Tensorflow框架:InceptionV3网络概念及实现
卷积神经网络迁移学习-Inception
• 有论文依据表明可以保留训练好的inception模型中所有卷积层的参数,只替换最后一层全连接层。在最后 这一层全连接层之前的网络称为瓶颈层。
• 原理:在训练好的inception模型中,因为将瓶颈层的输出再通过一个单层的全连接层,神经网络可以很好 的区分1000种类别的图像,所以可以认为瓶颈层输出的节点向量可以被作为任何图像的一个更具有表达能 力的特征向量。于是在新的数据集上可以直接利用这个训练好的神经网络对图像进行特征提取,然后将提 取得到的特征向量作为输入来训练一个全新的单层全连接神经网络处理新的分类问题。
• 一般来说在数据量足够的情况下,迁移学习的效果不如完全重新训练。但是迁移学习所需要的训练时间和 训练样本要远远小于训练完整的模型。
• 这其中说到inception模型,其实它是和Alexnet结构完全不同的卷积神经网络。在Alexnet模型中,不同卷积 层通过串联的方式连接在一起,而inception模型中的inception结构是将不同的卷积层通过并联的方式结合 在一起
Inception
Inception 网络是 CNN 发展史上一个重要的里程碑。在 Inception 出现之前,大部分流行 CNN 仅仅是把卷积层堆叠得越来越多,使网络越来越深,以此希望能够得到更好的性能。但是存 在以下问题:
- 图像中突出部分的大小差别很大。
- 由于信息位置的巨大差异,为卷积操作选择合适的卷积核大小就比较困难。信息分布更全局性的图像偏好较大的卷积核,信息分布比较局部的图像偏好较小的卷积核。
- 非常深的网络更容易过拟合。将梯度更新传输到整个网络是很困难的。
- 简单地堆叠较大的卷积层非常消耗计算资源。

狗在各个图片的占比不同~可能想要得到的部分在图中占比很小。
Inception module
解决方案:
为什么不在同一层级上运行具备多个尺寸的滤波器呢?网络本质上会变得稍微「宽一些」,而不是 「更深」。
作者因此设计了 Inception 模块。
Inception 模块( Inception module ):
它使用 3 个不同大小的滤波器(1x1、3x3、5x5)对输入执 行卷积操作,此外它还会执行最大池化。所有子层的输出最后会被级联起来,并传送至下一个 Inception 模块。 一方面增加了网络的宽度,另一方面增加了网络对尺度的适应性

实现降维的 Inception 模块:
如前所述,深度神经网络需要耗费大量计算资源。为了降低算力成 本,作者在 3x3 和 5x5 卷积层之前添加额外的 1x1 卷积层,来限制输入通道的数量。尽管添加额 外的卷积操作似乎是反直觉的,但是 1x1 卷积比 5x5 卷积要廉价很多,而且输入通道数量减少也 有利于降低算力成本。

InceptionV1–Googlenet
V1改进版–InceptionV2
改进一:
Inception V2 在输入的时候增加了BatchNormalization:
• 所有输出保证在0~1之间。
• 所有输出数据的均值接近0,标准差接近1的正太分布。使其落入激活函数的敏感区,避免梯度 消失,加快收敛。 • 加快模型收敛速度,并且具有一定的泛化能力。
• 可以减少dropout的使用。


改进二:
• 作者提出可以用2个连续的3x3卷积层(stride=1)组成的小网络来代替单个的5x5卷积 层,这便是Inception V2结构。
• 5x5卷积核参数是3x3卷积核的25/9=2.78倍。
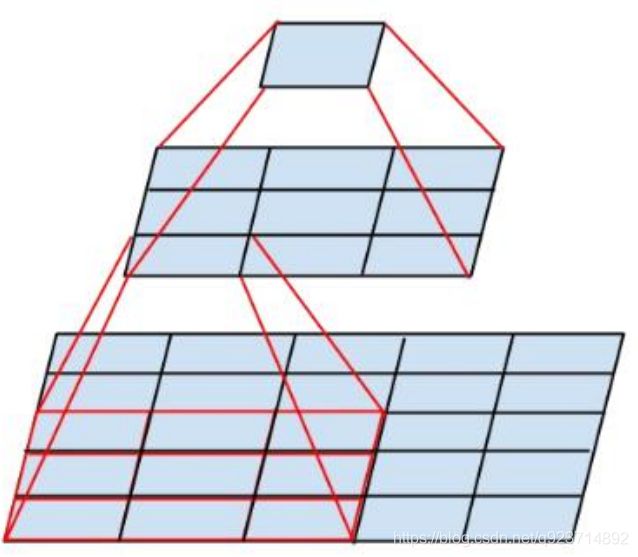

改进三:
此外,作者将 n*n 的卷积核尺寸分解为 1×n 和 n×1 两个卷积。

前面三个原则用来构建三种不同类型 的 Inception 模块。
V2改进版–InceptionV3
改进:
InceptionV3 整合了前面 Inception v2 中提到的所有升级,还使用了7x7 卷积
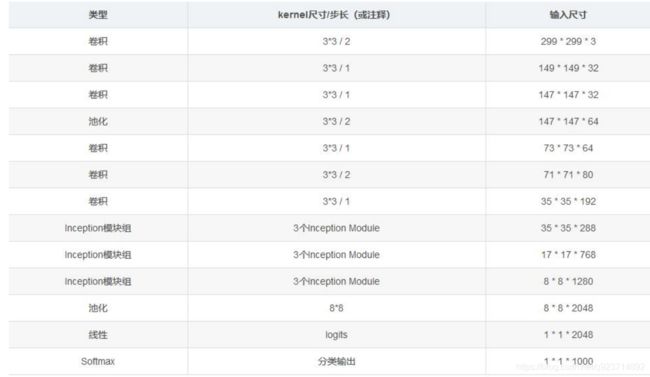
思想和Trick:
Inception V3设计思想和Trick:
(1)分解成小卷积很有效,可以降低参数量,减轻过拟合,增加网络非线性的表达能力。
(2)卷积网络从输入到输出,应该让图片尺寸逐渐减小,输出通道数逐渐增加,即让空间结 构化,将空间信息转化为高阶抽象的特征信息。
(3)Inception Module用多个分支提取不同抽象程度的高阶特征的思路很有效,可以丰富网络 的表达能力
InceptionV3代码实现
网络部分:
#-------------------------------------------------------------#
# InceptionV3的网络部分
#-------------------------------------------------------------#
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import absolute_import
import warnings
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Model
from keras import layers
from keras.layers import Activation,Dense,Input,BatchNormalization,Conv2D,MaxPooling2D,AveragePooling2D
from keras.layers import GlobalAveragePooling2D,GlobalMaxPooling2D
from keras.engine.topology import get_source_inputs
from keras.utils.layer_utils import convert_all_kernels_in_model
from keras.utils.data_utils import get_file
from keras import backend as K
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import decode_predictions
from keras.preprocessing import image
def conv2d_bn(x,
filters,
num_row,
num_col,
strides=(1, 1),
padding='same',
name=None):
if name is not None:
bn_name = name + '_bn'
conv_name = name + '_conv'
else:
bn_name = None
conv_name = None
x = Conv2D(
filters, (num_row, num_col),
strides=strides,
padding=padding,
use_bias=False,
name=conv_name)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(scale=False, name=bn_name)(x)
x = Activation('relu', name=name)(x)
return x
def InceptionV3(input_shape=[299,299,3],
classes=1000):
img_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
x = conv2d_bn(img_input, 32, 3, 3, strides=(2, 2), padding='valid')
x = conv2d_bn(x, 32, 3, 3, padding='valid')
x = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 3, 3)
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x)
x = conv2d_bn(x, 80, 1, 1, padding='valid')
x = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 3, 3, padding='valid')
x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x)
#--------------------------------#
# Block1 35x35
#--------------------------------#
# Block1 part1
# 35 x 35 x 192 -> 35 x 35 x 256
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(x, 48, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(branch5x5, 64, 5, 5)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D((3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 32, 1, 1)
# 64+64+96+32 = 256
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch5x5, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed0')
# Block1 part2
# 35 x 35 x 256 -> 35 x 35 x 288
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(x, 48, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(branch5x5, 64, 5, 5)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D((3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 64, 1, 1)
# 64+64+96+64 = 288
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch5x5, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed1')
# Block1 part3
# 35 x 35 x 288 -> 35 x 35 x 288
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(x, 48, 1, 1)
branch5x5 = conv2d_bn(branch5x5, 64, 5, 5)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D((3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 64, 1, 1)
# 64+64+96+64 = 288
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch5x5, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed2')
#--------------------------------#
# Block2 17x17
#--------------------------------#
# Block2 part1
# 35 x 35 x 288 -> 17 x 17 x 768
branch3x3 = conv2d_bn(x, 384, 3, 3, strides=(2, 2), padding='valid')
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 64, 1, 1)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(
branch3x3dbl, 96, 3, 3, strides=(2, 2), padding='valid')
branch_pool = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch3x3, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool], axis=3, name='mixed3')
# Block2 part2
# 17 x 17 x 768 -> 17 x 17 x 768
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(x, 128, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 128, 1, 7)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 128, 1, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 128, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 128, 1, 7)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 128, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 1, 7)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D((3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 192, 1, 1)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch7x7, branch7x7dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed4')
# Block2 part3 and part4
# 17 x 17 x 768 -> 17 x 17 x 768 -> 17 x 17 x 768
for i in range(2):
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(x, 160, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 160, 1, 7)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 160, 1, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 160, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 160, 1, 7)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 160, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 1, 7)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D(
(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 192, 1, 1)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch7x7, branch7x7dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed' + str(5 + i))
# Block2 part5
# 17 x 17 x 768 -> 17 x 17 x 768
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 192, 1, 7)
branch7x7 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 1, 7)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7dbl = conv2d_bn(branch7x7dbl, 192, 1, 7)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D((3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 192, 1, 1)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch7x7, branch7x7dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed7')
#--------------------------------#
# Block3 8x8
#--------------------------------#
# Block3 part1
# 17 x 17 x 768 -> 8 x 8 x 1280
branch3x3 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch3x3 = conv2d_bn(branch3x3, 320, 3, 3,
strides=(2, 2), padding='valid')
branch7x7x3 = conv2d_bn(x, 192, 1, 1)
branch7x7x3 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7x3, 192, 1, 7)
branch7x7x3 = conv2d_bn(branch7x7x3, 192, 7, 1)
branch7x7x3 = conv2d_bn(
branch7x7x3, 192, 3, 3, strides=(2, 2), padding='valid')
branch_pool = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch3x3, branch7x7x3, branch_pool], axis=3, name='mixed8')
# Block3 part2 part3
# 8 x 8 x 1280 -> 8 x 8 x 2048 -> 8 x 8 x 2048
for i in range(2):
branch1x1 = conv2d_bn(x, 320, 1, 1)
branch3x3 = conv2d_bn(x, 384, 1, 1)
branch3x3_1 = conv2d_bn(branch3x3, 384, 1, 3)
branch3x3_2 = conv2d_bn(branch3x3, 384, 3, 1)
branch3x3 = layers.concatenate(
[branch3x3_1, branch3x3_2], axis=3, name='mixed9_' + str(i))
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(x, 448, 1, 1)
branch3x3dbl = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 384, 3, 3)
branch3x3dbl_1 = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 384, 1, 3)
branch3x3dbl_2 = conv2d_bn(branch3x3dbl, 384, 3, 1)
branch3x3dbl = layers.concatenate(
[branch3x3dbl_1, branch3x3dbl_2], axis=3)
branch_pool = AveragePooling2D(
(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')(x)
branch_pool = conv2d_bn(branch_pool, 192, 1, 1)
x = layers.concatenate(
[branch1x1, branch3x3, branch3x3dbl, branch_pool],
axis=3,
name='mixed' + str(9 + i))
# 平均池化后全连接。
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D(name='avg_pool')(x)
x = Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x)
inputs = img_input
model = Model(inputs, x, name='inception_v3')
return model
def preprocess_input(x):
x /= 255.
x -= 0.5
x *= 2.
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = InceptionV3()
model.load_weights("inception_v3_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5")
img_path = 'elephant.jpg'
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(299, 299))
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
preds = model.predict(x)
print('Predicted:', decode_predictions(preds))
Inception模型优势:
- 采用了1x1卷积核,性价比高,用很少的计算量既可以增加一层的特征变换和非线性变换。
- 提出Batch Normalization,通过一定的手段,把每层神经元的输入值分布拉到均值0方差1 的正态分布,使其落入激活函数的敏感区,避免梯度消失,加快收敛。
- 引入Inception module,4个分支结合的结构。

