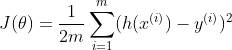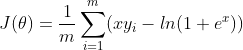逻辑回归的梯度下降
对于假设函数:![]()
0、分类
就是字面的意思,对某个事物进行分类,好的还是坏的,yes或者no,等等。一般实现时使用1或者0。也就是说得出的结果是两个离散值0,1,即![]() 。
。
线性回归应用在分类问题中的局限性:
当输出在(0,1)之间时,我们会得到一个期望的值,但是如果输出在1之外的话,线性回归可能得到一个很差的结果。
所以需要引进一个函数:Logistic函数 ![]()
logistic函数的定义域为![]() ,值域为
,值域为![]() 。就用这个函数对目标进行分类。
。就用这个函数对目标进行分类。
将假设函数![]() 与 logistic函数
与 logistic函数![]() 结合后为:
结合后为:
这时我们暂时可以这么认为:只要当![]() 时,那么我们可以认为结果为1,反之亦然。
时,那么我们可以认为结果为1,反之亦然。
一、Logistic回归模型
![]() ,
,![]()
![]()
现考虑有 n+1个独立的向量![]() (其实是n个,
(其实是n个,![]() 恒等于1),设条件概率
恒等于1),设条件概率![]() 为根据训练量相对于事件
为根据训练量相对于事件![]() 发生的概率。
发生的概率。
现在假设训练样本中有 m 个训练样本,其训练结果分别为![]() 。
。
设在给定条件下(第 i 个训练样本的向量![]() )
) ![]() 的概率为:
的概率为:![]() ;
;![]() 的概率为:
的概率为:![]()
![]() 该训练样本的输出结果概率为:
该训练样本的输出结果概率为:![]()
因为每个训练样本之间都是相互独立的,所以它们的联合分布就是彼此的乘积。故得到似然函数为:
![L(\theta)=\prod _{i=1}^{m}[g(x_{i})]^{y_{i}}[1-g(x_{i})]^{1-y_{i}}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/32e84232c6dc459482505346751b4a1d.gif) ,这就是我们的目标函数。我们的目标就是求出一组合适的系数向量
,这就是我们的目标函数。我们的目标就是求出一组合适的系数向量![]() 使
使![]() 取得最大值。
取得最大值。
直接求有点复杂,考虑对数:
其中:![]()
二、逻辑回归的梯度下降
现在我们的目标函数是 ![]() .
.
与线性回归的梯度下降的异同:
异:
其中,![]()
![]()
三、代码实现(C++)
与线性回归的梯度下降差不多,只不过多了个 logistic函数。
逻辑回归的梯度下降:
/* GD.h */
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Data {
vector feature;
double label;
Data(vectorf,double l):feature(f),label(l){}
};
class GD
{
public:
GD(string &trainfile,string &testfile,string& predictOutfile);
void train();
//void testTrain();
int storeModel();
void predict();
vector Weight;
private:
vector testDataSet;
vector trainDataSet;
vector predictVec;
private:
string trainFile;
string testFile;
string predictOutFile;
int featureNum =0;
double alpha=0.01; //步长
double epsion = 1e-6; //误差限
int maxIterTimes = 300;
double predictTrueThresh = 0.5;
string weightParamFile = "modelweight.txt";
private:
bool init();
bool loadTrainData();
void initWeight();
double wxCal(Data& data);
double lossCalc();
void UpdateW();
double gradient(int &index,vector& sigmoidVec);
inline double sigmoidCala(double wx);
//int storeModel();
bool loadTestData();
int storePredict();
double costCalc();
};
/* GD.cpp */
#include "GD.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
GD::GD(string &trainfile,string &testfile,string& predictOutfile) {
trainFile = trainfile;
testFile = testfile;
predictOutFile = predictOutfile;
init();
}
//初始化包括:加载训练文件、初始化权重
bool GD::init() {
trainDataSet.clear();
clock_t start = clock();
bool sign = loadTrainData();
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "load train file time is " << end - start << endl;
if (sign == false)
return false;
featureNum = trainDataSet[0].feature.size();
Weight.clear();
initWeight();
return true;
}
bool GD::loadTrainData() {
ifstream infile(trainFile.c_str());
string line;
if (!infile.good()) {
std::cout << "open train file failure" << endl;
exit(0);
}
while (!infile.eof()) {
getline(infile, line);
if (line.size() > 0) {
stringstream strCin(line);
char ch;
double data;
vector feature;
while (strCin) {
//char c = strCin.peek();
//if (int(c) != -1) {
strCin >> data;
feature.push_back(data);
strCin >> ch;
/*}
else {
return false;
}*/
}
double label = feature.back();
feature.pop_back();
trainDataSet.push_back(Data(feature, label));
}
}
infile.close();
//trainDataSet.pop_back();
return true;
}
void GD::initWeight() {
for (int i = 0; i < featureNum; i++)
Weight.push_back(1.0); //先初始化权重全为1
}
void GD::train() {
//for (int i = 0; i < maxIterTimes; i++) {
int k = 0;
double objCost = lossCalc();
UpdateW();
double newCost = lossCalc();
while (fabs(newCost - objCost) > epsion) {
objCost = newCost;
UpdateW();
newCost = lossCalc();
k++;
if (k > 300) break;
}
//}
}
double GD::wxCal(Data& data) {
double h_theta = 0;
double theta, x;
for (int i = 0; i < featureNum; i++) {
theta = Weight[i];
x = data.feature[i];
h_theta += theta * x;
}
return h_theta;
}
inline double GD::sigmoidCala(double wx) {
double expV = exp(-1 * wx);
double sigV = 1 / (1 + expV);
return sigV;
}
double GD::lossCalc() {
double lossV = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < trainDataSet.size(); i++) {
lossV -= (wxCal(trainDataSet[i]) * trainDataSet[i].label - log(1 + exp(wxCal(trainDataSet[i]))));
/*lossV -= trainDataSet[i].label * log(sigmoidCala(wxCal(trainDataSet[i])));
lossV -= (1 - trainDataSet[i].label) * log(1 - sigmoidCala(wxCal(trainDataSet[i])));*/
}
lossV = lossV / trainDataSet.size();
return lossV;
}
double GD::costCalc() {
double costV = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < trainDataSet.size(); i++) {
costV += pow(wxCal(trainDataSet[i]) - trainDataSet[i].label ,2);
}
costV = costV / (2.0*trainDataSet.size());
return costV;
}
void GD::UpdateW() {
vector sigmoidVec;
for (int i = 0; i < trainDataSet.size(); i++) {
double wxV = wxCal(trainDataSet[i]);
double sigmoidV = sigmoidCala(wxV);
sigmoidVec.push_back(sigmoidV);
}
vector temp;
double V = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Weight.size(); i++) {
Weight[i] += alpha * gradient(i,sigmoidVec);
}
//Weight = temp;
}
double GD::gradient(int &index,vector& sigmoidVec) {
double gV = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < trainDataSet.size(); i++) {
double sigV = sigmoidVec[i];
double label = trainDataSet[i].label;
gV += (label - sigV) * trainDataSet[i].feature[index];
//gV += (wxCal(trainDataSet[i]) - trainDataSet[i].label)*trainDataSet[i].feature[index];
}
gV = gV / trainDataSet.size();
return gV;
}
int GD::storeModel() {
clock_t start = clock();
ofstream outfile(weightParamFile.c_str());
string line;
if (!outfile.is_open()) printf("open model file failure \n");
for (int i = 0; i < featureNum; i++)
outfile << Weight[i] << " ";
outfile.close();
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "store model time is" << end - start << endl;
return 0;
}
bool GD::loadTestData() {
ifstream infile(testFile.c_str());
string line;
if (!infile.is_open()) {
printf("open test file failure \n");
exit(0);
}
//vector feature;
//string buffer;
//buffer.assign(istreambuf_iterator(infile),istreambuf_iterator());
//stringstream strSin(buffer);
//while (getline(strSin, line)) {
// if (line.size() > 0) {
// stringstream sin(line);
// double data;
// char ch;
// //int i = 0;
// while (sin) {
// sin >> data;
// feature.push_back(data);
// sin >> ch;
// //i++;
// }
// testDataSet.push_back(Data(feature, 0));
// }
//}
while (!infile.eof()) {
vector feature;
string line;
getline(infile, line);
if (line.size() > 0) {
stringstream sin(line);
double data;
char ch;
//int i = 0;
while (sin) {
sin >> data;
feature.push_back(data);
sin >> ch;
//i++;
}
testDataSet.push_back(Data(feature, 0));
}
}
infile.close();
}
int GD::storePredict() {
//int GD::storePredict(vector& predict) {
ofstream outfile(predictOutFile.c_str());
if (!outfile.is_open())
printf("open predict file failure\n");
for (int i = 0; i < predictVec.size(); i++) {
outfile << predictVec[i] << endl;
}
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
void GD::predict() {
clock_t start = clock();
loadTestData();
clock_t end = clock();
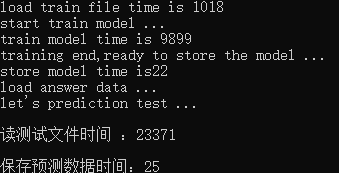
cout << endl<< "读测试文件时间 :" << end - start << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < testDataSet.size(); i++) {
double sigV = sigmoidCala(wxCal(testDataSet[i]));
int predictV = sigV >= predictTrueThresh ? 1 : 0;
predictVec.push_back(predictV);
}
clock_t start2 = clock();
storePredict();
clock_t end2 = clock();
cout << endl << "保存预测数据时间:" << end2 - start2 << endl;
}
/* main.cpp */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"GD.h"
#define TEST
using namespace std;
bool loadAnswerData(string& awFile, vector& awVec);
int main()
{
//ofstream outfile("trainData.txt");
//srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
//for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
// //原函数 y = 1 + 3x; 创造一个训练集
// double x1 = (rand() % (30));
// //double x2 = (rand() % (50) + 10);
// double y = 1 + 3 * x1;
// outfile << 1 <<","<< x1 << "," << y << endl;
//}
//outfile.close();
//cout << "训练文件已生成 " << endl;
//ofstream outTestfile("testData.txt");
//srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
//for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
// //原函数 y = 1 + 3x; 创造一个训练集
// double x1 = (rand() % (50));
// //double x2 = (rand() % (50) + 10);
// double y = 1 + 3 * x1;
// outfile << 1 << "," << x1 << "," << y << endl;
//}
//outTestfile.close();
//cout << "测试文件已生成 " << endl;
string trainFile = "train_data.txt";
string testFile = "test_data.txt";
string predictFile = "result.txt";
GD gradient(trainFile,testFile,predictFile);
clock_t start1 = clock();
printf("start train model ...\n");
gradient.train();
clock_t end1 = clock();
cout << "train model time is " << end1 - start1 << endl;
printf("training end,ready to store the model ... \n");
gradient.storeModel();
//vector theta;
//for (int i = 0; i < gradient.Weight.size(); i++) {
// theta.push_back(gradient.Weight[i]);
//}
//cout << "预测的原函数为:y = " << theta[0] << " + " << theta[1] << "x1" << theta[2] << "x2" << endl; //我知道所以才这么看结果
#ifdef TEST
vector answerVec;
string answerFile = "answer.txt";
printf("load answer data ...\n");
loadAnswerData(answerFile, answerVec);
#endif
printf("let's prediction test ...\n");
gradient.predict();
#ifdef TEST
vector predictVec;
loadAnswerData(predictFile, predictVec);
cout << "test data set size is " << predictVec.size() << endl;
int correctCount = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < predictVec.size(); j++) {
if (j < answerVec.size()) {
if (answerVec[j] == predictVec[j]) {
correctCount++;
}
}
else {
cout << "answer size less than the real predicted value" << endl;
}
}
double accurate = ((double)correctCount) / answerVec.size();
cout << "the prediction accuracy is " << accurate << endl;
#endif
return 0;
}
bool loadAnswerData(string& awFile, vector& awVec) {
ifstream infile(awFile.c_str());
if (!infile.is_open()) {
printf("open answer file failure \n");
exit(0);
}
while (!infile.eof()) {
int aw;
string line;
getline(infile, line);
if (line.size() > 0) {
stringstream sin(line);
sin >> aw;
awVec.push_back(aw);
}
}
infile.close();
return true;
} 结果:
![lnL(\theta)=\sum_{i=1}^{m}[y_{i}ln(g(x))+(1-y_{i})ln(1-g(x))]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c8b3dc8e83bd43f9bcc70f4652af41ad.gif)

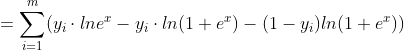
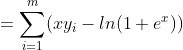
![\frac{\partial lnL(\theta)}{\partial \theta_{k}}=\sum _{i=1}^{m}x_{ik}[y_{i}-g(x)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f02af8292703447797f3e1cb4a3fb8ce.gif)