GoogLeNet网络结构详解与代码复现
参考内容来自up:5.1 GoogLeNet网络详解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
up的代码和ppt:GitHub - WZMIAOMIAO/deep-learning-for-image-processing: deep learning for image processing including classification and object-detection etc.
一、简介
GoogLeNet在2014年由Google团队提出,斩获当年ImageNet竞 赛中Classification Task (分类任务)
原论文地址:[1409.4842] Going Deeper with Convolutions (arxiv.org)
GoogLeNet 的创新点:
引入了 Inception 结构(融合不同尺度的特征信息)
使用1x1的卷积核进行降维以及映射处理 (虽然VGG网络中也有,但该论文介绍的更详细)
添加两个辅助分类器帮助训练
丢弃全连接层,使用平均池化层(大大减少模型参数,除去两个辅助分类器,网络大小只有vgg的1/20)
二、详解
1. inception 结构
传统的CNN结构如AlexNet、VggNet 网络都是串联的结构,即将一系列的卷积层和池化层进行串联得到的结构。
inception原始结构
GoogLeNet 提出了一种并联结构,下图是论文中提出的inception原始结构,将特征矩阵同时输入到多个分支进行处理,并将输出的特征矩阵按深度进行拼接,得到最终输出特征矩阵
注:每个分支所得特征矩阵的高和宽必须相同(通过调整stride和padding),以保证输出特征能在深度上进行拼接
1×1卷积核的降维功能
同样是对一个深度为512的特征矩阵使用64个大小为5x5的卷积核进行卷积:
不使用1x1卷积核进行降维的 话一共需要819200个参数,
如果使用1x1卷积核进行降维一共需要50688个参数,明显少了很多
注:CNN参数个数 = 卷积核尺寸×卷积核深度 × 卷积核组数 = 卷积核尺寸 × 输入特征矩阵深度 × 输出特征矩阵深度
2. 辅助分类器(Auxiliary Classifier)
原文中关于辅助分类器的描述:
•An average pooling layer with 5×5 filter size and stride 3, resulting in an4×4×512 output for the (4a), and 4×4×528 for the (4d) stage. (两个辅助分类器分别来自 inception4a和inception4d )
•A 1×1 convolution with 128 filters for dimension reduction and rectified linearactivation.
•A fully connected layer with 1024 units and rectified linear activation.
•A dropout layer with 70% ratio of dropped outputs.
•A linear layer with softmax loss as the classifier (predicting thesame 1000 classes as the main classifier, but removed at inference time).
辅助分类器的两个分支有什么用呢?
作用一:可以把他看做inception网络中的一个小细节,它确保了即便是隐藏单元和中间层也参与了特征计算,他们也能预测图片的类别,他在inception网络中起到一种调整的效果,并且能防止网络发生过拟合。
作用二:给定深度相对较大的网络,有效传播梯度反向通过所有层的能力是一个问题。通过将辅助分类器添加到这些中间层,可以期望较低阶段分类器的判别力。在训练期间,它们的损失以折扣权重(辅助分类器损失的权重是0.3)加到网络的整个损失上。
Inception V1的参数量=5607184,约为560w
AlexNet 和 VGG 都只有1个输出层,GoogLeNet 有3个输出层,其中的两个是辅助分类层。
如下图所示,网络主干右边的 两个分支 就是 辅助分类器,其结构一模一样。
在训练模型时,将两个辅助分类器的损失乘以权重(论文中是0.3)加到网络的整体损失上,再进行反向传播。
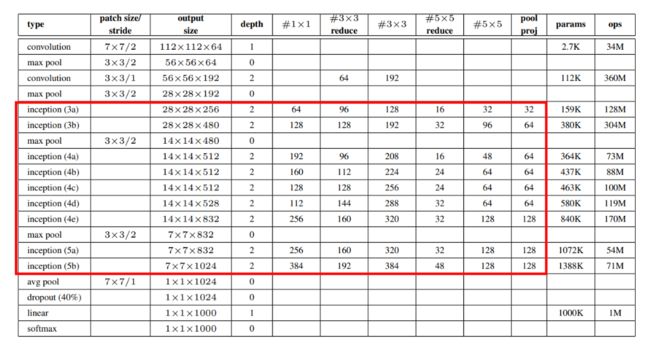
3. GoogLeNet 参数理解
下面是原论文中给出的网络参数列表,配合上图查看
计算公式:
对于Inception模块,所需要使用到参数有#1x1 , #3x3reduce, #3x3, #5x5reduce, #5x5, poolproj,这6个参数,分别对应着所使用的卷积核个数。
4. 使用参数比较
辅助分类器在训练过程才使用
使用VGG网络多的原因:
VGG网络搭建比较方便
GoogLeNet有两个辅助分类器,搭建和修改比较麻烦
只针对分类而言,GoogLeNet明显更优秀。
三、网络搭建
1. model.py
相比于 AlexNet 和 VggNet 只有卷积层和全连接层这两种结构,GoogLeNet多了 inception 和 辅助分类器(Auxiliary Classifier),而 inception 和 辅助分类器 也是由多个卷积层和全连接层组合的,因此在定义模型时可以将 卷积、inception 、辅助分类器定义成不同的类,调用时更加方便。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) #自适应平均池化下采样操作好处:不论输入的特征矩阵的高和宽时多少,都能得到指定的大小
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.conv1(x)
# N x 64 x 112 x 112
x = self.maxpool1(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv3(x)
# N x 192 x 56 x 56
x = self.maxpool2(x)
# N x 192 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3a(x)
# N x 256 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3b(x)
# N x 480 x 28 x 28
x = self.maxpool3(x)
# N x 480 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4a(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4c(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4d(x)
# N x 528 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
# N x 832 x 14 x 14
x = self.maxpool4(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5a(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5b(x)
# N x 1024 x 7 x 7
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
# N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# N x 1000 (num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
class Inception(nn.Module): #定义Inception结构
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
# 在官方的实现中,其实是3x3的kernel并不是5x5,这里我也懒得改了,具体可以参考下面的issue
# Please see https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/906 for details.
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1) #在深度方向拼接
class InceptionAux(nn.Module): #定义辅助分类器结构
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# aux1: N x 512 x 14 x 14, aux2: N x 528 x 14 x 14
x = self.averagePool(x)
# aux1: N x 512 x 4 x 4, aux2: N x 528 x 4 x 4
x = self.conv(x)
# N x 128 x 4 x 4
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 2048
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 1024
x = self.fc2(x)
# N x num_classes
return x
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module): #包含卷积和激活函数的卷积模板
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x2. train.py
训练部分跟AlexNet和VGG类似,有两点需要注意:
实例化网络时的参数
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=True, init_weights=True)GoogLeNet的网络输出 loss 有三个部分,分别是主干输出loss、两个辅助分类器输出loss(权重0.3)
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images.to(device))
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels.to(device))
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels.to(device))
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()import os
import sys
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import tqdm
from model import GoogLeNet
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # get data root path
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, "data_set", "flower_data") # flower data set path
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path)
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 32
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw)
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "val"),
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num,
val_num))
# test_data_iter = iter(validate_loader)
# test_image, test_label = test_data_iter.next()
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=True, init_weights=True)
# 如果要使用官方的预训练权重,注意是将权重载入官方的模型,不是我们自己实现的模型
# 官方的模型中使用了bn层以及改了一些参数,不能混用
# import torchvision
# net = torchvision.models.googlenet(num_classes=5)
# model_dict = net.state_dict()
# # 预训练权重下载地址: https://download.pytorch.org/models/googlenet-1378be20.pth
# pretrain_model = torch.load("googlenet.pth")
# del_list = ["aux1.fc2.weight", "aux1.fc2.bias",
# "aux2.fc2.weight", "aux2.fc2.bias",
# "fc.weight", "fc.bias"]
# pretrain_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrain_model.items() if k not in del_list}
# model_dict.update(pretrain_dict)
# net.load_state_dict(model_dict)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
epochs = 30
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './googleNet.pth'
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images.to(device))
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels.to(device))
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels.to(device))
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,
epochs,
loss)
# validate
net.eval()
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device)) # eval model only have last output layer
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3. predict.py
预测部分跟AlexNet和VGG类似,需要注意在实例化模型时不需要辅助分类器
# create model
model = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=False)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./googleNet.pth"但是在加载训练好的模型参数时,由于其中是包含有辅助分类器的,需要设置strict=False
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path), strict=False)import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import GoogLeNet
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img_path = "../tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
# create model
model = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=False).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "./googleNet.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device),
strict=False)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()训练结果:
由于数据少少,每类只有十多张,30个epoch下来最高只有0.48