T2:归并排序_顺序表+链表版
归并排序从小到大
-
- 排序思想
- 排序特点
- 顺序表版
-
- 完整代码
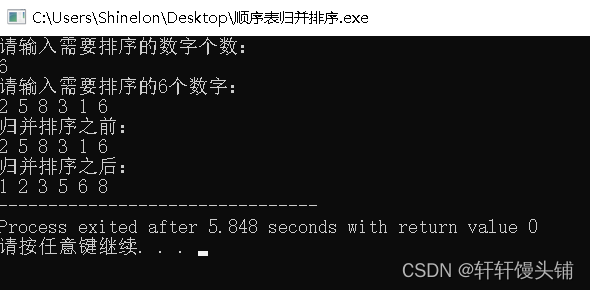
- 运行结果
- 单链表版
-
- 关键函数
-
- 尾插建立链表
- 归并排序函数
- 两段合并函数
- 完整代码
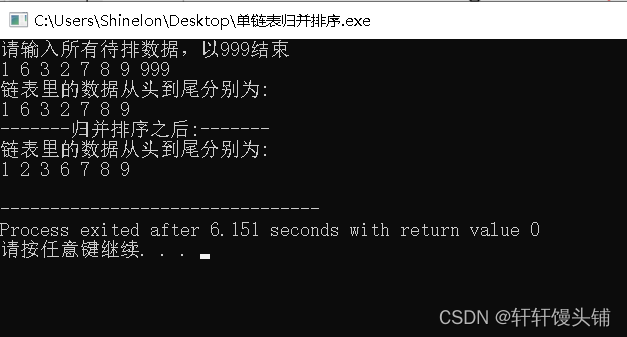
- 运行结果
排序思想
一个待排序列分成前后两半,分别排序,这两部分长度要么相等、要么相差一个,都排好之后再合并,这是一个递归的过程。所以完成这个排序就需要一个排序算法和一个归并算法。
- 对于顺序表而言,找到“断点”很容易,因为其随机存取的特点,直接取中间值即可。
- 对于单链表而言,不太容易,这里采用双指针法,设计思想很简单:快指针一次前进两步,慢指针一次前进一步,当快指针到达链表尽头时,慢指针就处于链表的中间位置,以此找到“断点”。
- 但是,不可否认的是,因为是同一种排序算法,因此基本思想是一致的。
排序特点
稳定排序算法
空间复杂度:O(n)
时间复杂度:最好O(logn);平均O(logn);最坏O(logn)
顺序表版
完整代码
#include运行结果
单链表版
以下采用不带头结点的排序办法。
关键函数
尾插建立链表
链接: 单链表各类基础操作
LinkList CreateList2(LinkList &L)
{
L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node));
L->next=NULL;
Node *s,*r=L;
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
while(x!=999)
{
s=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
s->value=x;
r->next=s;
r=s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
r->next=NULL;
return L->next;
}
归并排序函数
Node* merge_sort(Node* first)
{
if(first==NULL||first->next==NULL)
return first;
else
{
//用双指针法找到“断点”
Node *fast=first,*slow=first;
while(fast->next!=NULL && fast->next->next!=NULL)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
fast=slow;
slow=slow->next;
fast->next=NULL;
fast=merge_sort(first);
slow=merge_sort(slow);
return merge(fast,slow);
}
}
两段合并函数
Node* merge(Node* first1,Node* first2)
{
if(first1==NULL)
return first2;
if(first2==NULL)
return first1;
Node *res,*p;
if(first1->value < first2->value)
{
res=first1;
first1=first1->next;
}
else
{
res=first2;
first2=first2->next;
}
p=res;
while(first1!=NULL&&first2!=NULL)
{
if(first1->value < first2->value)
{
p->next=first1;
first1=first1->next;
}
else
{
p->next=first2;
first2=first2->next;
}
p=p->next;
}
//归并排序长度差不会超过1
if(first1!=NULL) p->next=first1;
if(first2!=NULL) p->next=first2;
return res;
}
完整代码
#include