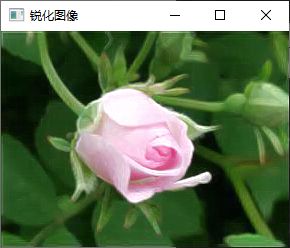
add(image,out,out);
imshow("锐化图像", out);2.Sobel输出类型为CV_16S
cout << image.depth() << endl;
Mat dst1;
Mat dst2;
Sobel(image, dst1, CV_16S, 1, 0);
Sobel(image, dst2, CV_16S, 0, 1);
dst1=abs(dst1);
dst2=abs(dst2);
add(dst1, dst2, out);
cout << out.depth() << endl;
out.convertTo(out, CV_8U);
imshow("梯度图像", out);
add(image,out,out);
imshow("锐化图像", out);
dst1.convertTo(dst1, CV_8U);
imshow("Gx", dst1);
dst2.convertTo(dst2, CV_8U);
imshow("Gy", dst2);2.2 Laplacian算子
详情:Laplacian()函数
二阶微分算子,对噪声敏感,不能检测边缘的方向。容易丢失一部分边缘的方向信息,造成一些不连续的检测边缘。
//GaussianBlur(image, image, Size(3, 3), 0);
Laplacian(image, out, CV_16S, 3);
out.convertTo(out, CV_8U);
imshow("梯度图像", out);
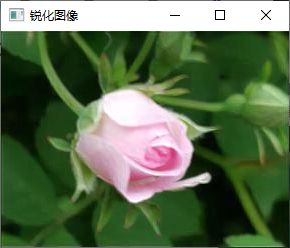
add(image, out, out);
imshow("锐化图像", out);1.没有高斯平滑的拉普拉斯算子
2.高斯平滑后的拉普拉斯算子-LoG算子
2.3 Roberts算子
通过交叉微分检测局部变化,边缘定位精度较高,但容易丢失一部分边缘。由于图像没经过平滑处理,因此不具备能抑制噪声能力,对陡峭边缘且含噪声少的图像效果较好。用模板做的。
![]()
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
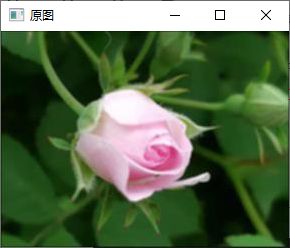
Mat image = imread("C:/Users/YY/Pictures/Saved Pictures/frose.jpg");
Mat out;
imshow("原图", image);
Mat k1 = (Mat_(2, 2) << 1, 0, 0, -1);
Mat k2 = (Mat_(2, 2) << 0, 1, -1, 0);
Mat dst1;
Mat dst2;
filter2D(image, dst1, -1,k1);//输出类型CV_8U
filter2D(image, dst2, -1, k2);
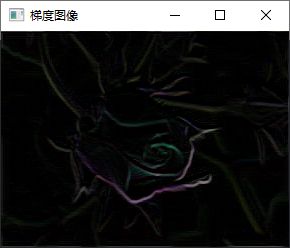
add(abs(dst1), abs(dst2), out);
imshow("梯度图像", out);
add(image,out,out);
imshow("锐化图像", out);
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
同样更改输出类型为CV_16S,结果如下:
filter2D(image, dst1, CV_16S, k1);
filter2D(image, dst2, CV_16S, k2);
add(abs(dst1), abs(dst2), out);
out.convertTo(out, CV_8U);
imshow("梯度图像", out);