TensorRT 系列 (0)C++ API 构建编译网络
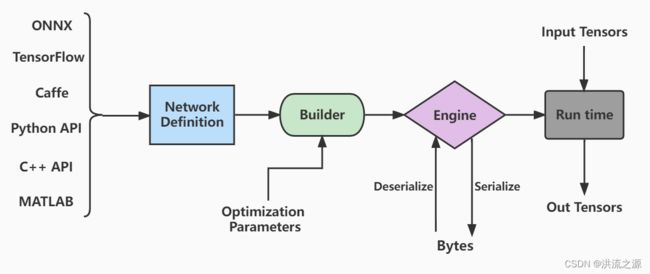
TensorRT的核心在于对模型算子的优化(合并算子、利用GPU特性选择特定核函数等多种策略),通过tensorRT,能够在Nvidia系列GPU上获得最好的性能,因此tensorRT的模型需要在目标GPU上实际运行的方式选择最优算法和配置,也因此tensorRT生成的模型只能在特定条件下运行(依赖于编译的trt版本、cuda版本、编译时的GPU型号)。TensorRT提供的C++、Python接口用于直接构建网络结构,本次主要介绍C++接口实现网络的构建与模型的编译,当然TensorRT也可以实现由其它框架的模型直接进行转换,如下是TensorRT工作流:
示例代码如下:
// tensorRT include
#include
#include
// cuda include
#include
// system include
#include
class TRTLogger : public nvinfer1::ILogger{
public:
virtual void log(Severity severity, nvinfer1::AsciiChar const* msg) noexcept override{
if(severity <= Severity::kVERBOSE){
printf("%d: %s\n", severity, msg);
}
}
};
nvinfer1::Weights make_weights(float* ptr, int n){
nvinfer1::Weights w;
w.count = n;
w.type = nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT;
w.values = ptr;
return w;
}
int main(){
// 本代码主要实现一个最简单的神经网络
TRTLogger logger; // logger是必要的,用来捕捉warning和info等
// ----------------------------- 1. 定义 builder, config 和network -----------------------------
// 这是基本需要的组件
//形象的理解是你需要一个builder去build这个网络
nvinfer1::IBuilder* builder = nvinfer1::createInferBuilder(logger);
// 创建一个构建配置,指定TensorRT应该如何优化模型,tensorRT生成的模型只能在特定配置下运行
nvinfer1::IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig();
// 创建网络定义,其中createNetworkV2(1)表示采用显性batch size,新版tensorRT(>=7.0)时,不建议采用0非显性batch size
// 因此贯穿以后,请都采用createNetworkV2(1)而非createNetworkV2(0)或者createNetwork
nvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(1);
// 构建一个模型
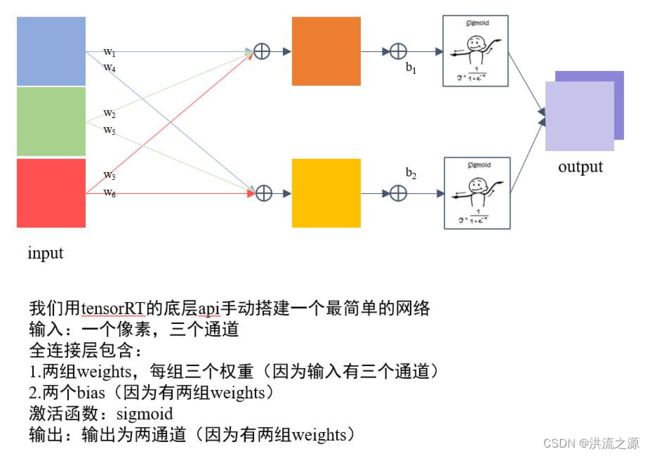
/*
Network definition:
image
|
linear (fully connected) input = 3, output = 2, bias = True w=[[1.0, 2.0, 0.5], [0.1, 0.2, 0.5]], b=[0.3, 0.8]
|
sigmoid
|
prob
*/
// ----------------------------- 2. 输入,模型结构和输出的基本信息 -----------------------------
const int num_input = 3; // in_channel
const int num_output = 2; // out_channel
float layer1_weight_values[] = {1.0, 2.0, 0.5, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5}; // 前3个给w1的rgb,后3个给w2的rgb
float layer1_bias_values[] = {0.3, 0.8};
//输入指定数据的名称、数据类型和完整维度,将输入层添加到网络
nvinfer1::ITensor* input = network->addInput("image", nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nvinfer1::Dims4(1, num_input, 1, 1));
nvinfer1::Weights layer1_weight = make_weights(layer1_weight_values, 6);
nvinfer1::Weights layer1_bias = make_weights(layer1_bias_values, 2);
//添加全连接层
auto layer1 = network->addFullyConnected(*input, num_output, layer1_weight, layer1_bias); // 注意对input进行了解引用
//添加激活层
auto prob = network->addActivation(*layer1->getOutput(0), nvinfer1::ActivationType::kSIGMOID); // 注意更严谨的写法是*(layer1->getOutput(0)) 即对getOutput返回的指针进行解引用
// 将我们需要的prob标记为输出
network->markOutput(*prob->getOutput(0));
printf("Workspace Size = %.2f MB\n", (1 << 28) / 1024.0f / 1024.0f); // 256Mib
config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 28);
builder->setMaxBatchSize(1); // 推理时 batchSize = 1
// ----------------------------- 3. 生成engine模型文件 -----------------------------
//TensorRT 7.1.0版本已弃用buildCudaEngine方法,统一使用buildEngineWithConfig方法
nvinfer1::ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config);
if(engine == nullptr){
printf("Build engine failed.\n");
return -1;
}
// ----------------------------- 4. 序列化模型文件并存储 -----------------------------
// 将模型序列化,并储存为文件
nvinfer1::IHostMemory* model_data = engine->serialize();
FILE* f = fopen("engine.trtmodel", "wb");
fwrite(model_data->data(), 1, model_data->size(), f);
fclose(f);
// 卸载顺序按照构建顺序倒序
model_data->destroy();
engine->destroy();
network->destroy();
config->destroy();
builder->destroy();
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
} Makefile :
cc := g++
name := pro
workdir := workspace
srcdir := src
objdir := objs
stdcpp := c++11
cuda_home := /home/liuhongyuan/miniconda3/envs/trtpy/lib/python3.8/site-packages/trtpy/trt8cuda112cudnn8
syslib := /home/liuhongyuan/miniconda3/envs/trtpy/lib/python3.8/site-packages/trtpy/lib
cpp_pkg := /home/liuhongyuan/miniconda3/envs/trtpy/lib/python3.8/site-packages/trtpy/cpp-packages
cuda_arch :=
nvcc := $(cuda_home)/bin/nvcc -ccbin=$(cc)
# 定义cpp的路径查找和依赖项mk文件
cpp_srcs := $(shell find $(srcdir) -name "*.cpp")
cpp_objs := $(cpp_srcs:.cpp=.cpp.o)
cpp_objs := $(cpp_objs:$(srcdir)/%=$(objdir)/%)
cpp_mk := $(cpp_objs:.cpp.o=.cpp.mk)
# 定义cu文件的路径查找和依赖项mk文件
cu_srcs := $(shell find $(srcdir) -name "*.cu")
cu_objs := $(cu_srcs:.cu=.cu.o)
cu_objs := $(cu_objs:$(srcdir)/%=$(objdir)/%)
cu_mk := $(cu_objs:.cu.o=.cu.mk)
# 定义opencv和cuda需要用到的库文件
link_cuda := cudart cudnn
link_trtpro :=
link_tensorRT := nvinfer
link_opencv :=
link_sys := stdc++ dl
link_librarys := $(link_cuda) $(link_tensorRT) $(link_sys) $(link_opencv)
# 定义头文件路径,请注意斜杠后边不能有空格
# 只需要写路径,不需要写-I
include_paths := src \
$(cuda_home)/include/cuda \
$(cuda_home)/include/tensorRT \
$(cpp_pkg)/opencv4.2/include
# 定义库文件路径,只需要写路径,不需要写-L
library_paths := $(cuda_home)/lib64 $(syslib) $(cpp_pkg)/opencv4.2/lib
# 把library path给拼接为一个字符串,例如a b c => a:b:c
# 然后使得LD_LIBRARY_PATH=a:b:c
empty :=
library_path_export := $(subst $(empty) $(empty),:,$(library_paths))
# 把库路径和头文件路径拼接起来成一个,批量自动加-I、-L、-l
run_paths := $(foreach item,$(library_paths),-Wl,-rpath=$(item))
include_paths := $(foreach item,$(include_paths),-I$(item))
library_paths := $(foreach item,$(library_paths),-L$(item))
link_librarys := $(foreach item,$(link_librarys),-l$(item))
# 如果是其他显卡,请修改-gencode=arch=compute_75,code=sm_75为对应显卡的能力
# 显卡对应的号码参考这里:https://developer.nvidia.com/zh-cn/cuda-gpus#compute
# 如果是 jetson nano,提示找不到-m64指令,请删掉 -m64选项。不影响结果
cpp_compile_flags := -std=$(stdcpp) -w -g -O0 -m64 -fPIC -fopenmp -pthread
cu_compile_flags := -std=$(stdcpp) -w -g -O0 -m64 $(cuda_arch) -Xcompiler "$(cpp_compile_flags)"
link_flags := -pthread -fopenmp -Wl,-rpath='$$ORIGIN'
cpp_compile_flags += $(include_paths)
cu_compile_flags += $(include_paths)
link_flags += $(library_paths) $(link_librarys) $(run_paths)
# 如果头文件修改了,这里的指令可以让他自动编译依赖的cpp或者cu文件
ifneq ($(MAKECMDGOALS), clean)
-include $(cpp_mk) $(cu_mk)
endif
$(name) : $(workdir)/$(name)
all : $(name)
run : $(name)
@cd $(workdir) && ./$(name) $(run_args)
$(workdir)/$(name) : $(cpp_objs) $(cu_objs)
@echo Link $@
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(cc) $^ -o $@ $(link_flags)
$(objdir)/%.cpp.o : $(srcdir)/%.cpp
@echo Compile CXX $<
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(cc) -c $< -o $@ $(cpp_compile_flags)
$(objdir)/%.cu.o : $(srcdir)/%.cu
@echo Compile CUDA $<
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(nvcc) -c $< -o $@ $(cu_compile_flags)
# 编译cpp依赖项,生成mk文件
$(objdir)/%.cpp.mk : $(srcdir)/%.cpp
@echo Compile depends C++ $<
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(cc) -M $< -MF $@ -MT $(@:.cpp.mk=.cpp.o) $(cpp_compile_flags)
# 编译cu文件的依赖项,生成cumk文件
$(objdir)/%.cu.mk : $(srcdir)/%.cu
@echo Compile depends CUDA $<
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(nvcc) -M $< -MF $@ -MT $(@:.cu.mk=.cu.o) $(cu_compile_flags)
# 定义清理指令
clean :
@rm -rf $(objdir) $(workdir)/$(name) $(workdir)/*.trtmodel
# 防止符号被当做文件
.PHONY : clean run $(name)
# 导出依赖库路径,使得能够运行起来
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH:=$(library_path_export)执行make run可编译运行代码。