【机器学习】详解 EfficientNet
- Paper 地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946
- PyTorch 实现:https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
- TensorFlow 实现:https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/tree/master/models/official/efficientnet
目录
一、摘要
二、介绍
三、网络放缩
3.1 问题构造
3.2 维度放缩
3.3 复合放缩
四、网络架构
五、对比实验
六、架构细节
6.1 图示
6.2 代码
七、EfficientNet V2
一、摘要
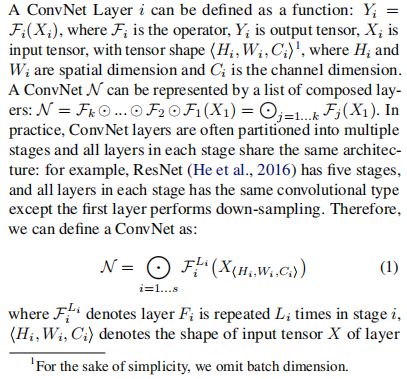
卷积神经网络 (ConvNets) 通常是在固定资源预算下开发的,若有更多资源可用,则可扩大规模以提高准确率。本文系统地研究了模型放缩,并证实了 仔细地平衡 网络深度、网络宽度和图像分辨率 可带来更好性能。基于这一观察,本文提出了一种新的放缩方法,该方法使用了一个简单但高效的 复合系数 (compound coeffificient) 统一地放缩深度/宽度/分辨率的所有维度。本文证明了这种方法在扩大 MobileNets 和 ResNet 方面的有效性。
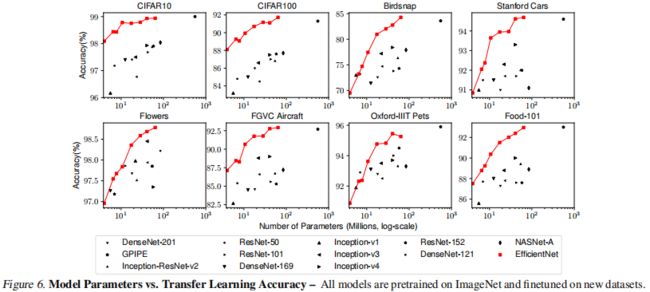
更进一步地,本文使用 神经架构搜索 (neural architecture search) 来设计一个新的基线网络,并对其扩展以获得一系列称为 EfficientNets 的模型,它比以前的 ConvNets 的准确性和效率更佳。特别地,EfficientNet-B7 在 ImageNet 上达到了 SOTA 的 84.3% 的 top-1 准确率,同时比现有最好的 ConvNet 小 8.4 倍、推理速度快 6.1 倍。EfficientNets 在 CIFAR-100 (91.7%)、Flowers (98.8%) 和其他 3 个迁移学习数据集上也能很好地迁移,并达到 SOTA 的准确率,而参数少了一个数量级。
二、介绍
扩大 ConvNets 被广泛用于获得更佳精度。例如,ResNet 可通过使用更多层从 ResNet-18 扩大到 ResNet-200;最近,GPipe 通过扩大基线模型 4 倍,获得了 84.3% 的ImageNet top-1 准确度。然而,扩大 ConvNets 的过程从未被很好地理解过,目前有很多方法可以做到这一点。最常见的方法是通过深度或宽度扩大 ConvNets。另一种不太常见但越来越流行的方法是通过图像分辨率扩大模型。以往,通常只按深度/宽度/图像尺寸这三个维度之一来放缩。尽管可以任意放缩两个或三个维度,但需要繁琐的手工调优,且常无法达到最佳的准确度和效率。
在本文中,我们想研究和重新思考扩大 ConvNets 的过程。特别地,我们调查中心问题:是否存在一个原则性方法来扩大 ConvNets,以达到更好的准确率和效率?我们的实证研究表明,平衡网络宽度/深度/分辨率的所有维度是至关重要的,且令人惊讶的是,这种平衡可通过简单地使用固定比例缩放来实现。基于此观察,我们提出了一种简单而有效的复合放缩方法。有别于传统实践中的任意放缩这些因子,我们的方法均匀/统一地缩放网络的宽度、深度及一组固定放缩系数的分辨率。例如,如果我们想使用 ![]() 倍以上的计算资源,那么我们可以简单地将网络深度增加
倍以上的计算资源,那么我们可以简单地将网络深度增加 ![]() ,宽度增加
,宽度增加 ![]() ,图像大小增加
,图像大小增加 ![]() ,其中
,其中 ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 是在原始小模型上进行小网格搜索所确定的常系数。图 2 阐述了我们的放缩方法和传统方法之间的区别。
是在原始小模型上进行小网格搜索所确定的常系数。图 2 阐述了我们的放缩方法和传统方法之间的区别。
直观上,复合放缩方法是有意义的,因为若输入图像更大,那么网络需要 更多层来增加感受野 和 更多的通道来捕捉更细粒度的模式。事实上,之前的理论和实证结果均表明网络宽度和深度之间存在一定的关系,但据我们所知,我们是第一个对网络宽度、深度和分辨率三个维度之间的关系进行实证量化的人。
本文证明了上述复合缩放方法在 MobileNets 和 ResNet 上工作得很好。值得注意的是,模型缩放的有效性在很大程度上依赖于基线网络。更进一步地,我们使用 神经架构搜索 来开发一个新的基线网络,并将其扩展以获得一系列称为 EfficientNets 的模型。图 1 总结了 ImageNet 的性能,其中 EfficientNets 明显优于其他 ConvNets。特别地,EfficientNets-B7 超过了现有的最佳 GPipe 准确度,却减少了 8.4 倍参数、提高了 6.1倍推理速度。与广泛使用的 ResNet-50 相比,EffcientNet-B4 在类似的 FLOPs 下将 top-1 准确度从 76.3% 提高到 83.0%(+6.7%)。除 ImageNet,EfficientNets 也有很好的迁移能力,在 8 个广泛使用的数据集中的 5 个上实现了 SOTA 的准确度,同时减少了比现有 ConvNets 至多 21 倍的参数。
三、网络放缩
3.1 问题构造
3.2 维度放缩
问题 2 的主要难点是最优的 ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 相互依赖,在不同的资源约束下,其值会发生变化。由于该困难,传统方法主要在以下维度之一中扩大 ConvNets:
相互依赖,在不同的资源约束下,其值会发生变化。由于该困难,传统方法主要在以下维度之一中扩大 ConvNets:
- 深度

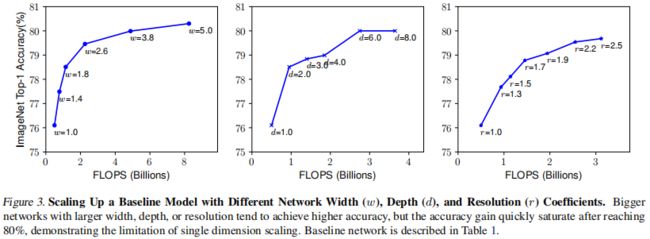
最常用的方法是放缩网络深度,这被许多 ConvNets 使用。直观地,更深的 ConvNets 可以捕获更丰富、更复杂的特征,并很好地泛化与新的任务。然而,由于梯度消失,深度网络的训练也更加困难。虽然诸如 Skip Connection 和 BN 等技术缓解了训练问题,极深网络的准确率增益仍会降低。例如,ResNet-1000 和 ResNet-101 有相似的准确度,尽管前者有更多的层。图3 (中) 显示了对不同深度系数 ![]() 的基线模型的放缩实证研究,进一步表明 极深的 ConvNets 的准确率回报减少了。
的基线模型的放缩实证研究,进一步表明 极深的 ConvNets 的准确率回报减少了。
- 宽度
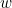
放缩网络宽度广泛用于小型模型。更宽的网络往往能够捕捉到更细粒度的特征,也更容易训练。然而。极宽但浅的网络在捕获更高层次的特征时往往存在困难。我们的经验结果显示于 图3 (左) ,当网络因具有更大的 ![]() 而变得更宽时,准确率很快饱和。
而变得更宽时,准确率很快饱和。
- 分辨率

有了更高分辨率的输入图像,ConvNets 可以潜在地捕获更细粒度的模式。从早期 ConvNets 的 224x224 开始,现代的 ConvNets 倾向于使用 299x299 或 331x331 以提高准确率。最近,GPipe 实现了 SOTA 的 ImageNet 准确率,分辨率为 480x480。如 600x600 等更高分辨率,也被广泛应用于目标检测 ConvNets 中。图3 (右) 显示了网络分辨率放缩的结果,更高的分辨率确实提高了准确率,但是对于非常高的分辨率,准确率增益会降低 (分辨率 ![]() 表示 224x224,
表示 224x224,![]() 表示 560x560)。
表示 560x560)。
以上分析使我们得出第一个结论:
- 观察结论 1:扩大网络宽度、深度或分辨率的任意维度都可以提高准确度,但对于更大的模型,准确度增益会降低。
3.3 复合放缩
我们从经验上观察到,不同的放缩维度不是独立的。直观地,对于分辨率较高的图像,应增加网络深度,从而更大的感受野 可以在更大图像中 有助于捕获 包含更多像素的相似特征。相应地,当分辨率较高时,也应增加网络宽度,以便于在高分辨率图像中 捕获 具有更多像素的 更多细粒度模式。这些直觉表明,我们需要协调和平衡不同的放缩维度,而非传统的一维放缩。
为验证我们的直觉,我们比较了不同网络深度和分辨率下的宽度放缩,如图4所示。如果只放缩网络宽度 ![]() 而不改变深度 (
而不改变深度 (![]() ) 和分辨率 (
) 和分辨率 (![]() ),准确率会很快饱和。具有更深的 (
),准确率会很快饱和。具有更深的 (![]() ) 和更高的分辨率 (
) 和更高的分辨率 (![]() ),宽度缩放在相同的 FLOPs 代价下达到更好的准确率。
),宽度缩放在相同的 FLOPs 代价下达到更好的准确率。
以上结果使我们得出第二个结论:
- 观察结论2:为追求更高的准确率和效率,在放缩 ConVnet 时,关键是要平衡网络宽度、深度和分辨率的各个维度。
事实上,之前的一些工作已尝试过任意平衡网络宽度和深度,但均需繁琐的手动调整。
本文提出了一种新的复合放缩方法,利用复合系数有原则地均匀/统一放缩网络宽度、深度和分辨率:
其中,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 均为常数,可由小网格搜索决定。直观地,
均为常数,可由小网格搜索决定。直观地,![]() 是一个用户特定的系数,用于控制多少资源可用于模型放缩,而
是一个用户特定的系数,用于控制多少资源可用于模型放缩,而 ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 表明如何分配这些额外资源以分别用于网络宽度、深度和分辨率。 值得注意的是,常规卷积操作的 FLOPS 与
表明如何分配这些额外资源以分别用于网络宽度、深度和分辨率。 值得注意的是,常规卷积操作的 FLOPS 与 ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 成正比,即令网络深度加倍将使 FLOPS 加倍,但使网络宽度或分辨率加倍则将使 FLOPS 增加 4 倍。因为卷积操作通常决定了 ConvNets 的运算成本,根据上式放缩一个 ConvNet 将近似增加
成正比,即令网络深度加倍将使 FLOPS 加倍,但使网络宽度或分辨率加倍则将使 FLOPS 增加 4 倍。因为卷积操作通常决定了 ConvNets 的运算成本,根据上式放缩一个 ConvNet 将近似增加 ![]() 的总 FLOPS。在本文,我们约束
的总 FLOPS。在本文,我们约束 ![]() 以便于对任意新
以便于对任意新 ![]() ,总 FLOPS 将近似增加
,总 FLOPS 将近似增加 ![]() 。
。
四、网络架构
由于模型缩放不会改变基线网络中的层算子 ![]() ,因此具有一个良好的基线网络也是至关重要的。我们将使用现有的 ConyNets 来评估我们的放缩方法,但为更好地证明我们的放缩方法的有效性。我们还开发了一种新的手机尺寸的基准 —— EfficientNet。
,因此具有一个良好的基线网络也是至关重要的。我们将使用现有的 ConyNets 来评估我们的放缩方法,但为更好地证明我们的放缩方法的有效性。我们还开发了一种新的手机尺寸的基准 —— EfficientNet。
受到启发,我们通过利用 多目标 NAS 来优化基线网络,这种搜索既优化了准确度,也优化了 FLOPS。具体地,使用相同的搜索空间 并 用 ![]() 作为优化目标,其中
作为优化目标,其中 ![]() 和
和 ![]() 表示模型
表示模型 ![]() 的准确率和 FLOPS,
的准确率和 FLOPS,![]() 是目标 FLOPS 且
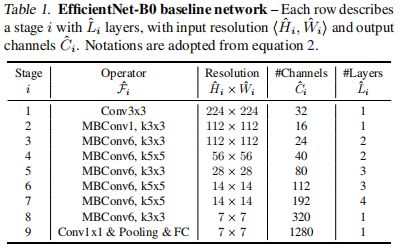
是目标 FLOPS 且 ![]() 是一个超参数,用于控制准确率和 FLOPS 之间的权衡。不同于之前的工作,这里我们优化的是 FLOPS 而非延迟,因为我们不针对任何特定的硬件设备。我们的搜索产生了一个高效的网络 —— EfficientNet - B0。由于我们使用相同的搜索空间,架构类似于 MnasNet,但 EfficientNet - B0 稍微大一些,因其 FLOPS 目标更大 (我们的 FLOPS 目标是 400M)。表 1 显示了 EfficientNet - B0 的架构。其主要构造块 (Building Block) 为 mobile inverted bottleneck MBConv,我们也对其加入了 通道注意力 进行优化。
是一个超参数,用于控制准确率和 FLOPS 之间的权衡。不同于之前的工作,这里我们优化的是 FLOPS 而非延迟,因为我们不针对任何特定的硬件设备。我们的搜索产生了一个高效的网络 —— EfficientNet - B0。由于我们使用相同的搜索空间,架构类似于 MnasNet,但 EfficientNet - B0 稍微大一些,因其 FLOPS 目标更大 (我们的 FLOPS 目标是 400M)。表 1 显示了 EfficientNet - B0 的架构。其主要构造块 (Building Block) 为 mobile inverted bottleneck MBConv,我们也对其加入了 通道注意力 进行优化。
从基线 EfficientNet - B0 开始,我们通过两个步骤应用我们的复合放缩方法来扩展它:
- 步骤1:首先固定
,假设有两倍以上的资源可用,则基于式 2 和 3 对
,
,
进行小网格搜索。特别地,在
的约束下,我们发现 EfficientNet - B0 的最佳值为
。
- 步骤2:然后将
,
,
固定为常数,并根据式 3 使用不同的
扩大基线网络,从而得到 EfficientNet - B1 ~ EfficientNet - B7 (详见表2)。
值得注意的是,通过直接围绕大模型搜索 ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 有可能获得更好的性能,但在大模型上的搜索成本会变得昂贵得令人难以接受。我们的方法解决了该问题,即 只在小的基线网络上先进行一次搜索 (步骤1),然后对所有其他模型使用相同的放缩系数 (步骤2)。
有可能获得更好的性能,但在大模型上的搜索成本会变得昂贵得令人难以接受。我们的方法解决了该问题,即 只在小的基线网络上先进行一次搜索 (步骤1),然后对所有其他模型使用相同的放缩系数 (步骤2)。
五、对比实验
![]()
六、架构细节
6.1 图示
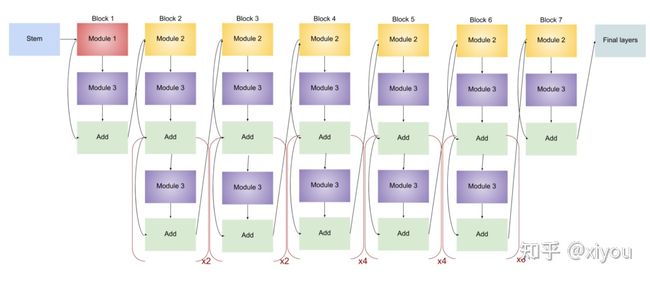
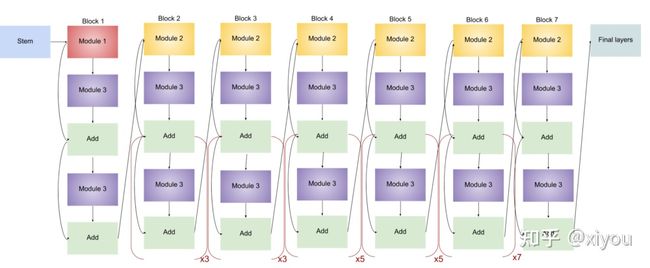
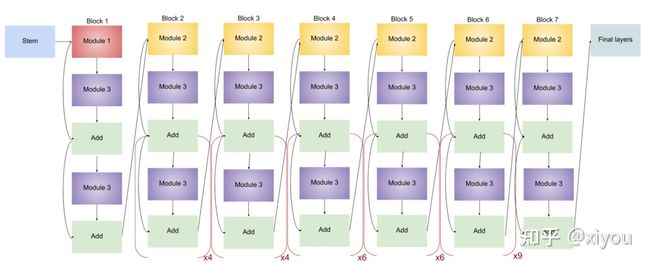
任何网络的 Stem 都是最关键的,确定后才会进行后续实验,上图的 头部/尾部架构 在 EfficientNet - B1 ~ EfficientNet - B7 都有出现,这些块还有不同数量的子块,子块数随版本的增加而增加。以下代码可用于查看模型架构:
import tensorflow as tf
IMG_SHAPE = (224, 224, 3)
model0 = tf.keras.applications.EfficientNetB0(input_shape=IMG_SHAPE, include_top=False, weights="imagenet")
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model0) # to draw and visualize
model0.summary() # to see the list of layers and parameters其中,EfficientNet-B0 总层数为 237、EfficientNet-B7 总层数为 813,但其实都可由以下 5 个模块和上述 2 个头部/尾部架构构成。
由上述 5 个模块 (Module) 构成以下三种块 (Block):
至此,所有用于构建 EfficientNet 的块已经确定,以下是各模型的架构 (×n means that modules inside the bracket are repeated n times):
- EfficientNet-B0
- EfficientNet-B1
- EfficientNet-B2
结构与 EfficientNet-B1 相同,唯一的区别是通道数不同,从而增加了参数量。
- EfficientNet-B3
- EfficientNet-B4
- EfficientNet-B5
- EfficientNet-B6
- EfficientNet-B7
综上,容易看出各模型之间的差异 —— 子块数量逐渐增多。下表显示了 EfficientNet-B0 中卷积核尺寸、分辨率大小、通道数和层数:
下表展示了不同网络架构下,各阶段的通道数 (各阶段分辨率大小一一对应):
6.2 代码
EfficientNet-PyTorch/efficientnet_pytorch/model.py
"""model.py - Model and module class for EfficientNet.
They are built to mirror those in the official TensorFlow implementation.
"""
# Author: lukemelas (github username)
# Github repo: https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
# With adjustments and added comments by workingcoder (github username).
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from .utils import (
round_filters,
round_repeats,
drop_connect,
get_same_padding_conv2d,
get_model_params,
efficientnet_params,
load_pretrained_weights,
Swish,
MemoryEfficientSwish,
calculate_output_image_size
)
VALID_MODELS = (
'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3',
'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7',
'efficientnet-b8',
# Support the construction of 'efficientnet-l2' without pretrained weights
'efficientnet-l2'
)
class MBConvBlock(nn.Module):
"""Mobile Inverted Residual Bottleneck Block.
Args:
block_args (namedtuple): BlockArgs, defined in utils.py.
global_params (namedtuple): GlobalParam, defined in utils.py.
image_size (tuple or list): [image_height, image_width].
References:
[1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861 (MobileNet v1)
[2] https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381 (MobileNet v2)
[3] https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244 (MobileNet v3)
"""
def __init__(self, block_args, global_params, image_size=None):
super().__init__()
self._block_args = block_args
self._bn_mom = 1 - global_params.batch_norm_momentum # pytorch's difference from tensorflow
self._bn_eps = global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
self.has_se = (self._block_args.se_ratio is not None) and (0 < self._block_args.se_ratio <= 1)
self.id_skip = block_args.id_skip # whether to use skip connection and drop connect
# Expansion phase (Inverted Bottleneck)
inp = self._block_args.input_filters # number of input channels
oup = self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.expand_ratio # number of output channels
if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
self._expand_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=inp, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
# image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 1) <-- this wouldn't modify image_size
# Depthwise convolution phase
k = self._block_args.kernel_size
s = self._block_args.stride
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
self._depthwise_conv = Conv2d(
in_channels=oup, out_channels=oup, groups=oup, # groups makes it depthwise
kernel_size=k, stride=s, bias=False)
self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, s)
# Squeeze and Excitation layer, if desired
if self.has_se:
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=(1, 1))
num_squeezed_channels = max(1, int(self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.se_ratio))
self._se_reduce = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=num_squeezed_channels, kernel_size=1)
self._se_expand = Conv2d(in_channels=num_squeezed_channels, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1)
# Pointwise convolution phase
final_oup = self._block_args.output_filters
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
self._project_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=final_oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self._bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=final_oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
def forward(self, inputs, drop_connect_rate=None):
"""MBConvBlock's forward function.
Args:
inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
drop_connect_rate (bool): Drop connect rate (float, between 0 and 1).
Returns:
Output of this block after processing.
"""
# Expansion and Depthwise Convolution
x = inputs
if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
x = self._expand_conv(inputs)
x = self._bn0(x)
x = self._swish(x)
x = self._depthwise_conv(x)
x = self._bn1(x)
x = self._swish(x)
# Squeeze and Excitation
if self.has_se:
x_squeezed = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)
x_squeezed = self._se_reduce(x_squeezed)
x_squeezed = self._swish(x_squeezed)
x_squeezed = self._se_expand(x_squeezed)
x = torch.sigmoid(x_squeezed) * x
# Pointwise Convolution
x = self._project_conv(x)
x = self._bn2(x)
# Skip connection and drop connect
input_filters, output_filters = self._block_args.input_filters, self._block_args.output_filters
if self.id_skip and self._block_args.stride == 1 and input_filters == output_filters:
# The combination of skip connection and drop connect brings about stochastic depth.
if drop_connect_rate:
x = drop_connect(x, p=drop_connect_rate, training=self.training)
x = x + inputs # skip connection
return x
def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
"""Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
Args:
memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
"""
self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
"""EfficientNet model.
Most easily loaded with the .from_name or .from_pretrained methods.
Args:
blocks_args (list[namedtuple]): A list of BlockArgs to construct blocks.
global_params (namedtuple): A set of GlobalParams shared between blocks.
References:
[1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946 (EfficientNet)
Example:
>>> import torch
>>> from efficientnet.model import EfficientNet
>>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
>>> model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
>>> model.eval()
>>> outputs = model(inputs)
"""
def __init__(self, blocks_args=None, global_params=None):
super().__init__()
assert isinstance(blocks_args, list), 'blocks_args should be a list'
assert len(blocks_args) > 0, 'block args must be greater than 0'
self._global_params = global_params
self._blocks_args = blocks_args
# Batch norm parameters
bn_mom = 1 - self._global_params.batch_norm_momentum
bn_eps = self._global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
# Get stem static or dynamic convolution depending on image size
image_size = global_params.image_size
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
# Stem
in_channels = 3 # rgb
out_channels = round_filters(32, self._global_params) # number of output channels
self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 2)
# Build blocks
self._blocks = nn.ModuleList([])
for block_args in self._blocks_args:
# Update block input and output filters based on depth multiplier.
block_args = block_args._replace(
input_filters=round_filters(block_args.input_filters, self._global_params),
output_filters=round_filters(block_args.output_filters, self._global_params),
num_repeat=round_repeats(block_args.num_repeat, self._global_params)
)
# The first block needs to take care of stride and filter size increase.
self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride)
if block_args.num_repeat > 1: # modify block_args to keep same output size
block_args = block_args._replace(input_filters=block_args.output_filters, stride=1)
for _ in range(block_args.num_repeat - 1):
self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
# image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride) # stride = 1
# Head
in_channels = block_args.output_filters # output of final block
out_channels = round_filters(1280, self._global_params)
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
self._conv_head = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
# Final linear layer
self._avg_pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
if self._global_params.include_top:
self._dropout = nn.Dropout(self._global_params.dropout_rate)
self._fc = nn.Linear(out_channels, self._global_params.num_classes)
# set activation to memory efficient swish by default
self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
"""Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
Args:
memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
"""
self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
for block in self._blocks:
block.set_swish(memory_efficient)
def extract_endpoints(self, inputs):
"""Use convolution layer to extract features
from reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
Args:
inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
Returns:
Dictionary of last intermediate features
with reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
Example:
>>> import torch
>>> from efficientnet.model import EfficientNet
>>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
>>> model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
>>> endpoints = model.extract_endpoints(inputs)
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_1'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112])
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_2'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56])
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_3'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28])
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_4'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14])
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_5'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 320, 7, 7])
>>> print(endpoints['reduction_6'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 7, 7])
"""
endpoints = dict()
# Stem
x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
prev_x = x
# Blocks
for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
if drop_connect_rate:
drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
if prev_x.size(2) > x.size(2):
endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = prev_x
elif idx == len(self._blocks) - 1:
endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
prev_x = x
# Head
x = self._swish(self._bn1(self._conv_head(x)))
endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
return endpoints
def extract_features(self, inputs):
"""use convolution layer to extract feature .
Args:
inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
Returns:
Output of the final convolution
layer in the efficientnet model.
"""
# Stem
x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
# Blocks
for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
if drop_connect_rate:
drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
# Head
x = self._swish(self._bn1(self._conv_head(x)))
return x
def forward(self, inputs):
"""EfficientNet's forward function.
Calls extract_features to extract features, applies final linear layer, and returns logits.
Args:
inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
Returns:
Output of this model after processing.
"""
# Convolution layers
x = self.extract_features(inputs)
# Pooling and final linear layer
x = self._avg_pooling(x)
if self._global_params.include_top:
x = x.flatten(start_dim=1)
x = self._dropout(x)
x = self._fc(x)
return x
@classmethod
def from_name(cls, model_name, in_channels=3, **override_params):
"""Create an efficientnet model according to name.
Args:
model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
override_params (other key word params):
Params to override model's global_params.
Optional key:
'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum',
'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
Returns:
An efficientnet model.
"""
cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
blocks_args, global_params = get_model_params(model_name, override_params)
model = cls(blocks_args, global_params)
model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
return model
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(cls, model_name, weights_path=None, advprop=False,
in_channels=3, num_classes=1000, **override_params):
"""Create an efficientnet model according to name.
Args:
model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
weights_path (None or str):
str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
advprop (bool):
Whether to load pretrained weights
trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
num_classes (int):
Number of categories for classification.
It controls the output size for final linear layer.
override_params (other key word params):
Params to override model's global_params.
Optional key:
'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
'batch_norm_momentum',
'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
Returns:
A pretrained efficientnet model.
"""
model = cls.from_name(model_name, num_classes=num_classes, **override_params)
load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=weights_path,
load_fc=(num_classes == 1000), advprop=advprop)
model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
return model
@classmethod
def get_image_size(cls, model_name):
"""Get the input image size for a given efficientnet model.
Args:
model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
Returns:
Input image size (resolution).
"""
cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
_, _, res, _ = efficientnet_params(model_name)
return res
@classmethod
def _check_model_name_is_valid(cls, model_name):
"""Validates model name.
Args:
model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
Returns:
bool: Is a valid name or not.
"""
if model_name not in VALID_MODELS:
raise ValueError('model_name should be one of: ' + ', '.join(VALID_MODELS))
def _change_in_channels(self, in_channels):
"""Adjust model's first convolution layer to in_channels, if in_channels not equals 3.
Args:
in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
"""
if in_channels != 3:
Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=self._global_params.image_size)
out_channels = round_filters(32, self._global_params)
self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)EfficientNet-PyTorch/efficientnet_pytorch/utils.py
"""utils.py - Helper functions for building the model and for loading model parameters.
These helper functions are built to mirror those in the official TensorFlow implementation.
"""
# Author: lukemelas (github username)
# Github repo: https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
# With adjustments and added comments by workingcoder (github username).
import re
import math
import collections
from functools import partial
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils import model_zoo
################################################################################
# Help functions for model architecture
################################################################################
# GlobalParams and BlockArgs: Two namedtuples
# Swish and MemoryEfficientSwish: Two implementations of the method
# round_filters and round_repeats:
# Functions to calculate params for scaling model width and depth ! ! !
# get_width_and_height_from_size and calculate_output_image_size
# drop_connect: A structural design
# get_same_padding_conv2d:
# Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
# Conv2dStaticSamePadding
# get_same_padding_maxPool2d:
# MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding
# MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding
# It's an additional function, not used in EfficientNet,
# but can be used in other model (such as EfficientDet).
# Parameters for the entire model (stem, all blocks, and head)
GlobalParams = collections.namedtuple('GlobalParams', [
'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient', 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum', 'batch_norm_epsilon',
'drop_connect_rate', 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth', 'include_top'])
# Parameters for an individual model block
BlockArgs = collections.namedtuple('BlockArgs', [
'num_repeat', 'kernel_size', 'stride', 'expand_ratio',
'input_filters', 'output_filters', 'se_ratio', 'id_skip'])
# Set GlobalParams and BlockArgs's defaults
GlobalParams.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(GlobalParams._fields)
BlockArgs.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(BlockArgs._fields)
# Swish activation function
if hasattr(nn, 'SiLU'):
Swish = nn.SiLU
else:
# For compatibility with old PyTorch versions
class Swish(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
# A memory-efficient implementation of Swish function
class SwishImplementation(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, i):
result = i * torch.sigmoid(i)
ctx.save_for_backward(i)
return result
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
i = ctx.saved_tensors[0]
sigmoid_i = torch.sigmoid(i)
return grad_output * (sigmoid_i * (1 + i * (1 - sigmoid_i)))
class MemoryEfficientSwish(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return SwishImplementation.apply(x)
def round_filters(filters, global_params):
"""Calculate and round number of filters based on width multiplier.
Use width_coefficient, depth_divisor and min_depth of global_params.
Args:
filters (int): Filters number to be calculated.
global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
Returns:
new_filters: New filters number after calculating.
"""
multiplier = global_params.width_coefficient
if not multiplier:
return filters
# TODO: modify the params names.
# maybe the names (width_divisor,min_width)
# are more suitable than (depth_divisor,min_depth).
divisor = global_params.depth_divisor
min_depth = global_params.min_depth
filters *= multiplier
min_depth = min_depth or divisor # pay attention to this line when using min_depth
# follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
new_filters = max(min_depth, int(filters + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_filters < 0.9 * filters: # prevent rounding by more than 10%
new_filters += divisor
return int(new_filters)
def round_repeats(repeats, global_params):
"""Calculate module's repeat number of a block based on depth multiplier.
Use depth_coefficient of global_params.
Args:
repeats (int): num_repeat to be calculated.
global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
Returns:
new repeat: New repeat number after calculating.
"""
multiplier = global_params.depth_coefficient
if not multiplier:
return repeats
# follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
return int(math.ceil(multiplier * repeats))
def drop_connect(inputs, p, training):
"""Drop connect.
Args:
input (tensor: BCWH): Input of this structure.
p (float: 0.0~1.0): Probability of drop connection.
training (bool): The running mode.
Returns:
output: Output after drop connection.
"""
assert 0 <= p <= 1, 'p must be in range of [0,1]'
if not training:
return inputs
batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
keep_prob = 1 - p
# generate binary_tensor mask according to probability (p for 0, 1-p for 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob
random_tensor += torch.rand([batch_size, 1, 1, 1], dtype=inputs.dtype, device=inputs.device)
binary_tensor = torch.floor(random_tensor)
output = inputs / keep_prob * binary_tensor
return output
def get_width_and_height_from_size(x):
"""Obtain height and width from x.
Args:
x (int, tuple or list): Data size.
Returns:
size: A tuple or list (H,W).
"""
if isinstance(x, int):
return x, x
if isinstance(x, list) or isinstance(x, tuple):
return x
else:
raise TypeError()
def calculate_output_image_size(input_image_size, stride):
"""Calculates the output image size when using Conv2dSamePadding with a stride.
Necessary for static padding. Thanks to mannatsingh for pointing this out.
Args:
input_image_size (int, tuple or list): Size of input image.
stride (int, tuple or list): Conv2d operation's stride.
Returns:
output_image_size: A list [H,W].
"""
if input_image_size is None:
return None
image_height, image_width = get_width_and_height_from_size(input_image_size)
stride = stride if isinstance(stride, int) else stride[0]
image_height = int(math.ceil(image_height / stride))
image_width = int(math.ceil(image_width / stride))
return [image_height, image_width]
# Note:
# The following 'SamePadding' functions make output size equal ceil(input size/stride).
# Only when stride equals 1, can the output size be the same as input size.
# Don't be confused by their function names ! ! !
def get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=None):
"""Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
Args:
image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
Returns:
Conv2dDynamicSamePadding or Conv2dStaticSamePadding.
"""
if image_size is None:
return Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
else:
return partial(Conv2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
class Conv2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
"""2D Convolutions like TensorFlow, for a dynamic image size.
The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
"""
# Tips for 'SAME' mode padding.
# Given the following:
# i: width or height
# s: stride
# k: kernel size
# d: dilation
# p: padding
# Output after Conv2d:
# o = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1)
# If o equals i, i = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1),
# => p = (i-1)*s+((k-1)*d+1)-i
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, 0, dilation, groups, bias)
self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
def forward(self, x):
ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
sh, sw = self.stride
oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw) # change the output size according to stride ! ! !
pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
return F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
class Conv2dStaticSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
"""2D Convolutions like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
"""
# With the same calculation as Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, image_size=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
# Calculate padding based on image size and save it
assert image_size is not None
ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
sh, sw = self.stride
oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2,
pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
else:
self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.static_padding(x)
x = F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
return x
def get_same_padding_maxPool2d(image_size=None):
"""Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
Args:
image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
Returns:
MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding or MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding.
"""
if image_size is None:
return MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding
else:
return partial(MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
class MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
"""2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with a dynamic image size.
The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
"""
def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False):
super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, return_indices, ceil_mode)
self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
def forward(self, x):
ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
kh, kw = self.kernel_size
sh, sw = self.stride
oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
return F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
class MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
"""2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
"""
def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, image_size=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
# Calculate padding based on image size and save it
assert image_size is not None
ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
kh, kw = self.kernel_size
sh, sw = self.stride
oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
else:
self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.static_padding(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
return x
################################################################################
# Helper functions for loading model params
################################################################################
# BlockDecoder: A Class for encoding and decoding BlockArgs
# efficientnet_params: A function to query compound coefficient
# get_model_params and efficientnet:
# Functions to get BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet
# url_map and url_map_advprop: Dicts of url_map for pretrained weights
# load_pretrained_weights: A function to load pretrained weights
class BlockDecoder(object):
"""Block Decoder for readability,
straight from the official TensorFlow repository.
"""
@staticmethod
def _decode_block_string(block_string):
"""Get a block through a string notation of arguments.
Args:
block_string (str): A string notation of arguments.
Examples: 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25_noskip'.
Returns:
BlockArgs: The namedtuple defined at the top of this file.
"""
assert isinstance(block_string, str)
ops = block_string.split('_')
options = {}
for op in ops:
splits = re.split(r'(\d.*)', op)
if len(splits) >= 2:
key, value = splits[:2]
options[key] = value
# Check stride
assert (('s' in options and len(options['s']) == 1) or
(len(options['s']) == 2 and options['s'][0] == options['s'][1]))
return BlockArgs(
num_repeat=int(options['r']),
kernel_size=int(options['k']),
stride=[int(options['s'][0])],
expand_ratio=int(options['e']),
input_filters=int(options['i']),
output_filters=int(options['o']),
se_ratio=float(options['se']) if 'se' in options else None,
id_skip=('noskip' not in block_string))
@staticmethod
def _encode_block_string(block):
"""Encode a block to a string.
Args:
block (namedtuple): A BlockArgs type argument.
Returns:
block_string: A String form of BlockArgs.
"""
args = [
'r%d' % block.num_repeat,
'k%d' % block.kernel_size,
's%d%d' % (block.strides[0], block.strides[1]),
'e%s' % block.expand_ratio,
'i%d' % block.input_filters,
'o%d' % block.output_filters
]
if 0 < block.se_ratio <= 1:
args.append('se%s' % block.se_ratio)
if block.id_skip is False:
args.append('noskip')
return '_'.join(args)
@staticmethod
def decode(string_list):
"""Decode a list of string notations to specify blocks inside the network.
Args:
string_list (list[str]): A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
Returns:
blocks_args: A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
"""
assert isinstance(string_list, list)
blocks_args = []
for block_string in string_list:
blocks_args.append(BlockDecoder._decode_block_string(block_string))
return blocks_args
@staticmethod
def encode(blocks_args):
"""Encode a list of BlockArgs to a list of strings.
Args:
blocks_args (list[namedtuples]): A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
Returns:
block_strings: A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
"""
block_strings = []
for block in blocks_args:
block_strings.append(BlockDecoder._encode_block_string(block))
return block_strings
def efficientnet_params(model_name):
"""Map EfficientNet model name to parameter coefficients.
Args:
model_name (str): Model name to be queried.
Returns:
params_dict[model_name]: A (width,depth,res,dropout) tuple.
"""
params_dict = {
# Coefficients: width,depth,res,dropout
'efficientnet-b0': (1.0, 1.0, 224, 0.2),
'efficientnet-b1': (1.0, 1.1, 240, 0.2),
'efficientnet-b2': (1.1, 1.2, 260, 0.3),
'efficientnet-b3': (1.2, 1.4, 300, 0.3),
'efficientnet-b4': (1.4, 1.8, 380, 0.4),
'efficientnet-b5': (1.6, 2.2, 456, 0.4),
'efficientnet-b6': (1.8, 2.6, 528, 0.5),
'efficientnet-b7': (2.0, 3.1, 600, 0.5),
'efficientnet-b8': (2.2, 3.6, 672, 0.5),
'efficientnet-l2': (4.3, 5.3, 800, 0.5),
}
return params_dict[model_name]
def efficientnet(width_coefficient=None, depth_coefficient=None, image_size=None,
dropout_rate=0.2, drop_connect_rate=0.2, num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""Create BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet model.
Args:
width_coefficient (float)
depth_coefficient (float)
image_size (int)
dropout_rate (float)
drop_connect_rate (float)
num_classes (int)
Meaning as the name suggests.
Returns:
blocks_args, global_params.
"""
# Blocks args for the whole model(efficientnet-b0 by default)
# It will be modified in the construction of EfficientNet Class according to model
blocks_args = [
'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25',
'r2_k3_s22_e6_i16_o24_se0.25',
'r2_k5_s22_e6_i24_o40_se0.25',
'r3_k3_s22_e6_i40_o80_se0.25',
'r3_k5_s11_e6_i80_o112_se0.25',
'r4_k5_s22_e6_i112_o192_se0.25',
'r1_k3_s11_e6_i192_o320_se0.25',
]
blocks_args = BlockDecoder.decode(blocks_args)
global_params = GlobalParams(
width_coefficient=width_coefficient,
depth_coefficient=depth_coefficient,
image_size=image_size,
dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
num_classes=num_classes,
batch_norm_momentum=0.99,
batch_norm_epsilon=1e-3,
drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate,
depth_divisor=8,
min_depth=None,
include_top=include_top,
)
return blocks_args, global_params
def get_model_params(model_name, override_params):
"""Get the block args and global params for a given model name.
Args:
model_name (str): Model's name.
override_params (dict): A dict to modify global_params.
Returns:
blocks_args, global_params
"""
if model_name.startswith('efficientnet'):
w, d, s, p = efficientnet_params(model_name)
# note: all models have drop connect rate = 0.2
blocks_args, global_params = efficientnet(
width_coefficient=w, depth_coefficient=d, dropout_rate=p, image_size=s)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('model name is not pre-defined: {}'.format(model_name))
if override_params:
# ValueError will be raised here if override_params has fields not included in global_params.
global_params = global_params._replace(**override_params)
return blocks_args, global_params
# train with Standard methods
# check more details in paper(EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks)
url_map = {
'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b0-355c32eb.pth',
'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b1-f1951068.pth',
'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b2-8bb594d6.pth',
'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b3-5fb5a3c3.pth',
'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b4-6ed6700e.pth',
'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b5-b6417697.pth',
'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b6-c76e70fd.pth',
'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b7-dcc49843.pth',
}
# train with Adversarial Examples(AdvProp)
# check more details in paper(Adversarial Examples Improve Image Recognition)
url_map_advprop = {
'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b0-b64d5a18.pth',
'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b1-0f3ce85a.pth',
'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b2-6e9d97e5.pth',
'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b3-cdd7c0f4.pth',
'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b4-44fb3a87.pth',
'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b5-86493f6b.pth',
'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b6-ac80338e.pth',
'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b7-4652b6dd.pth',
'efficientnet-b8': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b8-22a8fe65.pth',
}
# TODO: add the petrained weights url map of 'efficientnet-l2'
def load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=None, load_fc=True, advprop=False, verbose=True):
"""Loads pretrained weights from weights path or download using url.
Args:
model (Module): The whole model of efficientnet.
model_name (str): Model name of efficientnet.
weights_path (None or str):
str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
load_fc (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights for fc layer at the end of the model.
advprop (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights
trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
"""
if isinstance(weights_path, str):
state_dict = torch.load(weights_path)
else:
# AutoAugment or Advprop (different preprocessing)
url_map_ = url_map_advprop if advprop else url_map
state_dict = model_zoo.load_url(url_map_[model_name])
if load_fc:
ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
assert not ret.missing_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
else:
state_dict.pop('_fc.weight')
state_dict.pop('_fc.bias')
ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
assert set(ret.missing_keys) == set(
['_fc.weight', '_fc.bias']), 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
assert not ret.unexpected_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.unexpected_keys)
if verbose:
print('Loaded pretrained weights for {}'.format(model_name))七、EfficientNet V2
参考资料:
【论文解读】一文看懂EfficientnetB0~B7模型所有细节 - 知乎
后ResNet时代的顶流EfficientNet