在协作开发、版本升级、服务器升级、接口返回的过程中,有可能因为一些bug,和我们预期的结果不一致。为了便于开发&测试人员能够更快的发现bug,保证整个产品的质量以及进度,于是就有了断言功能。
定义测试用例
验证测试用例
例如接口返回:
{
"errcode": 0,
"errstr": "success",
"post": {
"body": "test"
},
"get": [],
"request": {
"body": "test"
},
"file": [],
"put": "",
"header": {
"User-Agent": "ApiPOST Runtime +https://www.apipost.cn",
"Accept": "/",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"Hello": "Tom",
"Cookie": "cookie-test5=nihao;cookie-test1=0;cookie-test2=0;cookie-test8=renge;cookie-test3=%25E4%25BD%25A0%25E5%25A5%25BD;cookie-test4=%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD;httponly-cookie=httponly-value",
"Host": "echo.apipost.cn",
"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=--------------------------856985481572999749293071",
"Content-Length": "163"
},
"cookie": {
"cookie-test5": "nihao",
"cookie-test1": "0",
"cookie-test2": "0",
"cookie-test8": "renge",
"cookie-test3": "%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD",
"cookie-test4": "你好",
"httponly-cookie": "httponly-value"
},
"bigint": 248963637882912768
}定义测试用例:
apt.assert('response.raw.status==200');
apt.assert('response.raw.type=="json"');
apt.assert('response.json.errcode==0');
apt.assert('response.raw.responseTime<100');
apt.assert('response.json.header.Host=="echo.Apipost.cn"');点击发送按钮后:
绿色表示测试通过,红色表示测试不通过。特别注意:==每个测试用例是一行,不能换行。==
例:apt.assert('response.json.header.Host=="echo.Apipost.cn"');
1)response.json.header.Host 表示响应json下面的header数组中的Host字段,
2)必须都为1,才会通过。
常见的测试用例可以通过后执行脚本获取:
使用 Apipost 的断言格式
// 检查response body中是否包含某个string
apt.assert('response.raw.responseText=="test"'); // 检查响应文本是否等于test字符串
apt.assert('response.raw.responseText.indexOf("test") > -1'); // 检查响应文本是否含有test字符串
// 检测返回JSON中的某个值是否等于预期的值
apt.assert('response.json.hasOwnProperty("errcode")'); // 检测返回json对象的是否含有errcode字段
apt.assert('response.json.errcode=="success"'); // 检测返回json对象的errcode字段是否等于success字符串
apt.assert('response.json.errcode.indexOf("success") > -1'); // 检测返回json对象的errcode字段是否含有success字符串
apt.assert('response.json.errcode!="success"'); // 检测返回json对象的errcode字段是否不等于success字符串
apt.assert('response.json.errcode>=1'); // 检测返回json对象的errcode字段是否大于1
apt.assert('response.json.errcode==null'); // 检测返回json对象的errcode字段是否是null
// 测试response Headers中的某个元素是否存在(如:Content-Type)
apt.assert('response.headers.hasOwnProperty("content-type")');
// 验证Status code(响应码)的值是不是等于200
apt.assert('response.raw.status==200');
// 验证Response time(请求耗时)是否大于某个值
apt.assert('response.raw.responseTime>=100');使用 Postman 的断言格式
自 Apipost 7 版本起,已完全兼容 Postman 格式的断言语法,低版本的需要升级至最新版。
测试脚本示例
hello word! 第一个测试脚本
要编写您的第一个测试脚本,请在 Apipost 中打开一个请求,然后选择“后执行脚本”选项卡。输入以下 JavaScript 代码:
apt.test("响应码为 200", function () {
apt.response.to.have.status(200);
});此测试检查 API 返回的响应代码。如果响应代码是200,则测试将通过,否则将失败。选择发送并转到响应区域中的断言与校验选项卡。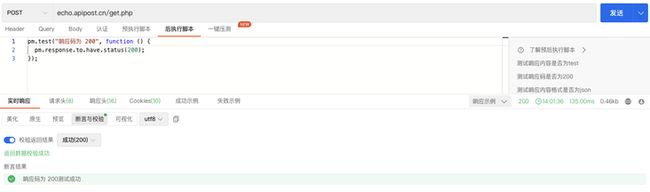
以多种方式构建您的测试断言,以适应您对结果输出方式的逻辑和偏好。以下代码是使用expect语法实现与上述代码相同测试的另一种方法:
apt.test("Status code is 200", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.code).to.eql(200);
});使用多个断言您的测试可以包含多个断言作为单个测试的一部分。使用它来将相关的断言组合在一起:
apt.test("The response has all properties", () => {
//parse the response JSON and test three properties
const responseJson = apt.response.json;
apt.expect(responseJson.type).to.eql('vip');
apt.expect(responseJson.name).to.be.a('string');
apt.expect(responseJson.id).to.have.lengthOf(1);
});如果包含的任何断言失败,则整个测试将失败。所有断言都必须成功才能使测试通过。
解析响应体数据
要对您的响应执行断言,您首先需要将数据解析为您的断言可以使用的 JavaScript 对象。
要解析 JSON 数据,请使用以下语法:const responseJson = apt.response.json;
要解析 XML,请使用以下内容:
const responseJson = xml2Json(apt.response.text());要解析 CSV,请使用CSV 解析实用程序:
const responseJson = csv2array(apt.response.text());处理不解析的响应
如果您无法将响应正文解析为 JavaScript,因为它的格式不是 JSON、XML、HTML、CSV 或任何其他可解析的数据格式,您仍然可以对数据进行断言。
测试响应主体是否包含字符串:
apt.test("Body contains string",() => {
apt.expect(apt.response.text()).to.include("customer_id");
});这不会告诉您遇到字符串的位置,因为它是对整个响应主体进行测试。测试响应是否与字符串匹配(通常只对短响应有效):
apt.test("Body is string", function () {
apt.response.to.have.body("whole-body-text");
});对 HTTP 响应进行断言
您的测试可以检查请求响应的各个方面,包括body、status codes、headers、cookies、response times等等。测试响应体检查响应正文中的特定值:
apt.test("Person is Jane", () => {
const responseJson = apt.response.json;
apt.expect(responseJson.name).to.eql("Jane");
apt.expect(responseJson.age).to.eql(23);
});测试状态码测试响应状态码:
apt.test("Status code is 201", () => {
apt.response.to.have.status(201);
});如果你想测试状态代码是否是一组中的一个,请将它们全部包含在一个数组中并使用oneOf:
apt.test("Successful POST request", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.code).to.be.oneOf([201,202]);
});查看状态码文本:
apt.test("Status code name has string", () => {
apt.response.to.have.status("Created");
});测试标头检查是否存在响应标头:
apt.test("Content-Type header is present", () => {
apt.response.to.have.header("Content-Type");
});测试具有特定值的响应标头:
apt.test("Content-Type header is application/json", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.headers['Content-Type']).to.eql('application/json');
});测试 cookie测试响应中是否存在 cookie:
apt.test("Cookie JSESSIONID is present", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.cookies['cookie-test1']).to.not.be.undefined;
});测试特定的 cookie 值:
apt.test("Cookie isLoggedIn has value 1", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.cookies['cookie-test1']).to.eql('0');
});测试响应时间测试响应时间是否在指定范围内:
apt.test("Response time is less than 200ms", () => {
apt.expect(apt.response.responseTime).to.be.below(200);
});apt.response.to.be.*
apt.response.to.be 是用来快速断言的一系列内置规则。apt.response.to.be.info
检查状态码是否为1XXapt.response.to.be.success
检查状态码是否为2XXapt.response.to.be.redirection
检查状态码是否为3XXapt.response.to.be.clientError
检查状态码是否为4XXapt.response.to.be.serverError
检查状态码是否为5XXapt.response.to.be.error
检查状态码是否为4XX或5XXapt.response.to.be.ok
检查状态码是否为200apt.response.to.be.accepted
检查状态码是否为202apt.response.to.be.badRequest
检查状态码是否为400apt.response.to.be.unauthorized
检查状态码是否为401apt.response.to.be.forbidden
检查状态码是否为403apt.response.to.be.notFound
检查状态码是否为404apt.response.to.be.rateLimited
检查状态码是否为429