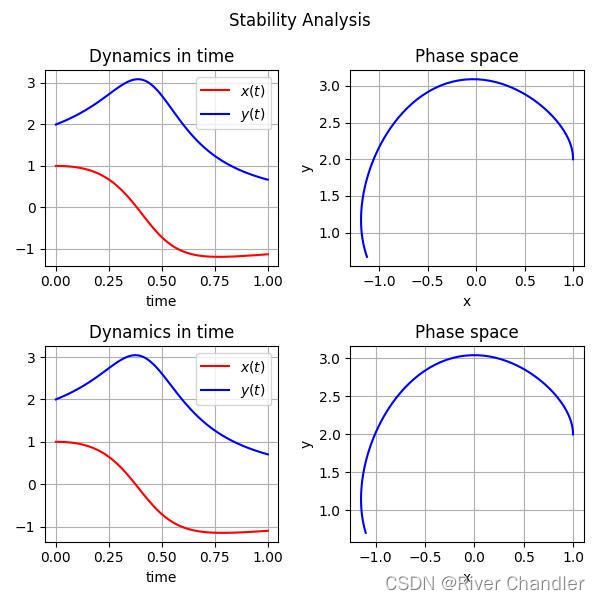
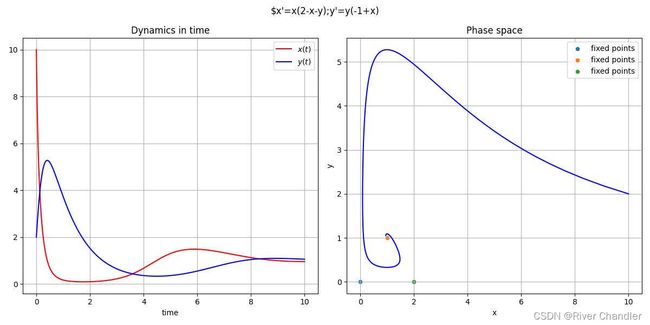
常微分方程组解稳定性的分析
文章未完
相空间的绘制
我们随机选一个方程,随机选的,不是有数学手册吗,一般来说考题不可能出数学手册上的例子
import scipy.integrate as si
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
## dx/dt = x**2-y**2+x+y
## dy/dt = x*y**2 - x**2*y
f = lambda x,y:x**2-y**2+x+y
g = lambda x,y:x*y**2 - x**2*y
dt = 0.01
time_start = 0
time_end = 1
time = np.arange(time_start,time_end+dt,dt)
def system_Euler():
global f
global g
global time
x = np.zeros(time.size)
y = np.zeros(time.size)
x[0],y[0] = 1,2
for i in range(1,len(time)):
x[i] = x[i-1]+(f(x[i-1],y[i-1]))*dt
y[i] = y[i-1]+(g(x[i-1],y[i-1]))*dt
return x,y
def system_odeint(X,t=0):
return np.array([X[0]**2-X[1]**2+X[0]+X[1],X[0]*X[1]**2-X[0]**2*X[1]])
system_init = np.array([1,2])
####################
x,y = system_Euler()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6),tight_layout=True)
fig.suptitle("Stability Analysis")
ax1 = plt.subplot(221)
ax1.plot(time,x, 'r-', label='$x(t)$')
ax1.plot(time,y, 'b-', label='$y(t)$')
ax1.set_title("Dynamics in time")
ax1.set_xlabel("time")
ax1.grid()
ax1.legend()
ax2 = plt.subplot(222)
ax2.plot(x,y,color="blue")
ax2.set_xlabel("x")
ax2.set_ylabel("y")
ax2.set_title("Phase space")
ax2.grid()
#####################33
X,infodict = si.odeint(system_odeint,system_init,time,full_output=True)
x,y = X.T
ax3 = plt.subplot(223)
ax3.plot(time,x, 'r-', label='$x(t)$')
ax3.plot(time,y, 'b-', label='$y(t)$')
ax3.set_title("Dynamics in time")
ax3.set_xlabel("time")
ax3.grid()
ax3.legend()
ax4 = plt.subplot(224)
ax4.plot(x,y,color="blue")
ax4.set_xlabel("x")
ax4.set_ylabel("y")
ax4.set_title("Phase space")
ax4.grid()
plt.savefig("0.jpg")
plt.pause(0.01)
一阶微分方程的稳定点
import scipy.integrate as si
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import sympy as sy
import copy
## dx/dt = 2*x - x**2 - x*y
## dy/dt = x*y - y
f = lambda X:X[0]*2 - X[0]**2 - X[0]*X[1]
g = lambda X:-X[1] + X[0]*X[1]
dt = 0.01
time_start = 0
time_end = 10
time = np.arange(time_start,time_end+dt,dt)
system_init = np.array([10,2])
def system_odeint(X,t=0):
global f
global g
return np.array([f(X),g(X)])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,6),tight_layout=True)
fig.suptitle("$x'=x(2-x-y);y'=y(-1+x)")
X,infodict = si.odeint(system_odeint,system_init,time,full_output=True)
x,y = X.T
def find_fixed_points():
global f
global g
global X
r = sy.symbols("r")
c = sy.symbols("c")
R = sy.Function("R")
C = sy.Function("C")
R = 2*r - r**2 -r*c
C = -c + r*c
REqual = sy.Eq(R,0)
CEqual = sy.Eq(C,0)
return sy.solve((REqual,CEqual),r,c)
ax1 = plt.subplot(121)
ax1.plot(time,x, 'r-', label='$x(t)$')
ax1.plot(time,y, 'b-', label='$y(t)$')
ax1.set_title("Dynamics in time")
ax1.set_xlabel("time")
ax1.grid()
ax1.legend()
ax2 = plt.subplot(122)
ax2.plot(x,y,color="blue")
ax2.set_xlabel("x")
ax2.set_ylabel("y")
ax2.set_title("Phase space")
ax2.grid()
fixed_points = find_fixed_points()
for point in fixed_points:
ax2.scatter(point[0],point[1],s=20,label="fixed points")
ax2.legend()
plt.savefig("0.jpg")
plt.pause(0.01)
微分方程稳定性的理论分析
李雅普诺夫先生,一个很棒的人
一阶自洽微分方程平衡点稳定性的结论
设有微分方程![]() ,若等号右端不显含自变量t,则称之自治方程。
,若等号右端不显含自变量t,则称之自治方程。
代数方程![]() 的实根
的实根![]() 称为方程的平衡点(奇点,奇解)
称为方程的平衡点(奇点,奇解)
二阶自洽微分方程平衡点稳定性的结论
一阶自洽线性常系数方程组
显然,方程组有唯一平衡点,假定
![]()
特征方程:
特征根:
|
|
平衡点类型 |
稳定性 |
|
|
稳定结点 |
稳定 |
|
|
不稳定结点 |
不稳定 |
|
|
鞍点 |
不稳定 |
|
|
稳定退化结点 |
稳定 |
|
|
不稳定退化结点 |
不稳定 |
|
|
稳定焦点 |
稳定 |
|
|
不稳定焦点 |
不稳定 |
|
|
中心 |
不稳定 |
一个典型的非线性振动系统
![]()
显然他可以转换成一个近可积哈密顿系统
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import odeint as sio
from numpy.linalg import solve as sol
import random
random.seed(0)
dt = 0.001
time_start = 0
time_end = 2
time = np.arange(time_start,time_end+dt,dt)
def RK4(diff,time):
global dt
global init
X = np.zeros((time.size,len(init)))
X[0] = init
for i in range(time.size-1):
s0 = diff(time[i],X[i])
s1 = diff(time[i]+dt/2,X[i]+dt*s0/2.)
s2 = diff(time[i]+dt/2,X[i]+dt*s1/2.)
s3 = diff(time[i+1],X[i]+dt*s2)
X[i+1] = X[i] + dt*(s0+2*(s1+s2)+s3)/6.
return time,X
def diff(time,Xi):
xi,yi = Xi
epision = 0.1
global omega
diffxi = yi
diffyi = xi**2 - xi + epision*np.cos(omega*time)
return np.array([diffxi,diffyi])
omega = 0.4
createvar = locals()
for i in range(20):
init = np.array([1+(i>0)*random.uniform(0,0.01),1+(i>0)*random.uniform(0,0.01)])
createvar["t"+str(i)],createvar["X"+str(i)] = RK4(diff,time)
for i in range(20):
plt.plot(eval("X"+str(i))[:,0],eval("X"+str(i))[:,1])#,label="omega:"+str(round(omega,2)))
plt.legend()
plt.pause(0.01)