深度学习——学习总结(1)
前言
学习深度学习也有小半年了,因为平时还要上课,学习速度比较慢。目前三大框架——tensorflow、keras、pytorch 的基础内容都学了一遍。但不时回想前面的学习内容时,或多或少都有一些遗忘,因此在这里记录、回顾一下自己在学习这三个框架中写过的代码。
先来说说我眼中的神经网络。神经网络是利用输入层输入数据去经过n个包含m个节点的隐藏层,其中层与层之间每个神经元之间的链接上都有一个权值,从而去进行一些线性、非线性运算。最后得到输出数据来模拟人脑的思考、脑中神经元信息的传递。因此可以用神经网络来做很多分类、回归、重构的工作。
普通神经网络
共享单车项目
这是我学习深度学习后接触的第一个项目,其中只用到的简单的全链接网络。
项目目标
根据已有的一些数据来训练一个能够预测共享单车未来一段时间被使用的情况的网络。
数据
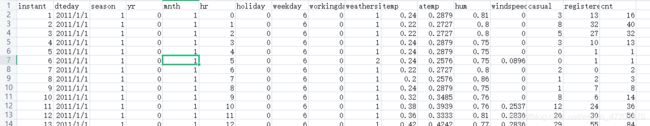
数据是excel文件,里面存有信息每一行包括:日期(季节、年月日、时刻)、天气、是否为节假日、温度、风速、使用人数。
思路
取其中一批数据作为训练数据、一批作为验证数据、另一批作为测试数据。训练时:用features作为输入,targets作为输出进行训练。用训练数据训练得到的参数去用验证集验证和用测试集测试(验证和测试时,只输入features,观察得到的targets与真实数据中的targets是否相近)。
选取季节、年月日、时刻、星期几、天气类型、温度、风速作为features(为了简化没有考虑节假日的情况)。未注册的使用人数、注册的使用人数、总使用人数作为targets。
数据处理
哑变量处理。其中因为年月日、温度、星期几、时刻,它们的数值并不能代表程度(如:温度高低,风速大小),因此需要把它们当作哑变量进行处理,防止它们数值的差异对结果造成影响。
量纲处理。另外像温度、风速、使用人数之间数据的大小差异大(如:t1时刻风速60,t2时刻风速4,相差56;而t1时刻温度21,t2时刻温度18,只相差了3),因此需要对这类型的数据进行一个归一化,统一到一定的范围。
网络结构
一个输入层、一个隐藏层(隐藏层输出后经过一个sigmoid函数)、一个输出层。
代码
作为第一个神经网络代码,没有用到任何框架,前项运算、反向传播、激活函数等都没有用api写,这样更能了解神经网络的底层逻辑。(注重看网络的训练代码)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
data_path = r'hour.csv'
rides = pd.read_csv(data_path)
'''一.预处理
生成哑变量'''
dummy_fileds = ['season','mnth','hr','weekday','weathersit']
for each in dummy_fileds:
dummies = pd.get_dummies(rides[each],prefix = each)
rides = pd.concat([rides,dummies],axis = 1)
print(rides.shape)
'''去除多余参数'''
fileds_drop = ['instant','season','mnth','hr','weekday','weathersit',
'dteday','atemp','workingday']
data = rides.drop(fileds_drop,axis = 1)
'''量纲归一化'''
quant_features = ['temp','hum','cnt','windspeed','casual','registered']
scaled_features = {}
#????????????????????为什么变成[]就不对了
for each in quant_features:
mean,std = data[each].mean(),data[each].std()
scaled_features[each] = [mean,std]
data.loc[:,each] = (data[each] - mean)/std
'''二.训练数据集'''
test_date = data[-21*24:]
data = data[:-21*24]
target_fileds = ['cnt','casual','registered']
test_features,test_targets = test_date.drop(target_fileds,axis = 1),test_date[target_fileds]
features,targets = data.drop(target_fileds,axis = 1),data[target_fileds]
train_features,train_targets = features[:60*24],targets[:60*24]
val_features,val_targets = features[60*24:],targets[60*24:]
'''超参数'''
iterations = 6000
learning_rate = 0.5
hidden_notes = 8
output_notes = 1
input_notes = train_features.shape[1]
weight_input_hidden = np.random.normal(0.0,input_notes**0.5,(input_notes,hidden_notes))
weight_hidden_output = np.random.normal(0.0,hidden_notes**0.5,(hidden_notes,output_notes))
Ir = learning_rate
activation_function = lambda x : 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
'''训练参数'''
def train(features,targets,weight_hidden_output,weight_input_hidden):
n_records = features.shape[0]#这是什么??
delta_hidden_outputs = np.zeros(weight_hidden_output.shape)
delta_hidden_inputs = np.zeros(weight_input_hidden.shape)
hidden_inputs = np.dot(features,weight_input_hidden)
hidden_outputs = activation_function(hidden_inputs)
final_inputs = np.dot(hidden_outputs,weight_hidden_output)
final_outputs = final_inputs
error = final_outputs-targets[:,None]
#反向传播,计算每层残差
delta_output = error
delta_hidden_outputs = np.dot(delta_output,np.transpose(weight_hidden_output))#反向时要将w转置
delta_hidden_inputs = hidden_outputs*(1-hidden_outputs)*delta_hidden_outputs#sigmoid求导后:f(x)*(1-f(x))
delta_weight_i_h = np.dot(features.T,delta_hidden_inputs)
delta_weight_h_o = np.dot(hidden_outputs.T,delta_output)
#更新参数
weight_input_hidden -= Ir*delta_weight_i_h/n_records
weight_hidden_output -= Ir*delta_weight_h_o/n_records
def run(features):
hidden_inputs = np.dot(features,weight_input_hidden)
hidden_outputs = activation_function(hidden_inputs)
final_inputs = np.dot(hidden_outputs,weight_hidden_output)
final_outputs = final_inputs
return final_outputs
'''算均方差'''
def MSE(y,Y):
return np.mean((y-Y)**2)
import sys
losses = {'train':[],'validation':[]}
for ii in range(6000):
batch = np.random.choice(train_features.index,size = 128)
X,y = train_features.iloc[batch].values,train_targets.iloc[batch]['cnt'].values
train(X,y,weight_hidden_output,weight_input_hidden)
train_loss =MSE(run(train_features).T,train_targets['cnt'].values)
_loss = MSE(run(val_features).T,val_targets['cnt'].values)
sys.stdout.write("\rprogress:{:2.1f}".format(100*ii/float(iterations))\
+ "%...training loss:" + str(train_loss)[:5] \
+ "%...validation loss:" +str(val_loss)[:5])
sys.stdout.flush()
losses['train'].append(train_loss)
losses['validation'].append(val_loss)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(losses['train'],label = 'training loss')
plt.plot(losses['validation'],label = 'validation loss')
plt.legend()
#预测并输出结果
_,ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (8,4))
mean,std = scaled_features['cnt']
predictions = run(test_features).T * std + mean
ax.plot(predictions.T,label = 'Predictions')
ax.plot((test_targets['cnt']*std+mean).values,label = 'Actual')
ax.legend()
dates = pd.to_datetime(rides.iloc[test_date.index]['dteday'])
dates = dates.apply(lambda d:d.strftime('%b %d'))
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(dates))[12::24])
_ = ax.set_xticklabels(dates[12::24],rotation = 45)
Mnist数据集分类(Tensorflow)
这里开始就用了tensorflow的框架。tensorflow最大的特点就是你所有的运算过程、运算节点都会被存在一张图(tensorboard)里面(不同图里面的节点之间不能进行操作)。你只需要把数据传入节点(placeholder),它便会依次往下计算。然后就是你想运行某个节点时必须定义一个tf.Session,然后sess.run(你想运行的节点)。
这里还引入了一个交叉熵(cross_entropy)的概念。图像需要借助交叉熵来求cost值。交叉熵:-(yi*log(yi_)),yi是标签(one-hot形式),yi_是概率(交叉熵通常和softmax连用,因此标签和概率都不只是一个数据,可以理解为一组数组。
因此这里的优化方式和之前共享单车的不太一样,共享单车是计算输出的结果和真实结果的loss,然后去将这个loss尽可能的降为0;而使用了交叉熵后是将交叉熵的计算结果经可能降为0(也就是正确值的概率尽可能接近1)。因为one-hot标签中只有一个为1,其他全部为0,因此和概率相乘后它保留的概率只有一个,也就是正确的那一个值的概率,因为是log(yi),yi越接近1,log(yi)越接近0。
目标
输入图片,判断是数字几,计算网络分类的正确率。
数据
数据是100000张手写体数字黑白图片,0—10每个数字10000张。
思路
成批输入图片,与标签计算它们的交叉熵,优化使交叉熵接近0。最后用arg_max(取最大的一个值位置)计算分类结果的正确率。
网络结构
一个输入层、一个隐藏层、一个输出层(输出之后经过softmax层)。
代码
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('./datasets',one_hot=True)
learning_rate = 0.1
batch_size = 128
epochs = 100
features = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784,10],stddev=0.1))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
logits = tf.matmul(features,weights) + bias
probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_sum(-labels*tf.log(probs),axis = 1)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
#cost=tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels,logits=logits)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
#计算正确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(logits,1),tf.arg_max(labels,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)+1#去除最后一批多余的数据
for epochs in range(epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_features,batch_labels = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(optimizer,feed_dict = {features:batch_features,labels:batch_labels})
if(epochs%10==0):
val_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {features : mnist.validation.images,\
labels:mnist.validation.labels})
print('Epochs{:<3} val_acc={:.3f}'.format(epochs,val_acc))
test_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {features:mnist.test.images,labels:mnist.test.labels})
print('test_acc',test_acc )
Mnist数据集重构(tensorflow)
原本图像重构需要用到卷积网络进行特征提取,但由于mnist数据集的图像的特性:1.数据图片无背景2.图像都居中,3.大小相同。因此这里只用了一个全链接层。
网络结构
1个输入层,一个全连接层(编码层),一个输出层,一个解码层
因为代码和各种数据处理和上面的分类任务很相似,只是在输出后加了一个decode层进行图片重构。直接上代码:
#mnist数据集之所以能用传统神经网络来做,是因为1.数据图片无背景2.图像都居中,3.大小相同
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('./datasets',validation_size=0)
#不做分类,所以one holder不用设置
img = mnist.train.images[2]
#noisy_img = img + 0.1*np.random.randn(*img.shape)
#noisy_img = np.clip(noisy_img,0.,1.)
plt.imshow(img.reshape(28,28),cmap='Greys_r')
encoding_dim1 = 100
batch_size = 200
epochs = 100
noisy_factor = 0.1
image_size = mnist.train.images.shape[1]
tf.reset_default_graph()
input_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,(None,image_size),name='inputs')
tragets = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,(None,image_size),name='tragets')
weight_inputs_to_hidden = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([image_size,encoding_dim1],stddev=0.1))
bais = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([encoding_dim1]))
encoded = tf.matmul(input_,weight_inputs_to_hidden)+bais
encoded = tf.nn.relu(encoded)
#encoding=tf.layers.dense(input_,encoding_dim1,activation=tf.nn.relu)
logits = tf.layers.dense(encoded,image_size)
#重构图
decoded = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits,name='output1')
loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=tragets,logits=logits)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(cost)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(epochs):
for ii in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
imgs = batch[0]
feed = {input_:imgs,tragets:imgs}
batch_cost,_ = sess.run([cost,opt],feed_dict=feed)
print("epochs:{}/{}".format(i+1,epochs),
"Training loss:{:.4f}".format(batch_cost))
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=10,sharex=True,sharey=True,figsize=(20,4))
in_imgs = mnist.test.images[:10]
reconstructed,compressed = sess.run([decoded,encoded],feed_dict={input_:in_imgs})
for images,row in zip([in_imgs,reconstructed],axes):
for img,ax in zip(images,row):
ax.imshow(img.reshape((28,28)),cmap='Greys_r')
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)