毕设:基于Yolov5的手势识别应用与实现_2_手势关键帧获取
1、所需环境
所需环境:python+opencv
作者计算机安装的软件版本为Python3.8.5和OpenCV-python 4.5.5.64
安装Python和pycharm
安装OpenCV
2、两间差分法处理视频
作者计划实现的功能具体为孤立词手语的手势识别,孤立词手语的手势与连续词手语的手势有相似之处,但存在一点关键的区别,孤立词的手语不像连续词手语那样存在过度帧(也就是孤立词的两个有效的手语动作之间的动作没有实际意义),因此孤立词的手语与动态手势类似,可以分为三个阶段:准备动作阶段,有效动作阶段,结束动作阶段。
故我们可以刨除准备动作与结束动作,专注于训练对有效动作的识别。所以作者使用两间差分法来提取手语教学视频中的有效动作帧来作为训练范例动作。
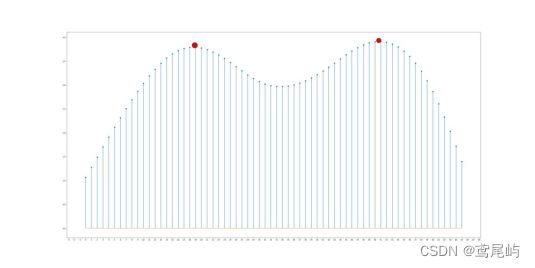
两间差分法原理很简单,关键在于把前后两帧的图像进行对比,对比的评判标准是两帧画面的平均像素强度,根据两帧画面的平均像素强度差异的来衡量两帧图像之间的变化大小。因此基于帧间差分的平均像素强度差异,当视频中的某一帧与前一帧的平均像素强度存在较大差异,便认定其为关键帧,并将其提取出来。与此同时为了保证提取效果,作者定义具有平均帧间差分强度局部最大值的帧作为视频的关键帧。这样做的好处是可以提取处一个视频内多个具有关键特征的画面,但与此同时也有可能会出现提取处错误画面的缺点。
代码实现:
参考文章:python两间差分法处理视频实现
作者:cungudafa
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import os
import time
import operator # 内置操作符函数接口(后面排序用到)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import argrelextrema # 极值点
def smooth(x, window_len=13, window='hanning'):
"""使用具有所需大小的窗口使数据平滑。
"""
print(len(x), window_len)
s = np.r_[2 * x[0] - x[window_len:1:-1],
x, 2 * x[-1] - x[-1:-window_len:-1]]
#print(len(s))
if window == 'flat': # moving average平移
w = np.ones(window_len, 'd')
else:
w = getattr(np, window)(window_len)
y = np.convolve(w / w.sum(), s, mode='same')
return y[window_len - 1:-window_len + 1]
class Frame:
"""用于保存有关每个帧的信息
"""
def __init__(self, id, diff):
self.id = id
self.diff = diff
def __lt__(self, other):
if self.id == other.id:
return self.id < other.id
return self.id < other.id
def __gt__(self, other):
return other.__lt__(self)
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.id == other.id and self.id == other.id
def __ne__(self, other):
return not self.__eq__(other)
def rel_change(a, b):
x = (b - a) / max(a, b)
print(x)
return x
def getEffectiveFrame(videopath,dirfile):
# 如果文件目录不存在则创建目录
if not os.path.exists(dirfile):
os.makedirs(dirfile)
(filepath, tempfilename) = os.path.split(videopath)#分离路径和文件名
(filename, extension) = os.path.splitext(tempfilename)#区分文件的名字和后缀
#Setting fixed threshold criteria设置固定阈值标准
USE_THRESH = False
#fixed threshold value固定阈值
THRESH = 0.6
#Setting fixed threshold criteria设置固定阈值标准
USE_TOP_ORDER = False
#Setting local maxima criteria设置局部最大值标准
USE_LOCAL_MAXIMA = True
#Number of top sorted frames排名最高的帧数
NUM_TOP_FRAMES = 50
#smoothing window size平滑窗口大小
len_window = int(50)
print("target video :" + videopath)
print("frame save directory: " + dirfile)
# load video and compute diff between frames加载视频并计算帧之间的差异
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(str(videopath))
curr_frame = None
prev_frame = None
frame_diffs = []
frames = []
success, frame = cap.read()
i = 0
while(success):
luv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LUV)
curr_frame = luv
if curr_frame is not None and prev_frame is not None:
#logic here
diff = cv2.absdiff(curr_frame, prev_frame)#获取差分图
diff_sum = np.sum(diff)
diff_sum_mean = diff_sum / (diff.shape[0] * diff.shape[1])#平均帧
frame_diffs.append(diff_sum_mean)
frame = Frame(i, diff_sum_mean)
frames.append(frame)
prev_frame = curr_frame
i = i + 1
success, frame = cap.read()
cap.release()
# compute keyframe
keyframe_id_set = set()
if USE_TOP_ORDER:
# sort the list in descending order以降序对列表进行排序
frames.sort(key=operator.attrgetter("diff"), reverse=True)# 排序operator.attrgetter
for keyframe in frames[:NUM_TOP_FRAMES]:
keyframe_id_set.add(keyframe.id)
if USE_THRESH:
print("Using Threshold")#使用阈值
for i in range(1, len(frames)):
if (rel_change(np.float(frames[i - 1].diff), np.float(frames[i].diff)) >= THRESH):
keyframe_id_set.add(frames[i].id)
if USE_LOCAL_MAXIMA:
print("Using Local Maxima")#使用局部极大值
diff_array = np.array(frame_diffs)
sm_diff_array = smooth(diff_array, len_window)#平滑
frame_indexes = np.asarray(argrelextrema(sm_diff_array, np.greater))[0]#找极值
for i in frame_indexes:
keyframe_id_set.add(frames[i - 1].id)# 记录极值帧数
plt.figure(figsize=(40, 20))
plt.locator_params("x", nbins = 100)
# stem 绘制离散函数,polt是连续函数
plt.stem(sm_diff_array,linefmt='-',markerfmt='o',basefmt='--',label='sm_diff_array')
plt.savefig(dirfile + filename+'_plot.png')
# save all keyframes as image将所有关键帧另存为图像
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(str(videopath))
curr_frame = None
keyframes = []
success, frame = cap.read()
idx = 0
while(success):
if idx in keyframe_id_set:
name = filename+'_' + str(idx) + ".jpg"
cv2.imwrite(dirfile + name, frame)
keyframe_id_set.remove(idx)
idx = idx + 1
success, frame = cap.read()
cap.release()
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("[INFO]Effective Frame.")
start = time.time()
videos_path= 'dataset/vedio/onehand/'
outfile = 'dataset/vedio/extract_result/'#处理完的帧
video_files = [os.path.join(videos_path, video_file) for video_file in os.listdir(videos_path)]
#
for video_file in video_files:
getEffectiveFrame(video_file,outfile)
print("[INFO]Extract Result time: ", time.time() - start)
运行结果:
视频灰度图变化趋势:
视频关键帧截图:
手语视频来源:手语词典 Spreadthesign
以上便是获取手语关键帧的过程,接下来我们会根据获取到的手势进行识别模型数据集的录制。