语义分割系列22-GCNet(pytorch实现)
GCNet:《GCNet: Non-local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond》
论文链接:ICCV2019:GCNet

本文将介绍:
- GCNet: Non-local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond论文详解
- Non Local、Global context (GC) block的实现原理与区别
- Global context (GC) block的pytorch代码实现
- GCNet在Camvid数据集上的复现
目录
- 引文
- 论文主体
-
-
- Non Local 与简化 Non Local 对比
- Global Context Block 细节与代码
-
- 模型测试
-
-
- Backbone选择了ResNet50(8倍下采样,使用扩张卷积)
- GCBlock
- GCNet
- Dataset camvid
- 训练过程
- 训练结果
-
引文
-
在以往的大量工作中证明,捕获视觉场景中的全局依赖能提高分割任务的效果。在传统的CNN网络工作中,远程依赖的建立(等同于感受野的扩增)主要依靠堆叠卷积层来实现,但是这种方法效率低且难以优化,因为长距离位置之间的信息难以传递,而且卷积层的堆叠可能会导致卷积核退化的问题。为了解决这个问题,Non-Local通过自注意力(self-attention)机制来建立远程依赖。对于每一个查询(query),计算该query位置与全局所有位置(key)的关系来建立注意力图(attention map),然后将注意力图与value进行加权汇总,生成最终的输出。
-
Non-Local对比以往的工作而言(如叠加卷积、ASPP、PPM等等),其建立远程关系的能力十分优秀,但是Non-Local十分巨大的计算量成为了其进一步应用的缺陷。因此,后续一些工作也针对减少Non-Local的计算量开展了一些研究,包括Criss-Cross attention(CCNet)、(Asymmetric Non-local)ANNNet。而本文同样基于Non-local的计算量进行了优化。
本文主要工作:
- 对比了Non Local和简化版本的Non Local的计算效果
- 引入Context model到简化版本的Non Local结构中,提出Global Context(GC)block
论文主体
Non Local 与简化 Non Local 对比
首先通过卷积计算出Key和Query :
k e y = W k ( X ) key =W_k(X) key=Wk(X) , q u e r y = W q ( X ) query=W_q(X) query=Wq(X)
然后计算Matmul(K, Q)与SoftMax得到Attention map:
A t t e n = S o f t M a x ( k e y ⊙ q u e r y ) Atten =SoftMax(key \odot query) Atten=SoftMax(key⊙query) ,
q u e r y = W q ( X ) query=W_q(X) query=Wq(X) 最后Attention map与Value进行计算Matmul(Attention,V),得到输出Out:
O u t = W k ( A t t e n ⊙ v a l u e ) Out=W_k(Atten \odot value) Out=Wk(Atten⊙value)
对于Simplified Non-Local结构,简化了query运算,query和key计算时权重共享,也就是query和key等同,这里就减少了计算query的一个过程,并忽略了最后一个卷积 W z W_z Wz,作者也给出了实际的证明——可视化了两种结构的attention map,发现效果差不多。因此作者后续的工作都基于Simplified Non-Local结构。

Global Context Block 细节与代码

作者基于Simplified Non Local 和SE block提出了Global Context(GC)block。
对于SE block的结构,主要由Context modeling构成,这个模块由SENet中所提出,后来在ENCNet中也有应用。在Context Modeling模块中,特征图通过一个全局平均池化,经由一系列卷积、ReLU之后,生成一个全局上下文特征(Context)(在ENCNet中,则是用这个全局上下文特征来实现通道注意力机制)。同时,这里也减少了许多计算量。
作者从SE block中得到灵感,将Context Modeling用在计算Attention map中,也就是用Context Modeling的输出来替代Attention Map,再接上卷积来实现value与Attention的输出,在这里,为了进一步简化计算作者设置了一个ratio(r=16),缩减了通道数。
当然,这里show the code更为直接:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GlobalContextBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, scale = 16):
super(GlobalContextBlock, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = self.in_channels//scale
self.Conv_key = nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, 1, 1)
self.SoftMax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
self.Conv_value = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, 1),
nn.LayerNorm([self.out_channels, 1, 1]),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(self.out_channels, self.in_channels, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
# key -> [b, 1, H, W] -> [b, 1, H*W] -> [b, H*W, 1]
key = self.SoftMax(self.Conv_key(x).view(b, 1, -1).permute(0, 2, 1).view(b, -1, 1).contiguous())
query = x.view(b, c, h*w)
# [b, c, h*w] * [b, H*W, 1]
concate_QK = torch.matmul(query, key)
concate_QK = concate_QK.view(b, c, 1, 1).contiguous()
value = self.Conv_value(concate_QK)
out = x + value
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn((2, 1024, 24, 24))
GCBlock = GlobalContextBlock(in_channels=1024)
out = GCBlock(x)
print("GCBlock output.shape:", out.shape)
print(out)
模型测试
由于原文中没有给出详细的模型图,所以这里作者创建了一个简单的GCNet模型。
当然,GCBlock也可以加载ResNet中的任意层内,提升一些性能,作者这里偷懒了没有这么做。
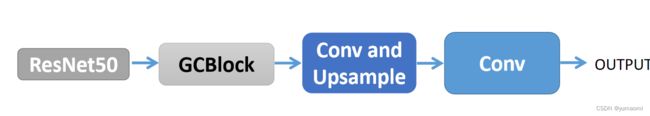
Backbone选择了ResNet50(8倍下采样,使用扩张卷积)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion: int = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride = 1, downsample = None, groups = 1,
base_width = 64, dilation = 1, norm_layer = None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError("BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64")
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes ,kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation,groups=groups, bias=False,dilation=dilation)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes ,kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation,groups=groups, bias=False,dilation=dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample= None,
groups = 1, base_width = 64, dilation = 1, norm_layer = None,):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.0)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, width, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(width, width, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(width, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,block, layers,num_classes = 1000, zero_init_residual = False, groups = 1,
width_per_group = 64, replace_stride_with_dilation = None, norm_layer = None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self._norm_layer = norm_layer
self.inplanes = 64
self.dilation = 2
if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:
# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace
# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution instead
replace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]
if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:
raise ValueError(
"replace_stride_with_dilation should be None "
f"or a 3-element tuple, got {replace_stride_with_dilation}"
)
self.groups = groups
self.base_width = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=1, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1])
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=1, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2])
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out", nonlinearity="relu")
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
def _make_layer(
self,
block,
planes,
blocks,
stride = 1,
dilate = False,
):
norm_layer = self._norm_layer
downsample = None
previous_dilation = self.dilation
if dilate:
self.dilation *= stride
stride = stride
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
norm_layer(planes * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(
block(
self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups, self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer
)
)
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(
block(
self.inplanes,
planes,
groups=self.groups,
base_width=self.base_width,
dilation=self.dilation,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
)
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _forward_impl(self, x):
out = []
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
return x
def forward(self, x) :
return self._forward_impl(x)
def _resnet(block, layers, pretrained_path = None, **kwargs,):
model = ResNet(block, layers, **kwargs)
if pretrained_path is not None:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_path), strict=False)
return model
def resnet50(pretrained_path=None, **kwargs):
return ResNet._resnet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],pretrained_path,**kwargs)
def resnet101(pretrained_path=None, **kwargs):
return ResNet._resnet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],pretrained_path,**kwargs)
GCBlock
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GlobalContextBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, scale = 16):
super(GlobalContextBlock, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = self.in_channels//scale
self.Conv_key = nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, 1, 1)
self.SoftMax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
self.Conv_value = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, 1),
nn.LayerNorm([self.out_channels, 1, 1]),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(self.out_channels, self.in_channels, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
# key -> [b, 1, H, W] -> [b, 1, H*W] -> [b, H*W, 1]
key = self.SoftMax(self.Conv_key(x).view(b, 1, -1).permute(0, 2, 1).view(b, -1, 1).contiguous())
query = x.view(b, c, h*w)
# [b, c, h*w] * [b, H*W, 1]
concate_QK = torch.matmul(query, key)
concate_QK = concate_QK.view(b, c, 1, 1).contiguous()
value = self.Conv_value(concate_QK)
out = x + value
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn((2, 1024, 24, 24))
GCBlock = GlobalContextBlock(in_channels=1024)
out = GCBlock(x)
print("GCBlock output.shape:", out.shape)
print(out)
GCNet
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GCNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(GCNet, self).__init__()
self.gc_block = GlobalContextBlock(in_channels=2048, scale = 16)
self.backbone = ResNet.resnet50(replace_stride_with_dilation=[1,2,4])
self.Conv_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2048, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=8, mode="bilinear", align_corners=True)
)
self.cls_seg = nn.Conv2d(512, num_classes, 3, padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function."""
output = self.backbone(x)
output = self.gc_block(output)
output = self.Conv_1(output)
output = self.cls_seg(output)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn((2, 3, 224, 224))
model = GCNet(num_classes=2)
out = model(x)
print("GCNet output.shape:", out.shape)
Dataset camvid
# 导入库
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0'
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tqdm import tqdm
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensorV2
torch.manual_seed(17)
# 自定义数据集CamVidDataset
class CamVidDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
"""CamVid Dataset. Read images, apply augmentation and preprocessing transformations.
Args:
images_dir (str): path to images folder
masks_dir (str): path to segmentation masks folder
class_values (list): values of classes to extract from segmentation mask
augmentation (albumentations.Compose): data transfromation pipeline
(e.g. flip, scale, etc.)
preprocessing (albumentations.Compose): data preprocessing
(e.g. noralization, shape manipulation, etc.)
"""
def __init__(self, images_dir, masks_dir):
self.transform = A.Compose([
A.Resize(224, 224),
A.HorizontalFlip(),
A.VerticalFlip(),
A.Normalize(),
ToTensorV2(),
])
self.ids = os.listdir(images_dir)
self.images_fps = [os.path.join(images_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
self.masks_fps = [os.path.join(masks_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
def __getitem__(self, i):
# read data
image = np.array(Image.open(self.images_fps[i]).convert('RGB'))
mask = np.array( Image.open(self.masks_fps[i]).convert('RGB'))
image = self.transform(image=image,mask=mask)
return image['image'], image['mask'][:,:,0]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
# 设置数据集路径
DATA_DIR = r'database/camvid/camvid/' # 根据自己的路径来设置
x_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_images')
y_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_labels')
x_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'valid_images')
y_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'valid_labels')
train_dataset = CamVidDataset(
x_train_dir,
y_train_dir,
)
val_dataset = CamVidDataset(
x_valid_dir,
y_valid_dir,
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)
训练过程
model = GCNet(num_classes=33).cuda()
from d2l import torch as d2l
from tqdm import tqdm
import pandas as pd
import monai
# training loop 100 epochs
epochs_num = 100
# 选用SGD优化器来训练
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
schedule = monai.optimizers.LinearLR(optimizer, end_lr=0.05, num_iter=int(epochs_num*0.75))
# 损失函数选用多分类交叉熵损失函数
lossf = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=255)
# 训练函数
def train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, optimizer, num_epochs, scheduler, devices=d2l.try_all_gpus()):
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0, 1], legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices).to(devices[0])
# 用来保存一些训练参数
loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
epochs_list = []
time_list = []
lr_list = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Sum of training loss, sum of training accuracy, no. of examples,
# no. of predictions
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
for i, (X, labels) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
#l, acc = d2l.train_batch_ch13(net, features, labels.long(), loss, optimizer, devices)
if isinstance(X, list):
X = [x.to(devices[0]) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(devices[0])
y = labels.long().to(devices[0])
net.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
pred = net(X)
l = loss(pred, y)
l.sum().backward()
optimizer.step()
l = l.sum()
acc = d2l.accuracy(pred, y)
metric.add(l, acc, labels.shape[0], labels.numel())
timer.stop()
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3], None))
if epoch < 75:
schedule.step()
test_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
print(f"epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs_num} --- loss {metric[0] / metric[2]:.3f} --- train acc {metric[1] / metric[3]:.3f} --- test acc {test_acc:.3f} --- lr {optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']} --- cost time {timer.sum()}")
#---------保存训练数据---------------
df = pd.DataFrame()
loss_list.append(metric[0] / metric[2])
train_acc_list.append(metric[1] / metric[3])
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
epochs_list.append(epoch+1)
time_list.append(timer.sum())
lr_list.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
df['epoch'] = epochs_list
df['loss'] = loss_list
df['train_acc'] = train_acc_list
df['test_acc'] = test_acc_list
df["lr"] = lr_list
df['time'] = time_list
df.to_excel("savefile/GCNet_camvid.xlsx")
#----------------保存模型-------------------
if np.mod(epoch+1, 5) == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f'checkpoints/GCNet_{epoch+1}.pth')
# 保存下最后的model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f'checkpoints/GCNet_last.pth')
train_ch13(model, train_loader, val_loader, lossf, optimizer, epochs_num, scheduler=schedule)

