情感分析入门3-Faster Sentiment Analysis
系列文章目录
情感分析入门 1-Simple Sentiment Analysis
情感分析入门 2-Updated Sentiment Analysis
上一节中,我们使用情感分析的所有常见技巧,得到了84%的准确率。这一节中,我们将实现一个模型得到类似的结果,同时训练得更快并且使用大约一半的参数。具体来说,我们实现的是论文"Bags of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification"中的FastText模型。
数据准备
FastText论文的核心之一是计算输入句子的n-grams并将其添加到句子的末尾。这里我们使用bi-grams。
函数genertrate_bigrams接收已经被分词的句子,计算bi-grams并且将其添加到tokenized list的末尾。
def generate_bigrams(x):
n_grams = set(zip(*[x[i:] for i in range(2)]))
for n_gram in n_grams:
x.append(' '.join(n_gram))
return x例子:
generate_bigrams(['This', 'film', 'is', 'terrible'])['This', 'film', 'is', 'terrible', 'film is', 'This film', 'is terrible']
Filed有参数preprocessing。我们在句子tokenized(transformed from a string into a list of tokens)之后,numericalized(transformed from a list of tokens to a list of indexes)之前,传入generate_bigrams函数。
import torch
from torchtext.legacy import data
from torchtext.legacy import datasets
SEED = 1234
torch.manual_seed(SEED)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
TEXT = data.Field(tokenize = 'spacy',
tokenizer_language = 'en_core_web_sm',
preprocessing = generate_bigrams)
LABEL = data.LabelField(dtype = torch.float)
#划分训练集、验证集和测试集
import random
train_data, test_data = datasets.IMDB.splits(TEXT, LABEL)
train_data, valid_data = train_data.split(random_state = random.seed(SEED))
#构建词典并载入pre-trained word embeddings
import random
train_data, test_data = datasets.IMDB.splits(TEXT, LABEL)
train_data, valid_data = train_data.split(random_state = random.seed(SEED))
#构造iterators
BATCH_SIZE = 64
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
train_iterator, valid_iterator, test_iterator = data.BucketIterator.splits(
(train_data, valid_data, test_data),
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
device = device)模型构建
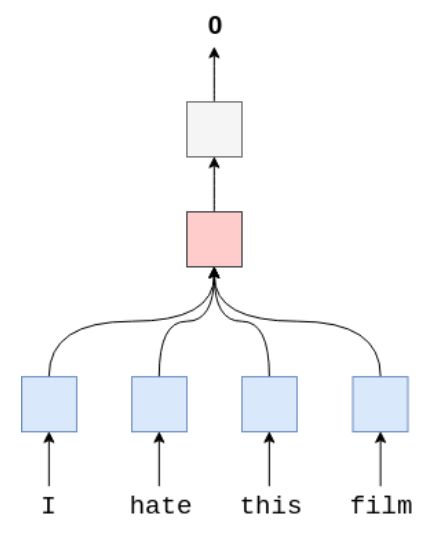
这个模型比之前的模型参数量更少,是因为它只有2层:embedding layer and linear layer。没有RNN层。首先使用Embedding layer计算word embedding(blue),之后计算所有word embedding的平均值(pink),并将其送入Linear layer(silver)。
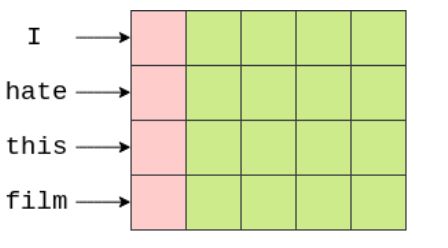
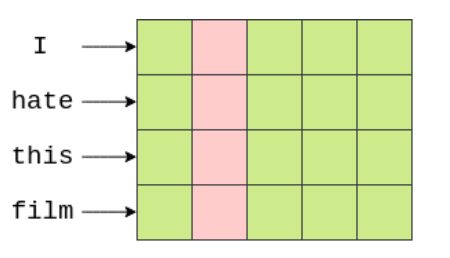
我们使用函数avg_pool2d计算平均值( the words along the vertical axis and the embeddings along the horizontal axis)。avg_pool2d使用大小为embedded.shape[1](句子长度)的filter。我们计算filter覆盖的所有元素的平均值,然后filter向右滑动,计算句子中每个单词的下一列嵌入值的平均值。
在filter覆盖了所有的embedding dimensions之后,我们得到了一个[1x5]张量。将这个张量输入线性层来生成预测。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class FastText(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, output_dim, pad_idx):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, padding_idx=pad_idx)
self.fc = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, text):
#text = [sent len, batch size]
embedded = self.embedding(text)
#embedded = [sent len, batch size, emb dim]
embedded = embedded.permute(1, 0, 2)
#embedded = [batch size, sent len, emb dim]
pooled = F.avg_pool2d(embedded, (embedded.shape[1], 1)).squeeze(1)
#pooled = [batch size, embedding_dim]
return self.fc(pooled)
#构建实例
INPUT_DIM = len(TEXT.vocab)
EMBEDDING_DIM = 100
OUTPUT_DIM = 1
PAD_IDX = TEXT.vocab.stoi[TEXT.pad_token]
model = FastText(INPUT_DIM, EMBEDDING_DIM, OUTPUT_DIM, PAD_IDX)
#计算参数量
def count_parameters(model):
return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f'The model has {count_parameters(model):,} trainable parameters')
#copy the pre-trained vectors to our embedding layer
pretrained_embeddings = TEXT.vocab.vectors
model.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_embeddings)
#zero the initial weight of unkown and padding tokens
UNK_IDX = TEXT.vocab.stoi[TEXT.unk_token]
model.embedding.weight.data[UNK_IDX] = torch.zeros(EMBEDDING_DIM)
model.embedding.weight.data[PAD_IDX] = torch.zeros(EMBEDDING_DIM)模型训练
#初始化优化器
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
#
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
model = model.to(device)
criterion = criterion.to(device)
#
def binary_accuracy(preds, y):
"""
Returns accuracy per batch, i.e. if you get 8/10 right, this returns 0.8, NOT 8
"""
#round predictions to the closest integer
rounded_preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds))
correct = (rounded_preds == y).float() #convert into float for division
acc = correct.sum() / len(correct)
return acc
#我们不再使用dropout,所以我们不需要使用model.train(),但正如第一节中提到的,it is good practice to use it。
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.train()
for batch in iterator:
optimizer.zero_grad()
predictions = model(batch.text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
acc = binary_accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc.item()
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
#Note: again, we leave model.eval() even though we do not use dropout.
def evaluate(model, iterator, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in iterator:
predictions = model(batch.text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
acc = binary_accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc.item()
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
#
import time
def epoch_time(start_time, end_time):
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
elapsed_mins = int(elapsed_time / 60)
elapsed_secs = int(elapsed_time - (elapsed_mins * 60))
return elapsed_mins, elapsed_secs
#
N_EPOCHS = 5
best_valid_loss = float('inf')
for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS):
start_time = time.time()
train_loss, train_acc = train(model, train_iterator, optimizer, criterion)
valid_loss, valid_acc = evaluate(model, valid_iterator, criterion)
end_time = time.time()
epoch_mins, epoch_secs = epoch_time(start_time, end_time)
if valid_loss < best_valid_loss:
best_valid_loss = valid_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'tut3-model.pt')
print(f'Epoch: {epoch+1:02} | Epoch Time: {epoch_mins}m {epoch_secs}s')
print(f'\tTrain Loss: {train_loss:.3f} | Train Acc: {train_acc*100:.2f}%')
print(f'\t Val. Loss: {valid_loss:.3f} | Val. Acc: {valid_acc*100:.2f}%')
#
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('tut3-model.pt'))
test_loss, test_acc = evaluate(model, test_iterator, criterion)
print(f'Test Loss: {test_loss:.3f} | Test Acc: {test_acc*100:.2f}%')用户输入
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
def predict_sentiment(model, sentence):
model.eval()
tokenized = generate_bigrams([tok.text for tok in nlp.tokenizer(sentence)])
indexed = [TEXT.vocab.stoi[t] for t in tokenized]
tensor = torch.LongTensor(indexed).to(device)
tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(1)
prediction = torch.sigmoid(model(tensor))
return prediction.item()
predict_sentiment(model, "This film is terrible")
predict_sentiment(model, "This film is great")