c#: NetTopologySuite凹凸多边形计算
环境:
- .net 6.0
- NetTopologySuite 2.5.0
- vs2022
- 平面二维
一、夹角计算
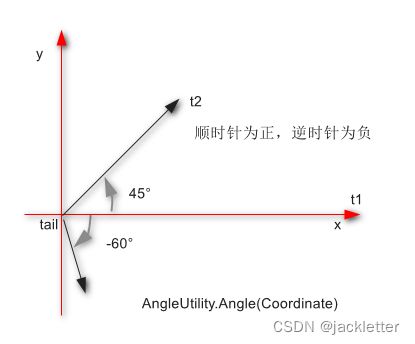
1.1 计算向量与x轴正方向的夹角
方法: AngleUtility.Angle(Coordinate p)
下图上的t2即为p,之所以这么写是为了和
AngleUtility.AngleBetweenOriented做比较
注意:
- 结果逆时针为正,顺时针为负;
- 相对于x轴;
1.2 计算两条线段的夹角(区分方向)
方法: AngleUtility.AngleBetweenOriented(Coordinate tip1, Coordinate tail, Coordinate tip2)
注意:
- 结果逆时针为正,顺时针为负;
- ∠t1 tail t2;
1.3 计算两条线段的夹角(不区分方向)
方法: AngleUtility.AngleBetween(Coordinate tip1, Coordinate tail, Coordinate tip2)
由于不考虑方向,两个线段的夹角总是处在 [0,180°) 范围内。
不在画图显示。
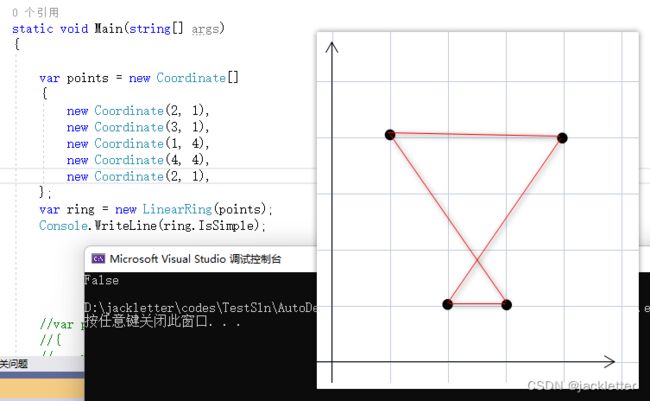
二、检测一个环是否是简单的(IsSimple)
2.1 简单的示例(IsSimple=true):
2.2 复杂的示例(IsSimple=false,自相交):
三、多边形的凹凸(convex/concave) 和 顺(Clockwise)/逆(CounterClockwise)时针
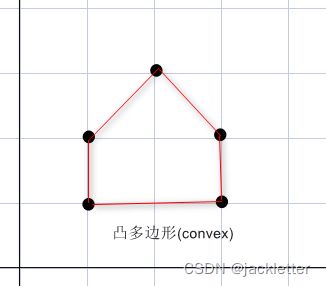
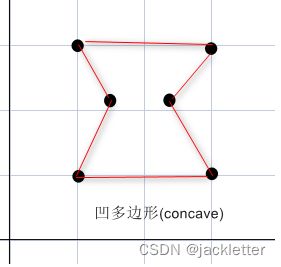
3.1 多边形的凹凸定义:
凸多边形(convex): 所有的内角都小于180°;
凹多边形(concave): 至少有一个内角大于180°;
3.2 多边形的顺逆时针
因为多边形是一个环状的东西,所以在平面上可以用顺逆时针表示它的方向,这在很多计算方法中有用。
多边形的方向应该是整体来看,单看局部点位是无法判断的,如下(仅凭下面三黑点两个红线是判断不出来的):

判断方法,NetTopologySuite已提供,对于上图判断示例如下:

3.3 计算多边形的各个内角值(判断凹凸性)
计算内角,我们可以使用NetTopologySuite的方法:AngleBetweenOriented,这里我们需要按照点位顺序计算。
比如:p1、p2、p3、p4、p5
那么,计算点p2的内角为:∠p1p2p3,再结合多边形的方向(顺逆时针),将它转为(0,360)范围内。
由此可得计算的方法,如下:
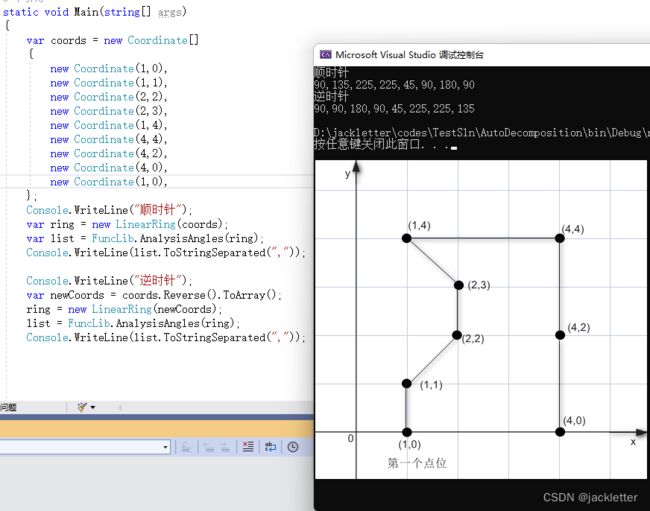
public static class FuncLib
{
public static List<double> AnalysisAngles(LinearRing ring)
{
if (ring == null || !ring.IsSimple) throw new Exception($"数据错误!");
var angels = new List<double>();
for (int i = 0, len = ring.Coordinates.Length - 1; i < len; i++)
{
var tail = ring[i];
var t2 = ring[(i + 1) % len];
var t1 = ring[(i - 1 + len) % len];
var angle = AngleUtility.AngleBetweenOriented(t1, tail, t2);
var angleDegree = AngleUtility.ToDegrees(angle);
if (ring.IsCCW)
{
//逆时针
if (angle > 0)
{
//concave
angleDegree = 360 - angleDegree;
}
else if (angle < 0)
{
//convex
angleDegree = -angleDegree;
}
else
{
//等于0 平行
angleDegree = 180;
}
}
else
{
//顺时针
if (angle < 0)
{
//concave
angleDegree = angleDegree + 360;
}
else if (angle > 0)
{
//convex
}
else
{
//等于0 平行
angleDegree = 180;
}
}
angels.Add(angleDegree);
}
return angels;
}
}
四、多边形边法线方向计算方法
这里说的多边形是简单多边形,不能是自相交的。
4.1 明确计算任务
4.2 计算思路
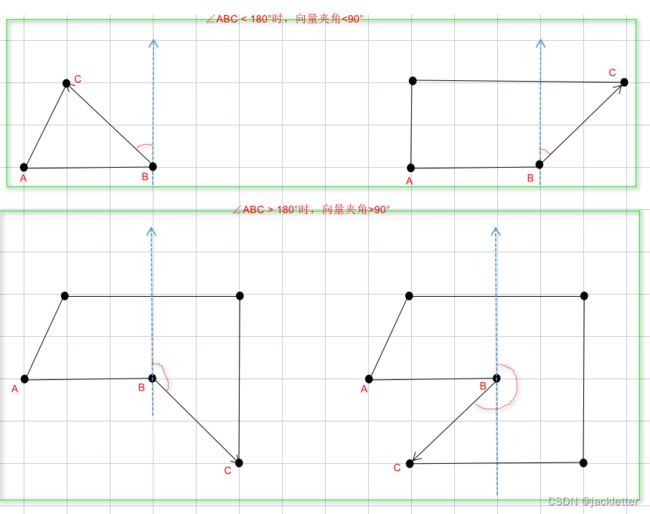
直接看下面几种情况示例:
由此,可以初步得出结论:
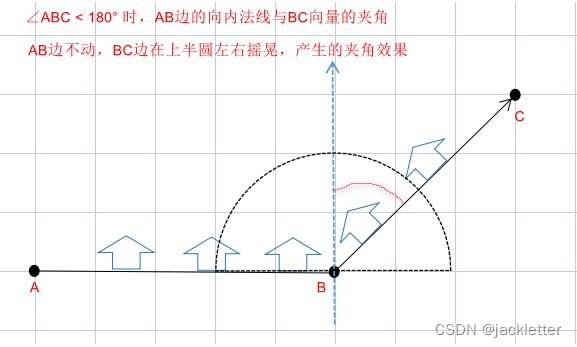
- 当∠ABC < 180° 时,AB边的法向向量方向与BC向量的夹角小于90°
- 当∠ABC > 180° 时,AB边的法向向量方向与BC向量的夹角大于90°
再考虑边界情况:
- 当∠ABC=180°,即三点共线时,因为BC边两个法向量与BC向量的夹角都是90°,所以改为计算BC的法向向量,以此后推,不可能所有的点都共线嘛;
- 当∠ABC=90°时,两向量夹角=0°;
- 当∠ABC=270°时,两向量夹角=180°;
- ∠ABC=0°或360°就不考虑了吧。。。
4.3 计算方法实现
public static List<Vector2D> AnalysisNormals(LinearRing ring)
{
if (ring == null || !ring.IsSimple) throw new Exception($"数据错误!");
//先算出内角(上面的算法)
var angels = AnalysisAngles(ring);
var normals = new List<Vector2D>();
var remainIndex = new List<int>();
var len = ring.Coordinates.Length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
var curIndex = i;
var nextIndex = (curIndex + 1) % len;
var next2Index = (curIndex + 2) % len;
var curP = ring[curIndex];
var rightP = ring[nextIndex];
var nextP = ring[next2Index];
var nextNormal = new Vector2D(rightP, nextP).Normalize();
var curNormal = new Vector2D(curP, rightP).Normalize();
var nextAngel = angels[nextIndex];
var normal1 = curNormal.Rotate(AngleUtility.ToRadians(90));
var normal2 = curNormal.Rotate(AngleUtility.ToRadians(-90));
var angel = AngleUtility.AngleBetween(new Coordinate(normal1.X, normal1.Y), new Coordinate(0, 0), new Coordinate(nextNormal.X, nextNormal.Y));
var angleDegree = AngleUtility.ToDegrees(angel);
if (nextAngel < 180)
{
if (angleDegree < 90) normals.Add(normal1);
else normals.Add(normal2);
}
else if (nextAngel > 180)
{
if (angleDegree > 90) normals.Add(normal1);
else normals.Add(normal2);
}
else
{
//等于180 三点共线
normals.Add(new Vector2D(0, 0));
remainIndex.Add(curIndex);
}
}
if (remainIndex.Count > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < remainIndex.Count; i++)
{
var curIndex = remainIndex[i];
var nextIndex = (curIndex + 1) % len;
var next2Index = (curIndex + 2) % len;
var end = nextIndex;
var t = next2Index;
while (t != end)
{
if (angels[t] != 180)
{
normals[curIndex] = normals[(t - 1 + len) % len];
break;
}
else
{
t++;
t = t % len;
}
}
}
}
return normals;
}
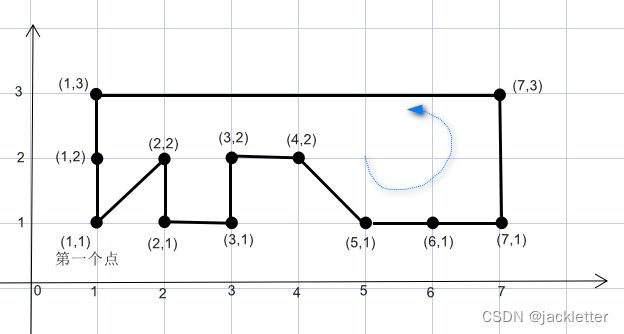
var normals = FuncLib.AnalysisNormals(new LinearRing(new[]
{
new Coordinate(1, 1),
new Coordinate(2, 2),
new Coordinate(2, 1),
new Coordinate(3, 1),
new Coordinate(3, 2),
new Coordinate(4, 2),
new Coordinate(5, 1),
new Coordinate(6, 1),
new Coordinate(7, 1),
new Coordinate(7, 3),
new Coordinate(1, 3),
new Coordinate(1, 2),
new Coordinate(1, 1),
}));
//四舍五入,长为1.4,让xy均为1,易读
for (int i = 0; i < normals.Count; i++)
{
normals[i] = normals[i] / 1.414 * 2;
normals[i] = new Vector2D(Math.Round(normals[i].X) + 0, Math.Round(normals[i].Y) + 0);
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", normals.Select(i => $"({i.X},{i.Y})")));