初级算法-链表
主要记录算法和数据结构学习笔记,新的一年更上一层楼!
初级算法-链表
- 一、移除链表元素
- 二、设计链表
- 三、反转链表
- 四、两两交换链表的结点
- 五、删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 六、链表相交
- 七、环形链表2
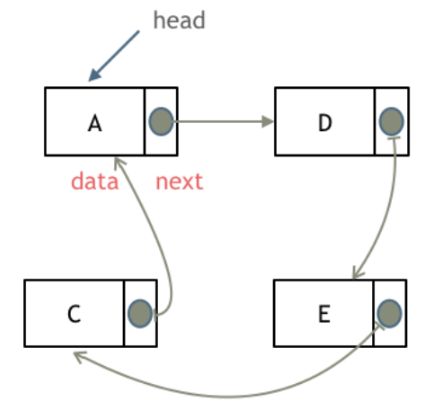
链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向null(空指针的意思)。
- 链表适用于顺序查找
- 二分查找:表必须有序,按关键字,大小有序排列
- 顺序查找在顺序线性表还是链式中时间复杂度都为O(n)
- 递归表>再入表>纯表>线性表
- 字典可采用线性表、散列表、跳表组织方式
- 线性表存在唯一的被称为“第一个”的数据元素,除第一个元素外,集合中的每个数据元素均只有一个直接前驱

单链表

双链表

循环链表 解决约瑟夫环

一、移除链表元素
1.题目:给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例1:

输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
提示:
1.列表中的节点数目在范围 [0, 104] 内。
2.1 <= Node.val <= 50。
3.0 <= val <= 50。
2.解题思路:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} val
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeElements = function(head, val) {
//初始化一个空节点,初始赋值为0,并且ret的下一个next指针指向head,指针指向为ret
const ret = new ListNode(0, head);
let cur = ret;
while(cur.next) {
if(cur.next.val === val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
continue;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return ret.next;
};
// 运行时间:80ms
// 内存消耗:45.6MB
二、设计链表
1.题目:在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
- addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
- addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
- addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
- deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
class LinkNode {
constructor(val, next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
* 单链表 储存头尾节点 和 节点数量
*/
var MyLinkedList = function() {
this._size = 0;
this._tail = null;
this._head = null;
};
/**
* Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1.
* @param {number} index
* @return {number}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.getNode = function(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return null;
// 创建虚拟头节点
let cur = new LinkNode(0, this._head);
// 0 -> head
while(index-- >= 0) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
};
MyLinkedList.prototype.get = function(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return -1;
// 获取当前节点
return this.getNode(index).val;
};
/**
* Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list.
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtHead = function(val) {
const node = new LinkNode(val, this._head);
this._head = node;
this._size++;
if(!this._tail) {
this._tail = node;
}
};
/**
* Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list.
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtTail = function(val) {
const node = new LinkNode(val, null);
this._size++;
if(this._tail) {
this._tail.next = node;
this._tail = node;
return;
}
this._tail = node;
this._head = node;
};
/**
* Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted.
* @param {number} index
* @param {number} val
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtIndex = function(index, val) {
if(index > this._size) return;
if(index <= 0) {
this.addAtHead(val);
return;
}
if(index === this._size) {
this.addAtTail(val);
return;
}
// 获取目标节点的上一个的节点
const node = this.getNode(index - 1);
node.next = new LinkNode(val, node.next);
this._size++;
};
/**
* Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid.
* @param {number} index
* @return {void}
*/
MyLinkedList.prototype.deleteAtIndex = function(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return;
if(index === 0) {
this._head = this._head.next;
// 如果删除的这个节点同时是尾节点,要处理尾节点
if(index === this._size - 1){
this._tail = this._head
}
this._size--;
return;
}
// 获取目标节点的上一个的节点
const node = this.getNode(index - 1);
node.next = node.next.next;
// 处理尾节点
if(index === this._size - 1) {
this._tail = node;
}
this._size--;
};
// MyLinkedList.prototype.out = function() {
// let cur = this._head;
// const res = [];
// while(cur) {
// res.push(cur.val);
// cur = cur.next;
// }
// };
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new MyLinkedList()
* var param_1 = obj.get(index)
* obj.addAtHead(val)
* obj.addAtTail(val)
* obj.addAtIndex(index,val)
* obj.deleteAtIndex(index)
*/
// 运行时间:120ms
// 内存消耗:49.3MB
三、反转链表
1.题目:反转一个单链表。
示例1
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
2.解题思路:
(1)双指针
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 双指针:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// temp = cur = null;
return pre;
};
// 运行时间:64ms
// 内存消耗:42.8MB
(2)递归1
// 递归:
var reverse = function(pre, head) {
if(!head) return pre;
const temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head
return reverse(pre, temp);
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head);
};
// 运行时间:72ms
// 内存消耗:43.3MB
(2)递归2
// 递归2
var reverse = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
// 从后往前翻
const pre = reverse(head.next);
head.next = pre.next;
pre.next = head;
return head;
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
let cur = head;
while(cur && cur.next) {
cur = cur.next;
}
reverse(head);
return cur;
};
// 运行时间:68ms
// 内存消耗:43.3MB
四、两两交换链表的结点
1.题目:
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例1
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
2.解题思路:
var swapPairs = function (head) {
let ret = new ListNode(0, head), temp = ret;
while (temp.next && temp.next.next) {
let cur = temp.next.next, pre = temp.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
temp.next = cur;
temp = pre;
}
return ret.next;
};
// 运行时间:64ms
// 内存消耗:41.3MB
五、删除链表的倒数第N个节点
1.题目
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
示例1
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5] 示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[] 示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
2.解题思路:
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let ret = new ListNode(0, head),
slow = fast = ret;
while(n--) fast = fast.next;
while (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next
};
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return ret.next;
};
// 运行时间:68ms
// 内存消耗:41.5MB
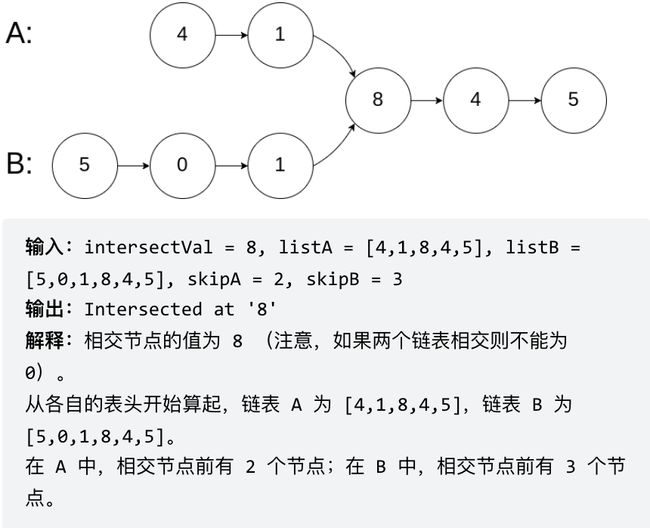
六、链表相交
1.题目:
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
var getListLen = function(head) {
let len = 0, cur = head;
while(cur) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
let curA = headA,curB = headB,
lenA = getListLen(headA), // 求链表A的长度
lenB = getListLen(headB);
if(lenA < lenB) { // 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
// 交换变量注意加 “分号” ,两个数组交换变量在同一个作用域下时
// 如果不加分号,下面两条代码等同于一条代码: [curA, curB] = [lenB, lenA]
[curA, curB] = [curB, curA];
[lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA];
}
let i = lenA - lenB; // 求长度差
while(i-- > 0) { // 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curA && curA !== curB) { // 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return curA;
};
#运行时间:96ms
#内存消耗:48.8MB
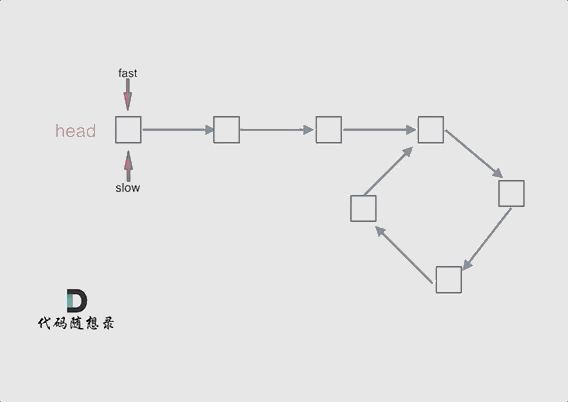
七、环形链表2
1.题目:给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
// 两种循环实现方式
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 先判断是否是环形链表
var detectCycle = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return null;
let slow =head.next, fast = head.next.next;
while(fast && fast.next && fast!== slow) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
if(!fast || !fast.next ) return null;
slow = head;
while (fast !== slow) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
};
#运行时间:92ms
#内存消耗:43.9MB
// 两种循环实现方式
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return null;
let slow =head.next, fast = head.next.next;
while(fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast == slow) {
slow = head;
while (fast !== slow) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
};
#运行时间:96ms
#内存消耗:44.2MB
1 2
数组思路-双指针 ↩︎
数组思路-逆序 ↩︎