吴恩达深度学习(笔记+作业)·第一课·第四周 深层神经网络
目录
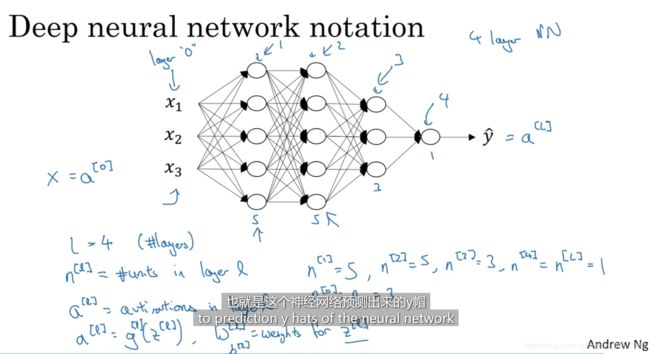
一、深层神经网络
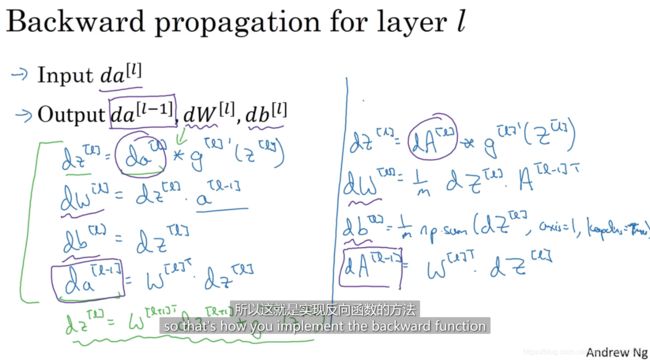
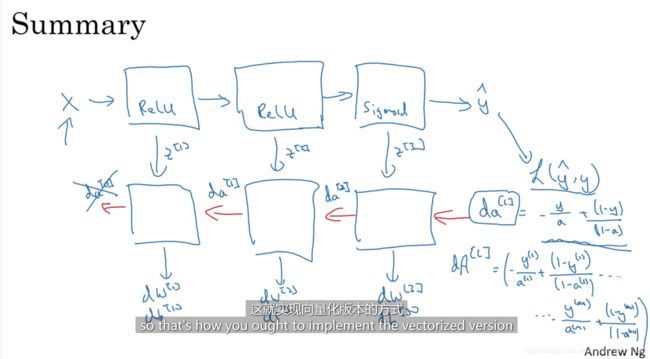
二、深层神经网络的前向传播和反向传播
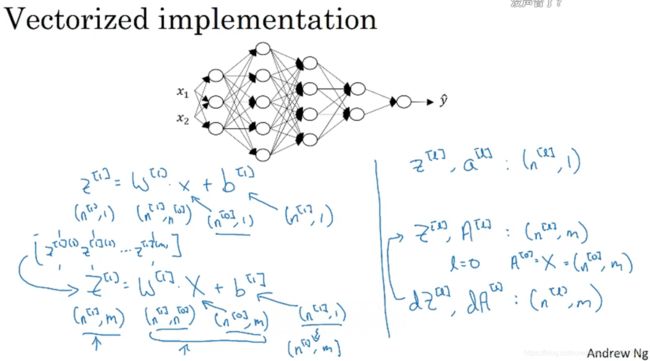
三、核对矩阵维数
四、参数和超参数
作业:
一、深层神经网络
二、深层神经网络的前向传播和反向传播
三、核对矩阵维数
拿出一张纸,计算各个矩阵的维度
四、参数和超参数
作业:
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
============================================
时间:2021.8.19
作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语
文件名:搭建多层神经网络.py
功能:【吴恩达课后编程作业】01 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第四周编程作业
1、Ctrl + Enter 在下方新建行但不移动光标;
2、Shift + Enter 在下方新建行并移到新行行首;
3、Shift + Enter 任意位置换行
4、Ctrl + D 向下复制当前行
5、Ctrl + Y 删除当前行
6、Ctrl + Shift + V 打开剪切板
7、Ctrl + / 注释(取消注释)选择的行;
8、Ctrl + E 可打开最近访问过的文件
9、Double Shift + / 万能搜索
============================================
"""
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import 第4周.编程题.testCases
from 第4周.编程题 import lr_utils
from 第4周.编程题.dnn_utils import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
# 指定随机种子
np.random.seed(1)
# 1. 初始化网络参数 layers_dims代表各个层的节点数
def initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims):
"""
此函数是为了初始化多层网络参数而使用的函数。
参数:
layers_dims - 包含我们网络中每个图层的节点数量的列表
返回:
parameters - 包含参数“W1”,“b1”,...,“WL”,“bL”的字典:
W1 - 权重矩阵,维度为(layers_dims [1],layers_dims [1-1])
bl - 偏向量,维度为(layers_dims [1],1)
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layers_dims)
for l in range(1, L):
parameters["W" + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l - 1]) / np.sqrt(layers_dims[l - 1])
parameters["b" + str(l)] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], 1))
# 确保我要的数据的格式是正确的
assert (parameters["W" + str(l)].shape == (layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l - 1]))
assert (parameters["b" + str(l)].shape == (layers_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
# 2.前向传播
# 2.1 线性部分
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
"""
实现前向传播的线性部分
参数:
A - 来自上一层(或输入数据)的激活,维度为(上一层的节点数量,示例的数量)
W - 权重矩阵,numpy数组,维度为(当前图层的节点数量,前一图层的节点数量)
b - 偏向量,numpy向量,维度为(当前图层节点数量,1)
返回:
Z - 激活功能的输入,也称为预激活参数
cache - 一个包含“A”,“W”和“b”的字典,存储这些变量以有效地计算后向传递
"""
Z = np.dot(W, A) + b
assert (Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
cache = (A, W, b)
return Z, cache
# 2.2 线性激活部分
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
"""
实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION 这一层的前向传播
参数:
A_prev - 来自上一层(或输入层)的激活,维度为(上一层的节点数量,示例数)
W - 权重矩阵,numpy数组,维度为(当前层的节点数量,前一层的大小)
b - 偏向量,numpy阵列,维度为(当前层的节点数量,1)
activation - 选择在此层中使用的激活函数名,字符串类型,【"sigmoid" | "relu"】
返回:
A - 激活函数的输出,也称为激活后的值
cache - 一个包含“linear_cache”和“activation_cache”的字典,我们需要存储它以有效地计算后向传递
"""
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
if activation == "sigmoid":
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cache
# 2.3 多层模型:结合线性求和与激活函数
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
实现[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR-> SIGMOID计算前向传播,也就是多层网络的前向传播,为后面每一层都执行LINEAR和ACTIVATION
参数:
X - 数据,numpy数组,维度为(输入节点数量,示例数)
parameters - initialize_parameters_deep()的输出
返回:
AL - 最后的激活值
caches - 包含以下内容的缓存列表:
linear_relu_forward()的每个cache(有L-1个,索引为从0到L-2)
linear_sigmoid_forward()的cache(只有一个,索引为L-1)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], "relu")
caches.append(cache)
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert (AL.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches
# 3.计算成本
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
实施等式(4)定义的成本函数。
参数:
AL - 与标签预测相对应的概率向量,维度为(1,示例数量)
Y - 标签向量(例如:如果不是猫,则为0,如果是猫则为1),维度为(1,数量)
返回:
cost - 交叉熵成本
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
cost = -np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(AL), Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - AL), 1 - Y)) / m
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert (cost.shape == ())
return cost
# 4. 反向传播
# 4.1 线性部分
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
"""
为单层实现反向传播的线性部分(第L层)
参数:
dZ - 相对于(当前第l层的)线性输出的成本梯度
cache - 来自当前层前向传播的值的元组(A_prev,W,b)
返回:
dA_prev - 相对于激活(前一层l-1)的成本梯度,与A_prev维度相同
dW - 相对于W(当前层l)的成本梯度,与W的维度相同
db - 相对于b(当前层l)的成本梯度,与b维度相同
"""
A_prev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
dW = np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T) / m
db = np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ)
assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
assert (dW.shape == W.shape)
assert (db.shape == b.shape)
return dA_prev, dW, db
# 4.2 线性激活部分
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation="relu"):
"""
实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION层的后向传播。
参数:
dA - 当前层l的激活后的梯度值
cache - 我们存储的用于有效计算反向传播的值的元组(值为linear_cache,activation_cache)
activation - 要在此层中使用的激活函数名,字符串类型,【"sigmoid" | "relu"】
返回:
dA_prev - 相对于激活(前一层l-1)的成本梯度值,与A_prev维度相同
dW - 相对于W(当前层l)的成本梯度值,与W的维度相同
db - 相对于b(当前层l)的成本梯度值,与b的维度相同
"""
linear_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db
elif activation == "sigmoid":
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db
# 4.3 多层网络反向传播
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
对[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID组执行反向传播,就是多层网络的向后传播
参数:
AL - 概率向量,正向传播的输出(L_model_forward())
Y - 标签向量(例如:如果不是猫,则为0,如果是猫则为1),维度为(1,数量)
caches - 包含以下内容的cache列表:
linear_activation_forward("relu")的cache,不包含输出层
linear_activation_forward("sigmoid")的cache
返回:
grads - 具有梯度值的字典
grads [“dA”+ str(l)] = ...
grads [“dW”+ str(l)] = ...
grads [“db”+ str(l)] = ...
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches)
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape)
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
current_cache = caches[L - 1]
grads["dA" + str(L - 1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL,
current_cache,
"sigmoid")
for l in reversed(range(L - 1)):
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache, "relu")
grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads
# 5.更新参数
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
使用梯度下降更新参数
参数:
parameters - 包含你的参数的字典
grads - 包含梯度值的字典,是L_model_backward的输出
返回:
parameters - 包含更新参数的字典
参数[“W”+ str(l)] = ...
参数[“b”+ str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # 整除
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l + 1)]
parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l + 1)]
return parameters
# 搭建多层神经网络
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, num_iter_avg=100, print_cost=False, isPlot=True):
"""
实现一个L层神经网络:[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR-> SIGMOID。
参数:
X - 输入的数据,维度为(n_x,例子数)
Y - 标签,向量,0为非猫,1为猫,维度为(1,数量)
layers_dims - 层数的向量,维度为(n_y,n_h,···,n_h,n_y)
learning_rate - 学习率
num_iterations - 迭代的次数
print_cost - 是否打印成本值,每100次打印一次
isPlot - 是否绘制出误差值的图谱
返回:
parameters - 模型学习的参数。 然后他们可以用来预测。
"""
np.random.seed(1)
costs = []
running_cost = 0
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
running_cost = running_cost + cost
# 打印成本值,如果print_cost=False则忽略
if print_cost:
if i % num_iter_avg == num_iter_avg - 1:
costs.append(running_cost / num_iter_avg)
print("第", i+1, "次迭代,成本值为:", running_cost / num_iter_avg)
running_cost = 0
# 迭代完成,根据条件绘制图
if isPlot:
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
# 加载数据集
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y, classes = lr_utils.load_dataset()
train_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
train_x = train_x_flatten / 255
train_y = train_set_y
test_x = test_x_flatten / 255
test_y = test_set_y
layers_dims = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1] # 5-layer model
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims, num_iterations=2500, print_cost=True, isPlot=True)
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
============================================
时间:2021.8.19
作者:
文件名:dnn_utils.py
功能:【吴恩达课后编程作业】01 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第四周编程作业
1、Ctrl + Enter 在下方新建行但不移动光标;
2、Shift + Enter 在下方新建行并移到新行行首;
3、Shift + Enter 任意位置换行
4、Ctrl + D 向下复制当前行
5、Ctrl + Y 删除当前行
6、Ctrl + Shift + V 打开剪切板
7、Ctrl + / 注释(取消注释)选择的行;
8、Ctrl + E 可打开最近访问过的文件
9、Double Shift + / 万能搜索
============================================
"""
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(Z):
"""
Implements the sigmoid activation in numpy
Arguments:
Z -- numpy array of any shape
Returns:
A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Z
cache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation
"""
A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
cache = Z
return A, cache
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
dZ = dA * s * (1-s)
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
def relu(Z):
"""
Implement the RELU function.
Arguments:
Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shape
Returns:
A -- Post-activation parameter, of the same shape as Z
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.
dZ[Z <= 0] = 0
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
============================================
时间:2021.8.19
作者:
文件名:lr_utils.py
功能:【吴恩达课后编程作业】01 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第四周编程作业
1、Ctrl + Enter 在下方新建行但不移动光标;
2、Shift + Enter 在下方新建行并移到新行行首;
3、Shift + Enter 任意位置换行
4、Ctrl + D 向下复制当前行
5、Ctrl + Y 删除当前行
6、Ctrl + Shift + V 打开剪切板
7、Ctrl + / 注释(取消注释)选择的行;
8、Ctrl + E 可打开最近访问过的文件
9、Double Shift + / 万能搜索
============================================
"""
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(Z):
"""
Implements the sigmoid activation in numpy
Arguments:
Z -- numpy array of any shape
Returns:
A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Z
cache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation
"""
A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
cache = Z
return A, cache
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
dZ = dA * s * (1-s)
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
def relu(Z):
"""
Implement the RELU function.
Arguments:
Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shape
Returns:
A -- Post-activation parameter, of the same shape as Z
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.
dZ[Z <= 0] = 0
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
import numpy as np
import h5py
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes